Using Primary, Partition, and Clustering Keys in ScyllaDB (or Cassandra)
Learn core data modeling concepts that are critical for optimizing performance in wide-column NoSQL databases.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn ScyllaDB and other NoSQL databases, the data model is based on the queries and not just around the domain entities. When creating the data model, we take into account both the conceptual data model and the application workflow: which queries will be performed by which users and how often.
One of the main goals of data modeling in ScyllaDB and other wide-column databases (e.g., Apache Cassandra) is to return results fast. To achieve that, you want:
- Even data distribution: Data should be evenly spread across the cluster so that every node holds roughly the same amount of data. ScyllaDB determines which node should store the data based on hashing the partition key. Therefore, choosing a suitable partition key is crucial. More on this later on.
- To minimize the number of partitions accessed in a read query: To make reads faster, we’d ideally have all the data required in a read query stored in a single Table. Although it’s fine to duplicate data across tables, in terms of performance, it’s better if the data needed for a read query is in one table.
Things you should NOT focus on:
- Avoiding data duplication: To get efficient reads, we sometimes have to duplicate data. More about that and denormalization later in this lesson. In a later session, we learn how to avoid duplication in some cases using Secondary Indexes.
- Minimizing the number of writes: writes in ScyllaDB aren’t free, but they are very efficient and “cheap.” ScyllaDB is optimized for high write throughput. Reads, while still very fast, are usually more expensive than writes and are harder to fine-tune. We’d usually be ready to increase the number of writes to increase read efficiency. Keep in mind that the number of tables also affects consistency.
In this tutorial, you will use an example based on a Veterinary Clinic named 4Paws Clinic. In this clinic, each admitted animal has a connected heart rate monitor, which logs heart rate and other vital information every five seconds.
What’s a Primary Key?
A Primary Key is defined within a table. It is one or more columns used to identify a row. All tables must include a definition for a Primary Key. For example, consider this table:
CREATE TABLE heartrate_v1 (
pet_chip_id uuid,
time timestamp,
heart_rate int,
PRIMARY KEY (pet_chip_id)
);In the example above the primary key is a single column – the pet_chip_id. If a Primary Key is made up of a single column, it is called a Simple Primary Key.
For the above table perform the query:
SELECT * from heartrate_v1 WHERE pet_chip_id = 123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426655440b23;What happens if we want to query our data by pet_chip_id but also by time? That is if our query is:
SELECT * from heartrate_v1 WHERE pet_chip_id = 123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426655440b23 AND time >='2019-03-04 07:01:00' AND time <='2019-03-04 07:02:00';In that case, the above query won’t work. We can define the Primary Key to include more than one column, in which case it is called a Composite (or Compound) key. Create the following table:
CREATE TABLE heartrate_v2 (
pet_chip_id uuid,
time timestamp,
heart_rate int,
PRIMARY KEY (pet_chip_id, time)
);And insert some data:
INSERT INTO heartrate_v2(pet_chip_id, time, heart_rate) VALUES (123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426655440b23, '2019-03-04 07:01:05', 100);
INSERT INTO heartrate_v2(pet_chip_id, time, heart_rate) VALUES (123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426655440b23, '2019-03-04 07:01:10', 90);
INSERT INTO heartrate_v2(pet_chip_id, time, heart_rate) VALUES (123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426655440b23, '2019-03-04 07:01:50', 96);
INSERT INTO heartrate_v2(pet_chip_id, time, heart_rate) VALUES (123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426655440b23, '2019-04-04 07:01:50', 99); Enter Partition Keys and Clustering Keys
In the case shown above, the first part of the Primary Key is called the Partition Key (pet_chip_id in the above example) and the second part is called the Clustering Key (time).
A Primary Key is composed of 2 parts:
-
The Partition Key is responsible for data distribution across the nodes. It determines which node will store a given row. It can be one or more columns.
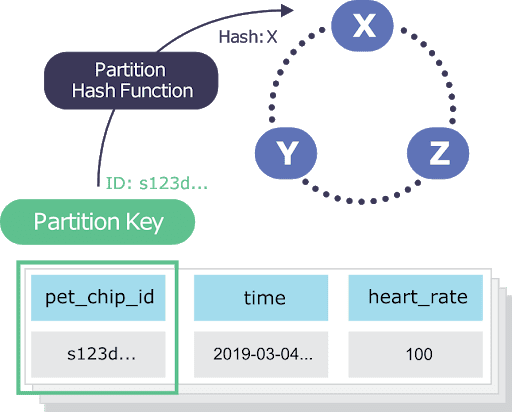
- The Clustering Key is responsible for sorting the rows within the partition. It can be zero or more columns.
Now execute the query we previously saw, according to time:
SELECT * from heartrate_v2 WHERE pet_chip_id = 123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426655440b23 AND time >='2019-03-04 07:01:00' AND time <='2019-03-04 07:02:00';Additionally, we previously had an issue with heartrate_v1, where a pet could only have one heart rate value recorded regardless of the time. Now that we defined the time to be a part of the primary key, each primary key, which is a combination of pet_chip_id and time, can have a heart rate value.
Read the data for the same pet:
SELECT * from heartrate_v2 WHERE pet_chip_id = 123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426655440b23 ;We can see that as opposed to the previous example. This time the value wasn’t overwritten.
The Partition Key and the Clustering Keys With Multiple Columns
As we just saw, both the Partition Key and the Clustering Key can include more than one column, for example, if our query is:
SELECT * from heartrate_v3 WHERE pet_chip_id = 123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426655440b23 AND time ='2019-03-04 07:01:00' AND pet_name = 'Duke';We could define the table as follows:
CREATE TABLE heartrate_v3 (
pet_chip_id uuid,
time timestamp,
heart_rate int,
pet_name text,
PRIMARY KEY ((pet_chip_id, time), pet_name)
);Create the above table, then insert some data:
INSERT INTO heartrate_v3(pet_chip_id, time, heart_rate, pet_name) VALUES (123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426655440b23, '2019-03-04 07:01:10', 90, 'Duke'); In this case, the partition key includes two columns: pet_chip_id and time, and the clustering key is pet_name. Keep in mind that every query must include all columns defined in the partition key.
Now try to execute this query:
SELECT * from heartrate_v3 WHERE pet_chip_id = 123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426655440b23; It fails, as the entire partition key is not given.
Now try this query:
SELECT * from heartrate_v3 WHERE pet_chip_id = 123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426655440b23 AND time ='2019-03-04 07:01:10' AND pet_name = 'Duke'; It succeeds as the complete partition key is given.
Similarly, if we want each partition to be based on the pet_chip_id but want to be able to query according to pet_name and heart_rate:
SELECT * from heartrate_v4 WHERE pet_chip_id = 123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426655440b23 AND pet_name = 'Duke' AND heart_rate = 100; it is possible to define (do this):
CREATE TABLE heartrate_v4 (
pet_chip_id uuid,
time timestamp,
heart_rate int,
pet_name text,
PRIMARY KEY (pet_chip_id, pet_name, heart_rate)
);Note:
- If there is more than one column in the Clustering Key (
pet_nameandheart_ratein the example above), the order of these columns defines the clustering order. For a given partition, all the rows are physically ordered inside ScyllaDB by the clustering order. This order determines what select query you can efficiently run on this partition. - In this example, the ordering is first by
pet_nameand then byheart_rate. - In addition to the Partition Key columns, a query may include the Clustering Key. If it does include the Clustering Key columns they must be used in the same order as they were defined.
Additional Data Modeling Exercises
If you want to continue learning about primary keys and other data modeling concepts, feel free to play around with these additional exercises and quizzes building on this same Veterinary Clinic example.
Published at DZone with permission of Guy Shtub. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments