What Are Anypoint Flow, Session, and Property Variables in MuleSoft?
Variables can set or remove a variable tied to message in current flow, across multiple flows, or on the outbound scope of a message.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeA MuleMessage is the object used to pass any data through Mule flow. MuleMessage consists of three parts:
Header, which contains set of named properties.
Payload, which actually contains message or data.
Attachment.
A Variable is used to set or remove a variable on message. The Scope Variable is limited to the flow where it is set. When a message leaves the flow, the variable doesn’t carry to next flow or application.
Flow Variable
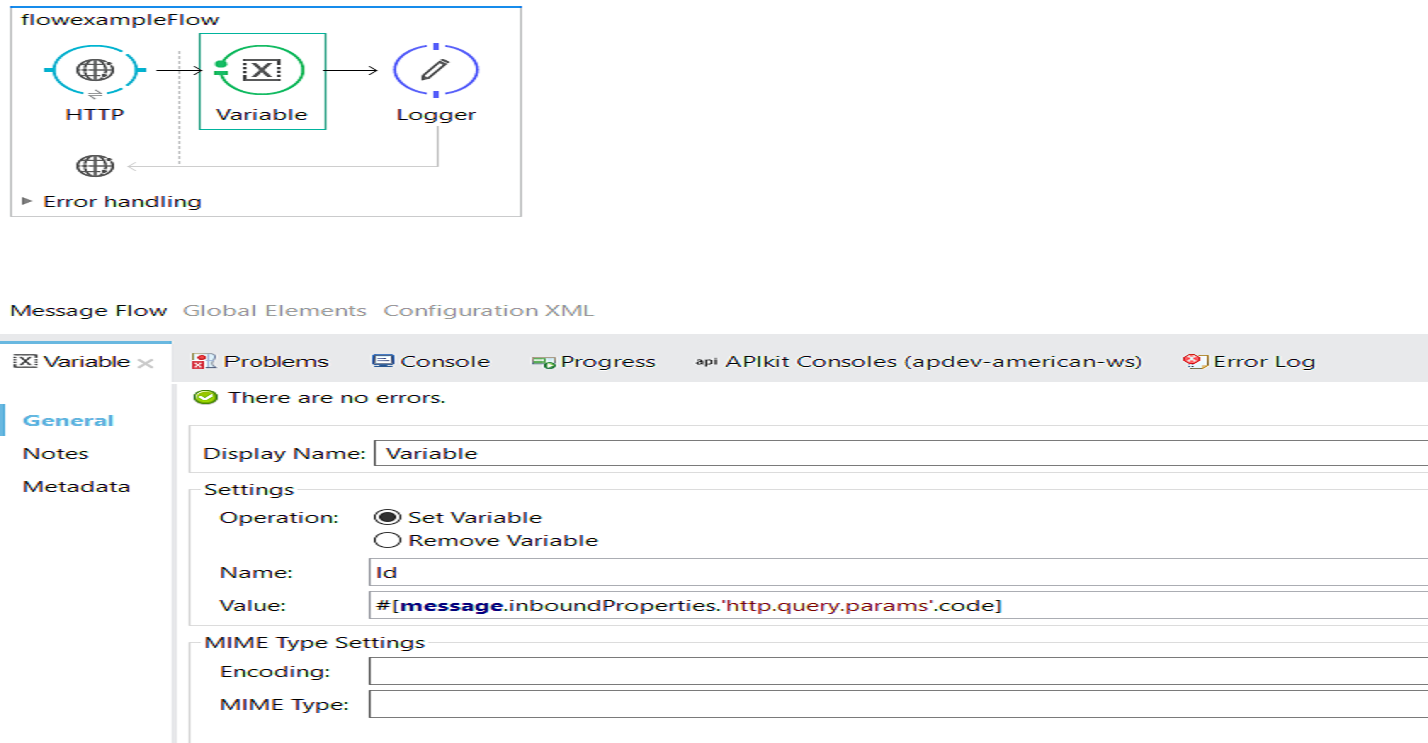
The Flow Variable is used to set or remove the variable tied to message in current flow. Variables set by flow variable transformer persist for the current flow and cannot cross the transport barrier.
The Flow Variable can be accessed in current flow, calling flows (sub flow/private flow) and even their child flows.
The Flow Variable can be accessed using syntax #[flowVars.Id] if the Id is the name of flow variable.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<mule
xmlns:file="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/file"
xmlns:http="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http"
xmlns="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core"
xmlns:doc="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/documentation"
xmlns:spring="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-current.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core/current/mule.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http/current/mule-http.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/file http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/file/current/mule-file.xsd">
<flow name="flowexampleFlow">
<http:listener config-ref="HTTP_Listener_Configuration" path="/GET" doc:name="HTTP"/>
<set-variable variableName="Id" value="#[message.inboundProperties.'http.query.params'.code]" doc:name="Variable"/>
<logger level="INFO" doc:name="Logger" message="#[flowVars.Id]"/>
</flow>
</mule>Session Variable
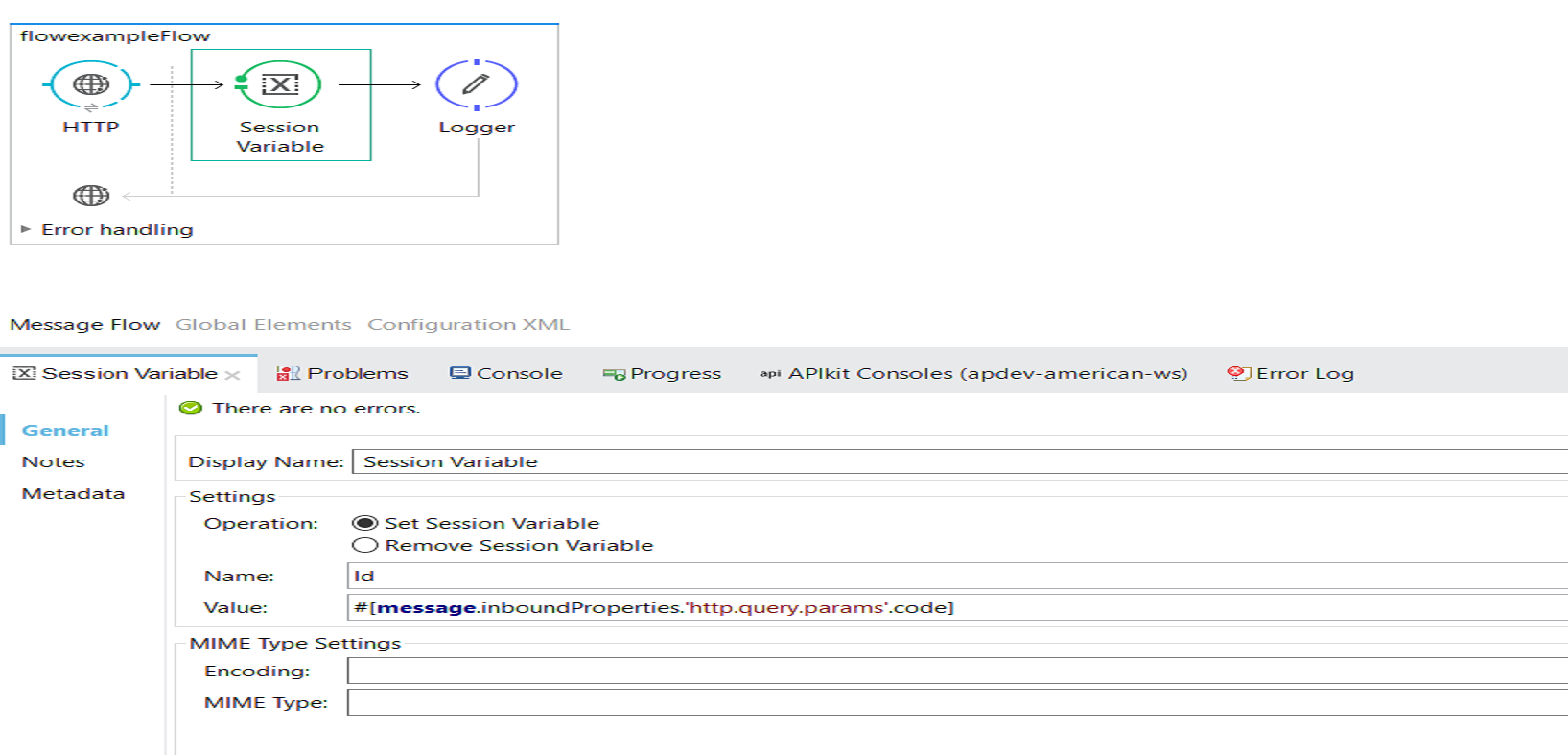
The Session Variable is used to set or remove the variable tied to current message for its entire lifecycle across multiple flows and even servers.
Variables set by the Session Variable transformer persist for the entire lifecycle regardless of transport barrier. The Session Variable can be accessed in current flow, calling/child, flow within the entire project, and even JVM systems.
Session Variable can be accessed using syntax #[sessionVars.Id] if the Id is the name of the Session Variable.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<mule xmlns:file="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/file" xmlns:http="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http" xmlns="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core" xmlns:doc="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/documentation"
xmlns:spring="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-current.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core/current/mule.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http/current/mule-http.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/file http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/file/current/mule-file.xsd">
<flow name="flowexampleFlow">
<http:listener config-ref="HTTP_Listener_Configuration" path="/GET" doc:name="HTTP"/>
<set-session-variable variableName="Id" value="#[message.inboundProperties.'http.query.params'.code]" doc:name="Session Variable"/>
<logger level="INFO" doc:name="Logger" message="#[sessionVars.Id]"/>
</flow>
</mule>
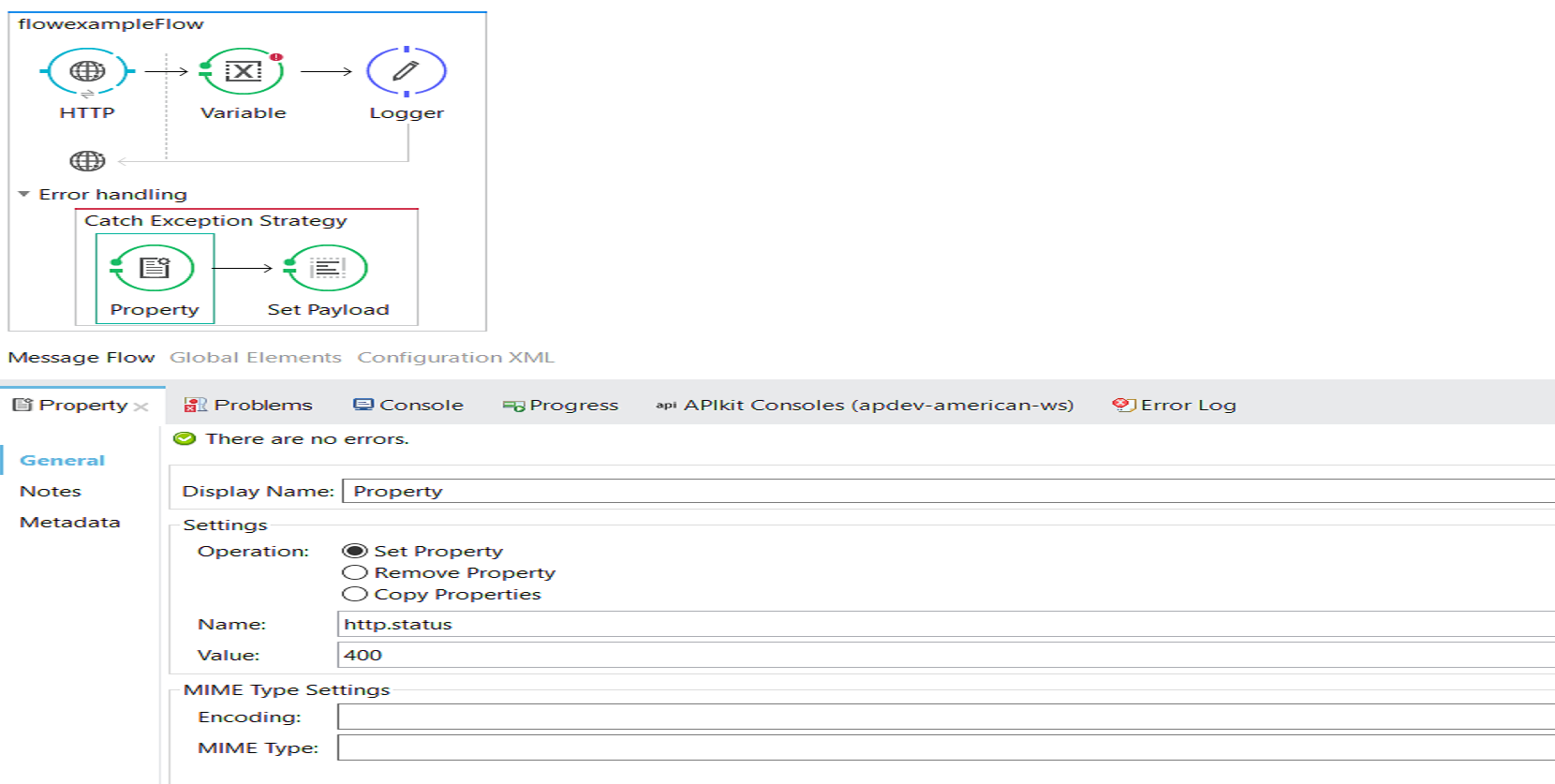
Property
The Property is used to set, remove, or copy the properties on the outbound scope of a message. Once a message hits an outbound connector, all properties in the outbound scope are sent with the message in the form of transport-specific metadata (HTTP headers for an HTTP outbound-connector, for example).
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<mule xmlns:file="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/file" xmlns:http="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http" xmlns="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core" xmlns:doc="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/documentation"
xmlns:spring="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-current.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core/current/mule.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http/current/mule-http.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/file http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/file/current/mule-file.xsd">
<flow name="flowexampleFlow">
<http:listener config-ref="HTTP_Listener_Configuration" path="/GET" doc:name="HTTP"/>
<set-variable variableName="Id" value="#[message.inboundProperties.'http.query.params'.Id]" doc:name="Variable"/>
<logger level="INFO" doc:name="Logger" message="#[flowVars.Id]"/>
<catch-exception-strategy doc:name="Catch Exception Strategy">
<set-property propertyName="http.status" value="400" doc:name="Property"/>
<set-payload value="Bad Request" doc:name="Set Payload"/>
</catch-exception-strategy>
</flow>
</mule>
I hope that this article clarifies any confusion that you may have had with Flow, Session, and Property Variables.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments