Validation Module in Mule
Learn how to use the Validation module in Mule to verify that the content of a message in your flow matches a given set of criteria.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThe Validation module provides an easy out-of-the-box way to verify that the content of a message in your flow matches a given set of criteria.
The Difference Between Mule's Filter Component and Validation Module
The main advantage of the Validation Module over using filters is traceability, as filters all raise identical exceptions, making it hard for us to know where the exception was caused. So if we have two filters in the same flow, we cannot know which one failed and we cannot customize the exception type. Validators, on the other hand, raise an exception with a meaningful message attached, so we can customize the exception type.
Note: This feature is supported by the Mule run-time as of Mule ESB 3.7.0 in both Community and Enterprise editions.
The validations module was designed following these principles:
If the message doesn’t meet the specified criteria, the validation fails and a ValidationException is thrown.
By default, this exception has a meaningful message attached. You can optionally customize this message and change the type of exception thrown, as long as the new exception type has a constructor that overrides Exception(String).
In case you want to throw an Exception type that lacks this constructor, or in which its creation is not trivial, or in which you want it to contain additional information.
How to Use Validator
There are two ways of using a validator: through a Message Processor, or through a MEL function.
Types of Built-In Validator
Below is not the complete list of Validators; please refer to the MuleSoft article on Validation components for the complete list.
Email Address Validator
<validation:is-email email=”#[json:email]” />Regular Expression Validator
<validation:matches-regex value=”#[json:Name]” regex=”/^[A-z]+$/” message=”Name can not contain Integer value” />Not Empty check Validator
<validation:is-not-empty value=”#[json:employeeId]” message=”Employee Id is mandatory to supply” />Size Validator
<validation:validate-size value=”#[json:age]” min=”2″ max=”3″ message=”Please provide correct age” />Not Null Validator
<validation:not-null expression=”#[value]” value=”#[payload]” />Number Validator
<validation:is-number value=”#[json:Id]” numberType=”INTEGER” message=”ID can not be String or any other data Type” />How to Validate Many Conditions at Once
There are scenarios in which you may want to evaluate several conditions, out of which more than one could fail simultaneously. In these cases, it’s ideal to generate a single error that contains all of the descriptions.
The solution is the All Validator.
Let’s walk through how to use All Validator in a Mule application. In this example, we are receiving the JSON Request through an HTTP call from the REST client, which will be validated against the ALL Validator Component.
Mule Flow:
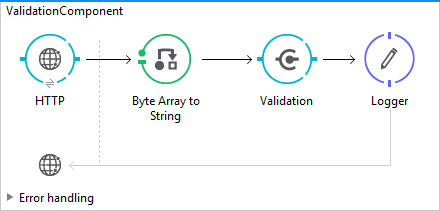
Code:
<?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=”UTF-8″?>
<mule xmlns:json=”http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/json”
xmlns:http=”http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http” xmlns:validation=”http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/validation”
xmlns=”http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core” xmlns:doc=”http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/documentation”
xmlns:spring=”http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans” xmlns:xsi=”http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance”
xsi:schemaLocation=”http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/json http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/json/current/mule-json.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http/current/mule-http.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/validation http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/validation/current/mule-validation.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-current.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core/current/mule.xsd”>
<http:listener-config name=”HTTP_Listener_Configuration”
host=”localhost” port=”8081″ basePath=”/validation” doc:name=”HTTP Listener Configuration” />
<validation:config name=”Validation_Configuration”
doc:name=”Validation Configuration” />
<flow name=”ValidationComponent”>
<http:listener config-ref=”HTTP_Listener_Configuration”
path=”/validation” doc:name=”HTTP” />
<byte-array-to-string-transformer
doc:name=”Byte Array to String” />
<validation:all config-ref=”Validation_Configuration”
doc:name=”Validation”>
<validation:validations>
<validation:is-number value=”#[json:id]”
numberType=”INTEGER” message=”ID can not be String data Type” />
<validation:is-not-empty value=”#[json:account]”
message=”Account Number Required” />
<validation:matches-regex value=”#[json:name]”
regex=”^[a-zA-Z]+$” message=”Name can not contain Integer value and other special charectors” />
<validation:validate-size value=”#[json:age]”
min=”2″ max=”3″ message=”Please provide correct age” />
<validation:is-email email=”#[json:email]” />
</validation:validations>
</validation:all>
<logger level=”INFO” message=”Validation Successful” doc:name=”Logger”></logger>
</flow>
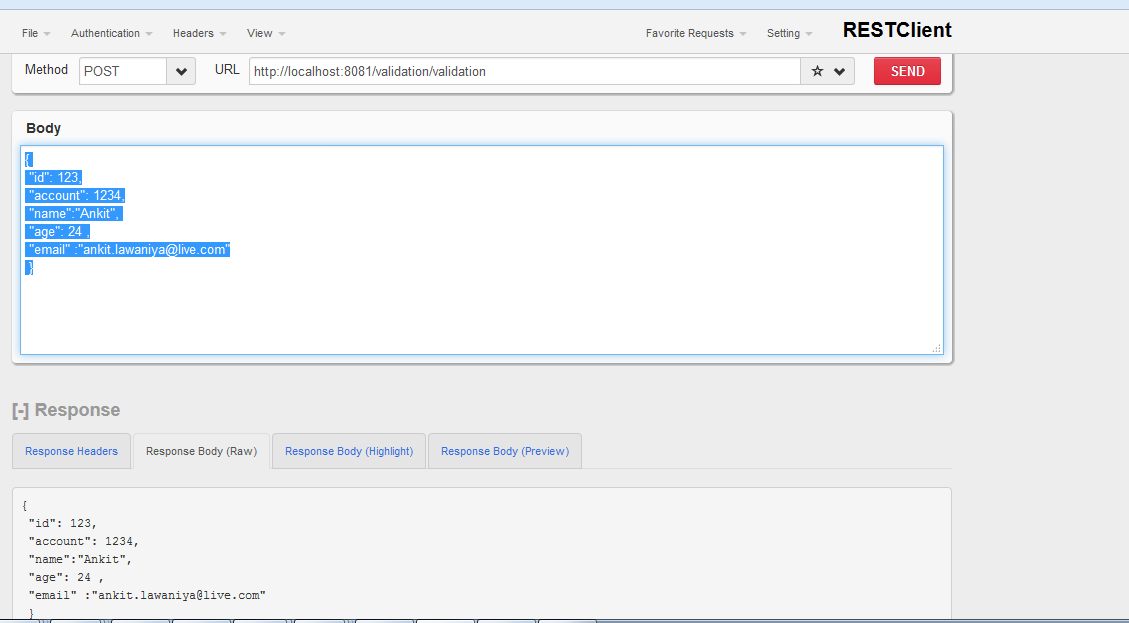
</mule>Success Request:
{
“id”: 123,
“account”: 1234,
“name”:”Ankit”,
“age”: 24 ,
“email” :”ankit.lawaniya@live.com”
}
Failed Request:
{
"id": "dummyId",
"account": 12,
"name":"Ankit1",
"age": 2 ,
"email" :"ankit.lawaniyalive.com"
}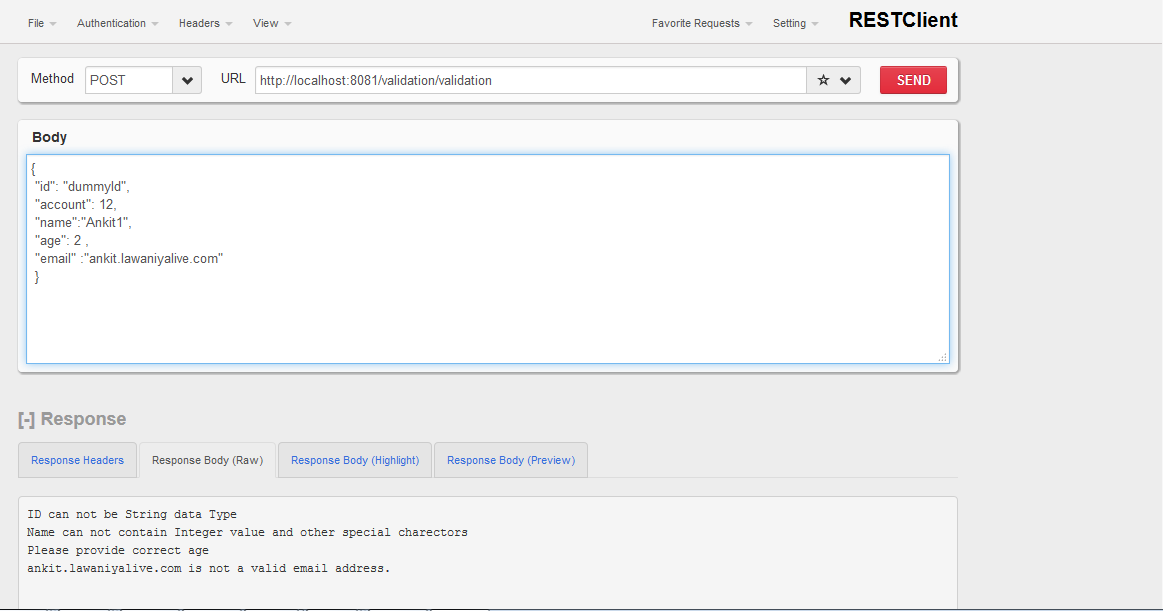
Below is the exception thrown for the validation failure:
Root Exception stack trace:
org.mule.extension.validation.api.MultipleValidationException: ID can not be String data Type
Name can not contain Integer value and other special charectors
Please provide correct age
ankit.lawaniyalive.com is not a valid email address
at org.mule.extension.validation.internal.ValidationStrategies.all(ValidationStrategies.java:71)Hope this helps.
Thanks. Keep learning.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments