Visitor Design Pattern In Java
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeToday, I am here to discuss another behavioral design pattern called Visitor Design Pattern. The Visitor design pattern lets us separate algorithms from the objects on which they operate.
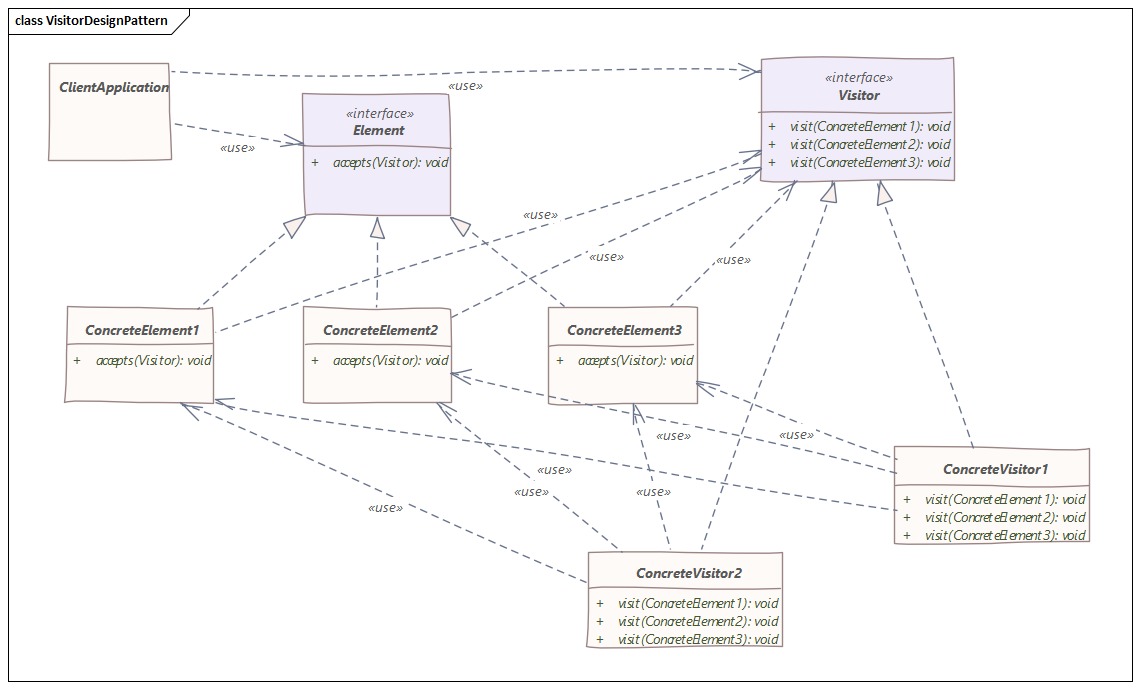
Visitor Design Pattern
- The Visitor Design Pattern provides a way of separating an algorithm from an object structure on which it operates.
- A practical result of this separation is the ability to add new operations to existing object structures without modifying the structures. It is one way to follow the open/closed principle.
- The Visitor Design Pattern is used when we like to perform an operation on a group/family of objects.
- The Visitor Design Pattern is one of the twenty-three well-known GoF design patterns which helps us to move the operational logic from the objects to another class.
- The Visitor allows adding new virtual functions to a family of classes, without modifying the classes.
- Instead, a visitor class is created that implements all of the appropriate specializations of the virtual function.
- The Visitor Design Pattern makes it possible to define a new operation for (some) classes of an object structure without changing the classes.
- When new operations are needed frequently and the object structure consists of many unrelated classes, it's inflexible to add new sub-classes each time a new operation is required.
- The Element accepts the visitor and delegates the operation to the accepted Visitor object.
- The Visitor object performs the operation on the element ("visits the element").
- The Visitor Design Pattern makes it possible to create new operations independently from the classes of an object structure by adding new visitor objects.
To understand this, let's take an example of a Shop, which sells books, fruits, vegetables, and electronics.
Shop Bill Processing Application Example
Lets first define ShopItemCategory enum:
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example1.items;
public enum ShopItemCategory {
BOOK("Book"), ELECTRONICS("Electronics"), FRUIT("Fruit"), VEGETABLE("Vegetable");
private String name;
ShopItemCategory(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
Now, define the ShopItem interface:
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example1.items;
public interface ShopItem {
String getName();
double getPrice();
double getWeight();
ShopItemCategory getCategory();
}
Now, define the concrete-shop-item class. Code for Book class:
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example1.items;
public class Book implements ShopItem {
private String title;
private double pricePerUnit;
public Book(String title, double pricePerUnit) {
this.title = title;
this.pricePerUnit = pricePerUnit;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public double getPricePerUnit() {
return pricePerUnit;
}
public void setPricePerUnit(int price) {
this.pricePerUnit = price;
}
public String getName() {
return getTitle();
}
public double getPrice() {
return getPricePerUnit();
}
public double getWeight() {
return 0.0d;
}
public ShopItemCategory getCategory() {
return ShopItemCategory.BOOK;
}
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("Book [title=").append(title)
.append(", price=").append(getPrice())
.append("]");
return builder.toString();
}
}
Code for Electronics class:
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example1.items;
public class Electronics implements ShopItem {
private String brand;
private double price;
public Electronics(String brand, double price) {
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return getBrand();
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public double getWeight() {
return 0.0d;
}
public ShopItemCategory getCategory() {
return ShopItemCategory.ELECTRONICS;
}
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("Electronics [brand=").append(brand)
.append(", price=").append(price)
.append("]");
return builder.toString();
}
}
Code for Fruit class:
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example1.items;
public class Fruit implements ShopItem {
private String name;
private double pricePerKg;
private double weight;
public Fruit(String name, double pricePerKg, double weight) {
this.name = name;
this.pricePerKg = pricePerKg;
this.weight = weight;
}
public double getPricePerKg() {
return pricePerKg;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return getPricePerKg();
}
public double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public ShopItemCategory getCategory() {
return ShopItemCategory.FRUIT;
}
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("Fruit [name=").append(name)
.append(", pricePerKg=").append(pricePerKg)
.append(", weight=").append(weight)
.append("]");
return builder.toString();
}
}
and code for Vegetable class:
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.ShopVisitor;
public class Vegetable implements ShopItem {
private String name;
private double pricePerKg;
private double weight;
public Vegetable(String name, double pricePerKg, double weight) {
this.name = name;
this.pricePerKg = pricePerKg;
this.weight = weight;
}
public double getPricePerKg() {
return pricePerKg;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return getPricePerKg();
}
public double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public double accept(ShopVisitor visitor) {
return visitor.visit(this);
}
public ShopItemCategory getCategory() {
return ShopItemCategory.VEGETABLE;
}
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("Vegetable [name=").append(name)
.append(", pricePerKg=").append(pricePerKg)
.append(", weight=").append(weight)
.append("]");
return builder.toString();
}
}
Since the shop get customers, let's define a Customer class:
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example1;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example1.items.ShopItem;
public abstract class Customer {
protected String name;
public Customer(String name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
public double calculateCost(ShopItem item) {
double price = item.getPrice();
double weight = item.getWeight();
return (weight == 0.0d) ? price : price * weight;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
Here, I have added a method to calculate cost of the shop item as well. Also, I made the class abstract to support different concrete customer classes.
Code for Person class:
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example1;
public class Person extends Customer {
public Person(String name) {
super(name);
}
public String toString() {
return "Person (" + name + ")";
}
}
And code for Student class:
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example1;
public class Student extends Customer {
public Student(String name) {
super(name);
}
public String toString() {
return "Student (" + name + ")";
}
}
Now code for a utility class, BillPrinter, for printing itemized bill:
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example1.util;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.DoubleAdder;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example1.Customer;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example1.items.ShopItem;
public class BillPrinter {
public static double calculateAndPrintBill(Customer customer, List<ShopItem> items) {
double totalCost = printItemisedBill(customer, items);
System.out.printf("Total Cost = %69.2f\n", totalCost);
System.out.println(
"============================================================================================================");
return totalCost;
}
public static double printItemisedBill(Customer customer, List<ShopItem> items) {
items.sort(Comparator.comparing(ShopItem::getCategory).thenComparing(ShopItem::getName));
System.out.printf(" Shopping Items Bill for the %s\n", customer);
System.out.println(
"============================================================================================================");
System.out.printf("%25s | %15s | %10s | %10s | %10s\n", "Shopping Item", "Category", "Price", "Weight", "Cost");
System.out.println(
"------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
DoubleAdder totalCost = new DoubleAdder();
items.stream().forEach(item -> {
String name = item.getName();
double price = item.getPrice();
double weight = item.getWeight();
double cost = customer.calculateCost(item);
totalCost.add(cost);
System.out.printf("%25s | %15s | %10.2f | %10s | %10.2f\n", name, item.getCategory().getName(),
price, (weight > 0.0d) ? weight : "-", cost);
});
System.out.println(
"============================================================================================================");
return totalCost.doubleValue();
}
}
Now, it's time to write the Main program to execute and test the output:
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example1;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example1.items.Book;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example1.items.Electronics;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example1.items.Fruit;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example1.items.ShopItem;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example1.items.ShopItemCategory;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example1.items.Vegetable;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example1.util.BillPrinter;
("serial")
public class Main {
protected static Map<ShopItemCategory, Map<String, Double>> shopItemsPriceList = new HashMap<ShopItemCategory, Map<String, Double>>();
static {
shopItemsPriceList.put(ShopItemCategory.BOOK, new HashMap<String, Double>() {
{
put("Java - Design Patterns", 10.4d);
put("Learn java in 24 days", 8.64d);
put("William Shakespeare", 12.43d);
put("Times Magazine", 8.76d);
}
});
shopItemsPriceList.put(ShopItemCategory.FRUIT, new HashMap<String, Double>() {
{
put("Banana", 2.0d);
put("Apple", 3.5d);
put("Mango", 5.5d);
put("Grape", 4.3d);
}
});
shopItemsPriceList.put(ShopItemCategory.VEGETABLE, new HashMap<String, Double>() {
{
put("Potato", 5.0d);
put("Tomato", 1.4d);
put("Onion", 2.43d);
put("Capsicum", 3.76d);
}
});
shopItemsPriceList.put(ShopItemCategory.ELECTRONICS, new HashMap<String, Double>() {
{
put("Casio Calculator", 4.3d);
put("Samsung Mobile", 410.65d);
put("iPhone X", 650.36d);
put("MacBook Pro", 3500.45d);
}
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer student = new Student("Racheal"); // Visitor #1
List<ShopItem> studentItems = prepareShopItems(new HashMap<String, Double>() {
{
put("Java - Design Patterns", 1.0d);
put("Learn java in 24 days", 8.64d);
put("Banana", 2.3d);
put("Apple", 1.4d);
put("Potato", 2.0d);
put("Tomato", 1.5d);
put("Casio Calculator", 1.0d);
put("iPhone X", 1.0d);
}
});
double totalCostForStudent = BillPrinter.calculateAndPrintBill(student, studentItems);
System.out.printf("Amount to pay = %10.2f\n", totalCostForStudent);
System.out.println("\n\n");
Customer person = new Person("Micheal"); // Visitor #2
List<ShopItem> personItems = prepareShopItems(new HashMap<String, Double>() {
{
put("Times Magazine", 1.0d);
put("William Shakespeare", 1.0d);
put("Banana", 2.8d);
put("Mango", 1.4d);
put("Potato", 2.8d);
put("Tomato", 2.5d);
put("Samsung Mobile", 1.0d);
put("MacBook Pro", 1.0d);
}
});
double totalCostForPerson = BillPrinter.calculateAndPrintBill(person, personItems);
System.out.printf("Amount to pay = %10.2f\n", totalCostForPerson);
}
private static List<ShopItem> prepareShopItems(HashMap<String, Double> hashMap) {
List<ShopItem> shopItems = new ArrayList<ShopItem>();
hashMap.forEach((item, quantity) -> {
for (ShopItemCategory category : ShopItemCategory.values()) {
Double price = shopItemsPriceList.get(category).get(item);
if (price != null) {
switch (category) {
case BOOK:
shopItems.add(new Book(item, price));
break;
case FRUIT:
shopItems.add(new Fruit(item, price, quantity));
break;
case VEGETABLE:
shopItems.add(new Vegetable(item, price, quantity));
break;
case ELECTRONICS:
shopItems.add(new Electronics(item, price));
break;
}
break;
}
}
});
return shopItems;
}
}
and below is the output:
xxxxxxxxxx
Shopping Items Bill for the Student (Racheal)
============================================================================================================
Shopping Item | Category | Price | Weight | Cost
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Java - Design Patterns | Book | 10.40 | - | 10.40
Learn java in 24 days | Book | 8.64 | - | 8.64
Casio Calculator | Electronics | 4.30 | - | 4.30
iPhone X | Electronics | 650.36 | - | 650.36
Apple | Fruit | 3.50 | 1.4 | 4.90
Banana | Fruit | 2.00 | 2.3 | 4.60
Potato | Vegetable | 5.00 | 2.0 | 10.00
Tomato | Vegetable | 1.40 | 1.5 | 2.10
============================================================================================================
Total Cost = 695.30
============================================================================================================
Amount to pay = 695.30
Shopping Items Bill for the Person (Micheal)
============================================================================================================
Shopping Item | Category | Price | Weight | Cost
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Times Magazine | Book | 8.76 | - | 8.76
William Shakespeare | Book | 12.43 | - | 12.43
MacBook Pro | Electronics | 3500.45 | - | 3500.45
Samsung Mobile | Electronics | 410.65 | - | 410.65
Banana | Fruit | 2.00 | 2.8 | 5.60
Mango | Fruit | 5.50 | 1.4 | 7.70
Potato | Vegetable | 5.00 | 2.8 | 14.00
Tomato | Vegetable | 1.40 | 2.5 | 3.50
============================================================================================================
Total Cost = 3963.09
============================================================================================================
Amount to pay = 3963.09
So far so good. Now, suppose the shop-owner wants to start supporting discounts on different shop-items based on item-category, item quantity/price, and customer type (student or common person).
To minimize the changes in the shop-item classes, we will use the Visitor pattern here. Visitor pattern will handle calculating the discount for each of the shop items.
Shop Bill Processing Application Example Using Visitor Design Pattern
Let's start updating the code to implement discount calculation functionality using Visitor pattern.
Code for ShopItemCategory enum:
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items;
public enum ShopItemCategory {
BOOK("Book"), ELECTRONICS("Electronics"), FRUIT("Fruit"), VEGETABLE("Vegetable");
private String name;
ShopItemCategory(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
Updated code for ShopItem interface:
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.ShopVisitor;
public interface ShopItem {
String getName();
double getPrice();
double getWeight();
ShopItemCategory getCategory();
// will accept different visitors
// every visitor type will have its own defined discount
// and hence will differ the final cost of the item.
double accept(ShopVisitor visitor);
}
Since the interface will act as an Element for us, I have added the method accept() to accept the visitor object. The Visitor object will perform the operation of calculating discounts for each item. Now, we have to implement the accept() method in each concrete shop-item class.
Updated code for Book class:
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example1.items;
public class Book implements ShopItem {
private String title;
private double pricePerUnit;
public Book(String title, double pricePerUnit) {
this.title = title;
this.pricePerUnit = pricePerUnit;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public double getPricePerUnit() {
return pricePerUnit;
}
public void setPricePerUnit(int price) {
this.pricePerUnit = price;
}
public String getName() {
return getTitle();
}
public double getPrice() {
return getPricePerUnit();
}
public double getWeight() {
return 0.0d;
}
public ShopItemCategory getCategory() {
return ShopItemCategory.BOOK;
}
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("Book [title=").append(title)
.append(", price=").append(getPrice())
.append("]");
return builder.toString();
}
}
Updated code for Electronics class:
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.ShopVisitor;
public class Electronics implements ShopItem {
private String brand;
private double price;
public Electronics(String brand, double price) {
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return getBrand();
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public double getWeight() {
return 0.0d;
}
public ShopItemCategory getCategory() {
return ShopItemCategory.ELECTRONICS;
}
public double accept(ShopVisitor visitor) {
return visitor.visit(this);
}
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("Electronics [brand=").append(brand)
.append(", price=").append(price)
.append("]");
return builder.toString();
}
}
Updated code for Fruit class:
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.ShopVisitor;
public class Fruit implements ShopItem {
private String name;
private double pricePerKg;
private double weight;
public Fruit(String name, double pricePerKg, double weight) {
this.name = name;
this.pricePerKg = pricePerKg;
this.weight = weight;
}
public double getPricePerKg() {
return pricePerKg;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return getPricePerKg();
}
public double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public ShopItemCategory getCategory() {
return ShopItemCategory.FRUIT;
}
public double accept(ShopVisitor visitor) {
return visitor.visit(this);
}
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("Fruit [name=").append(name)
.append(", pricePerKg=").append(pricePerKg)
.append(", weight=").append(weight)
.append("]");
return builder.toString();
}
}
Updated code for Vegetable class:
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.ShopVisitor;
public class Vegetable implements ShopItem {
private String name;
private double pricePerKg;
private double weight;
public Vegetable(String name, double pricePerKg, double weight) {
this.name = name;
this.pricePerKg = pricePerKg;
this.weight = weight;
}
public double getPricePerKg() {
return pricePerKg;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return getPricePerKg();
}
public double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public double accept(ShopVisitor visitor) {
return visitor.visit(this);
}
public ShopItemCategory getCategory() {
return ShopItemCategory.VEGETABLE;
}
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("Vegetable [name=").append(name)
.append(", pricePerKg=").append(pricePerKg)
.append(", weight=").append(weight)
.append("]");
return builder.toString();
}
}
Now we will define the ShopVisitor interface to create our visit() method for each shop-item.
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items.Book;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items.Electronics;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items.Fruit;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items.Vegetable;
public interface ShopVisitor {
static final double DISCOUNT_NONE = 0.0d;
static final double DISCOUNT_5_PERCENT = 0.05d;
static final double DISCOUNT_7_PERCENT = 0.07d;
static final double DISCOUNT_10_PERCENT = 0.10d;
static final double DISCOUNT_12_PERCENT = 0.12d;
static final double DISCOUNT_15_PERCENT = 0.15d;
double visit(Fruit item);
double visit(Vegetable item);
double visit(Book item);
double visit(Electronics item);
}
Now, to use visitor interface, we will make our Customer class to implement it.
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items.ShopItem;
public abstract class Customer implements ShopVisitor {
protected String name;
public Customer(String name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
public double calculateCost(ShopItem item, double price, double discount) {
double weight = item.getWeight();
double cost = (weight == 0.0d) ? price : price * weight;
return (discount == 0.0d) ? cost : (cost - (cost * discount));
}
}
Updated code for Person class:
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items.Book;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items.Electronics;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items.Fruit;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items.Vegetable;
public class Person extends Customer {
public Person(String name) {
super(name);
}
public String toString() {
return "Person Visitor (" + name + ")";
}
public double visit(Fruit item) {
double discount = DISCOUNT_NONE;
double weight = item.getWeight();
if (weight >= 2.0d) { // 5% discount if buy more then 2 kg fruit item
discount = DISCOUNT_5_PERCENT;
}
return discount;
}
public double visit(Vegetable item) {
double discount = DISCOUNT_NONE;
double weight = item.getWeight();
if (weight >= 2.0d) { // 10% discount if buy more the 2 kg vegetable item
discount = DISCOUNT_10_PERCENT;
}
return discount;
}
public double visit(Book item) {
return DISCOUNT_NONE; // no discount on books
}
public double visit(Electronics item) {
double discount = DISCOUNT_NONE;
double price = item.getPrice();
if (price >= 500.0d) { // 10% discount if electronic item cost more then 500
discount = DISCOUNT_10_PERCENT;
} else if (price >= 200.0d) { // 5% discount if electronic item cost more then 200
discount = DISCOUNT_5_PERCENT;
}
return discount;
}
}
Updated code for Student class:
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items.Book;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items.Electronics;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items.Fruit;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items.Vegetable;
public class Student extends Customer {
public Student(String name) {
super(name);
}
public String toString() {
return "Student Visitor (" + name + ")";
}
public double visit(Fruit item) {
double discount = DISCOUNT_NONE;
double weight = item.getWeight();
if (weight >= 2.0d) { // 7% discount if buy more then 2 kg fruit item
discount = DISCOUNT_7_PERCENT;
}
return discount;
}
public double visit(Vegetable item) {
double discount = DISCOUNT_NONE;
double weight = item.getWeight();
if (weight >= 2.0d) { // 12% discount if buy more the 2 kg vegetable item
discount = DISCOUNT_12_PERCENT;
}
return discount;
}
public double visit(Book item) {
// 15% flat discount on all book/magazine/stationary item
return DISCOUNT_15_PERCENT;
}
public double visit(Electronics item) {
double discount = DISCOUNT_NONE;
double price = item.getPrice();
if (price >= 500.0d) { // 15% discount if electronic item cost more then 500
discount = DISCOUNT_15_PERCENT;
} else if (price >= 200.0d) { // 10% discount if electronic item cost more then 200
discount = DISCOUNT_10_PERCENT;
}
return discount;
}
}
So, we can see that each visitor class has its own implementation of discount calculation.
Now, we need to update BillPrinter to accommodate discount values, along with the itemized bill print.
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.util;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.DoubleAdder;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.Customer;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items.ShopItem;
public class BillPrinter {
public static double calculateAndPrintBill(Customer customer, List<ShopItem> items) {
double totalCost = printItemisedBill(customer, items);
System.out.printf("Total Cost = %82.2f\n", totalCost);
System.out.println(
"============================================================================================================");
return totalCost;
}
public static double printItemisedBill(Customer customer, List<ShopItem> items) {
items.sort(Comparator.comparing(ShopItem::getCategory).thenComparing(ShopItem::getName));
System.out.printf(" Shopping Items Bill for the %s\n", customer);
System.out.println(
"============================================================================================================");
System.out.printf("%25s | %15s | %10s | %10s | %10s | %10s\n", "Shopping Item", "Category", "Price", "Weight",
"Discount", "Cost");
System.out.println(
"------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
DoubleAdder totalCost = new DoubleAdder();
items.stream().forEach(item -> {
String name = item.getName();
double price = item.getPrice();
double weight = item.getWeight();
double discount = item.accept(customer);
double cost = customer.calculateCost(item, price, discount);
totalCost.add(cost);
System.out.printf("%25s | %15s | %10.2f | %10s | %10s | %10.2f\n", name, item.getCategory().getName(),
price, (weight > 0.0d) ? weight : "-", (discount > 0.0d) ? discount : "-", cost);
});
System.out.println(
"============================================================================================================");
return totalCost.doubleValue();
}
}
Now, it's time to write our Main program to execute and test the code:
xxxxxxxxxx
package org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items.Book;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items.Electronics;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items.Fruit;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items.ShopItem;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items.ShopItemCategory;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.items.Vegetable;
import org.trishinfotech.visitor.example2.util.BillPrinter;
("serial")
public class Main {
protected static Map<ShopItemCategory, Map<String, Double>> shopItemsPriceList = new HashMap<ShopItemCategory, Map<String, Double>>();
static {
shopItemsPriceList.put(ShopItemCategory.BOOK, new HashMap<String, Double>() {
{
put("Java - Design Patterns", 10.4d);
put("Learn java in 24 days", 8.64d);
put("William Shakespeare", 12.43d);
put("Times Magazine", 8.76d);
}
});
shopItemsPriceList.put(ShopItemCategory.FRUIT, new HashMap<String, Double>() {
{
put("Banana", 2.0d);
put("Apple", 3.5d);
put("Mango", 5.5d);
put("Grape", 4.3d);
}
});
shopItemsPriceList.put(ShopItemCategory.VEGETABLE, new HashMap<String, Double>() {
{
put("Potato", 5.0d);
put("Tomato", 1.4d);
put("Onion", 2.43d);
put("Capsicum", 3.76d);
}
});
shopItemsPriceList.put(ShopItemCategory.ELECTRONICS, new HashMap<String, Double>() {
{
put("Casio Calculator", 4.3d);
put("Samsung Mobile", 410.65d);
put("iPhone X", 650.36d);
put("MacBook Pro", 3500.45d);
}
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student("Racheal"); // Visitor #1
List<ShopItem> studentItems = prepareShopItems(new HashMap<String, Double>() {
{
put("Java - Design Patterns", 1.0d);
put("Learn java in 24 days", 8.64d);
put("Banana", 2.3d);
put("Apple", 1.4d);
put("Potato", 2.0d);
put("Tomato", 1.5d);
put("Casio Calculator", 1.0d);
put("iPhone X", 1.0d);
}
});
double totalCostForStudent = BillPrinter.calculateAndPrintBill(student, studentItems);
System.out.printf("Amount to pay = %10.2f\n", totalCostForStudent);
System.out.println("\n\n");
Person person = new Person("Micheal"); // Visitor #2
List<ShopItem> personItems = prepareShopItems(new HashMap<String, Double>() {
{
put("Times Magazine", 1.0d);
put("William Shakespeare", 1.0d);
put("Banana", 2.8d);
put("Mango", 1.4d);
put("Potato", 2.8d);
put("Tomato", 2.5d);
put("Samsung Mobile", 1.0d);
put("MacBook Pro", 1.0d);
}
});
double totalCostForPerson = BillPrinter.calculateAndPrintBill(person, personItems);
System.out.printf("Amount to pay = %10.2f\n", totalCostForPerson);
}
private static List<ShopItem> prepareShopItems(HashMap<String, Double> hashMap) {
List<ShopItem> shopItems = new ArrayList<ShopItem>();
hashMap.forEach((item, quantity) -> {
for (ShopItemCategory category : ShopItemCategory.values()) {
Double price = shopItemsPriceList.get(category).get(item);
if (price != null) {
switch (category) {
case BOOK:
shopItems.add(new Book(item, price));
break;
case FRUIT:
shopItems.add(new Fruit(item, price, quantity));
break;
case VEGETABLE:
shopItems.add(new Vegetable(item, price, quantity));
break;
case ELECTRONICS:
shopItems.add(new Electronics(item, price));
break;
}
break;
}
}
});
return shopItems;
}
}
And below is the output of the program:
Shopping Items Bill for the Student Visitor (Racheal)
============================================================================================================
Shopping Item | Category | Price | Weight | Discount | Cost
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Java - Design Patterns | Book | 10.40 | - | 0.15 | 8.84
Learn java in 24 days | Book | 8.64 | - | 0.15 | 7.34
Casio Calculator | Electronics | 4.30 | - | - | 4.30
iPhone X | Electronics | 650.36 | - | 0.15 | 552.81
Apple | Fruit | 3.50 | 1.4 | - | 4.90
Banana | Fruit | 2.00 | 2.3 | 0.07 | 4.28
Potato | Vegetable | 5.00 | 2.0 | 0.12 | 8.80
Tomato | Vegetable | 1.40 | 1.5 | - | 2.10
============================================================================================================
Total Cost = 593.37
============================================================================================================
Amount to pay = 593.37
Shopping Items Bill for the Person Visitor (Micheal)
============================================================================================================
Shopping Item | Category | Price | Weight | Discount | Cost
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Times Magazine | Book | 8.76 | - | - | 8.76
William Shakespeare | Book | 12.43 | - | - | 12.43
MacBook Pro | Electronics | 3500.45 | - | 0.1 | 3150.40
Samsung Mobile | Electronics | 410.65 | - | 0.05 | 390.12
Banana | Fruit | 2.00 | 2.8 | 0.05 | 5.32
Mango | Fruit | 5.50 | 1.4 | - | 7.70
Potato | Vegetable | 5.00 | 2.8 | 0.1 | 12.60
Tomato | Vegetable | 1.40 | 2.5 | 0.1 | 3.15
============================================================================================================
Total Cost = 3590.48
============================================================================================================
Amount to pay = 3590.48
I hope that you now have a good idea of how to use the Visitor Design Pattern.
Source Code can be found here: Visitor-Design-Pattern-Sample-Code
Liked the article? Please don't forget to press that like button. Happy coding!
Need more articles, please visit my profile: Brijesh Saxena.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments