Waits in Selenium: How to Use Implicit and Explicit Wait Commands
Want to learn more about waits in Selenium?
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWhile writing your first selenium program, you might have come across wait commands. But do you know exactly what Selenium waits are? Well, waits in selenium are an essential piece of code that is required to execute a test case. In this article, I will give you a brief insight into the different types of wait commands that are widely used in practice.
What Are Selenium Waits?
Waits help the user to troubleshoot issues while re-directing to different web pages. This is achieved by refreshing the entire web page and re-loading the new web elements. At times, there can be Ajax calls as well. Thus, a time lag can be seen while reloading the web pages and reflecting the web elements.
Users are often found navigating through various web pages back and forth. Thus, navigate() commands/methods provided by the WebDriver help the user to simulate the real-time scenarios by navigating between the web pages with reference to the web browser’s history.
Why Do You Need Waits In Selenium?
Most web applications are developed using Ajax and JavaScript. When a page is loaded by the browser, the elements that we want to interact with may load at different time intervals. With this, it not only becomes difficult to identify the element, but also if the element is not located, it will throw an ElementNotVisibleException exception. By using waits, we can resolve this problem.
Now, let’s move further and understand the different types of waits.
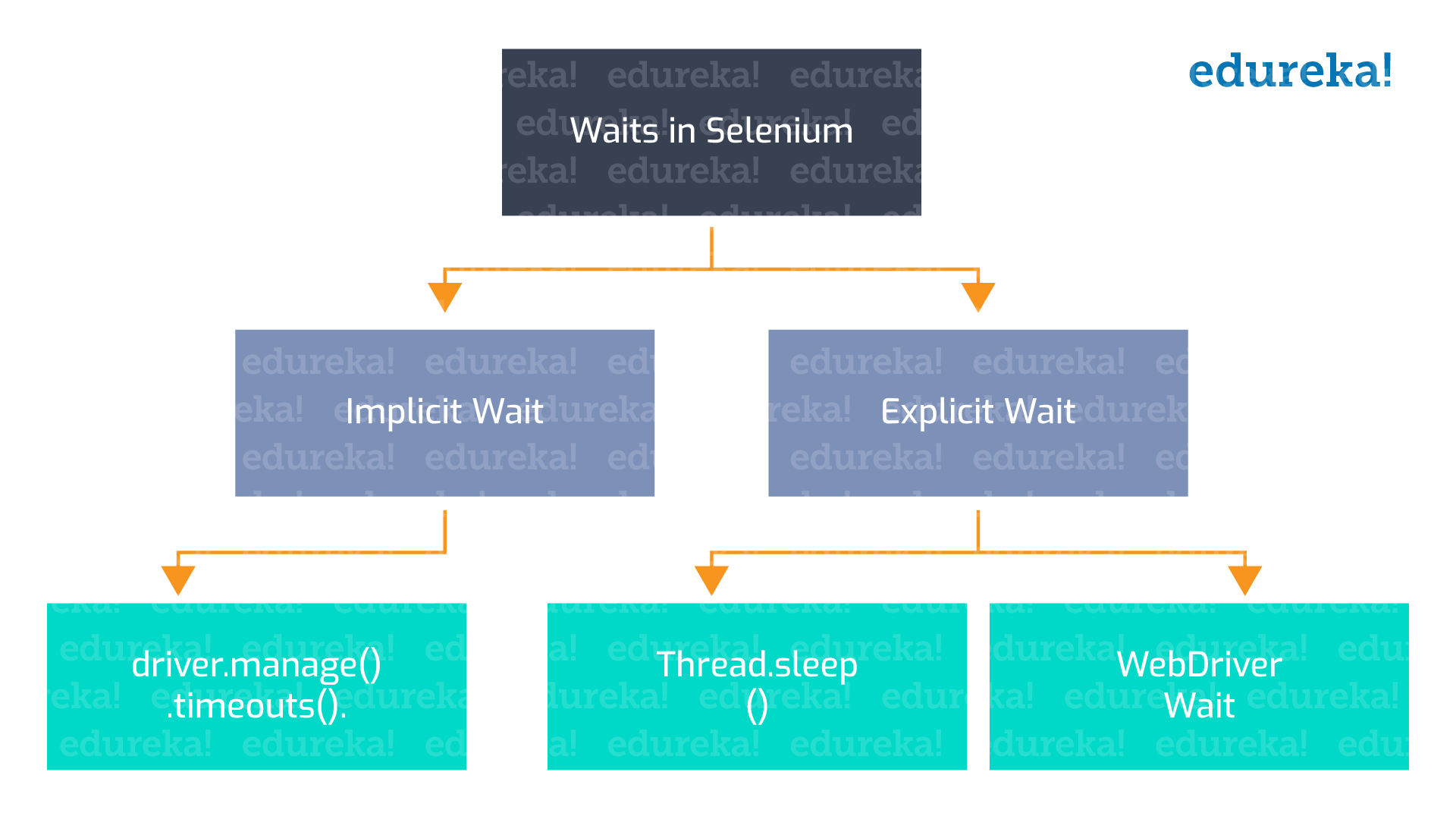
Types of Waits
Selenium supports two types of waits, and they are as follows
- Implicit Wait
- Explicit Wait
Note: The most widely used waits are implicit and explicit waits. Fluent waits are not preferable for real-time projects.
 First, let’s understand the implicit waits.
First, let’s understand the implicit waits.
Implicit Waits
The implicit wait will tell the WebDriver to wait a certain amount of time before it throws a "No Such Element Exception.” The default setting of implicit wait is zero. Once you set the time, the web driver will wait for that particular amount of time before throwing an exception.
Syntax: driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(TimeOut, TimeUnit.SECONDS);Let’s take an example of implicit waits and understand how it works.
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.ExpectedConditions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.WebDriverWait;
public classImplicitWait{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args) throwsInterruptedException{System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "C:\\Selenium-java-edureka\\chromedriver_win32\\chromedriver.exe");
WebDriver driver = newChromeDriver();
driver.manage().window().maximize();
driver.manage().deleteAllCookies();
driver.manage().timeouts().pageLoadTimeout(40, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // pageload timeoutdriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(20, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // Implicit Wait for 20 secondsdriver.get("https://login.yahoo.com/");driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@id='login-username']")).sendKeys("edureka@yahoo.com"); //Finding element and sending valuesThread.sleep(1000);driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@id='login-signin']")).click(); //Clicking on the next button ifelement is located}}In the above code, I have given an implicit wait at 20 seconds, which implies that the maximum wait time is 20 seconds for the particular element to load or to arrive at the output.
Note 1: Implicit, Explicit, and Fluent waits are dynamic waits. What are dynamic waits? Consider a situation where you have given a TimeOut value of 20 seconds. If the element is loaded in 5 seconds, then rest 15 seconds will be ignored. It won’t wait until the TimeOut value is completed, i.e 20 seconds. That’s why all waits are considered as dynamic waits.
Note 2: Implicitly wait is applied globally, which means it is always available for all the web elements throughout the driver instance. It implies that if the driver is interacting with 100 elements, then implicitly wait is applicable for all the 100 elements.
Explicit Waits
Explicit waits are a concept from the dynamic wait, which waits dynamically for specific conditions. It can be implemented by the WebDriverWait class. To understand the explicit wait in Selenium WebDriver, you should know the requirements and why we use wait statements in programs. I will give you a couple of examples so that you can get the complete idea of why waits in Selenium are important.
Conditions for Explicit Wait in Selenium WebDriver
Condition 1 – Suppose I have a web page that has some login form, and after login, it takes a lot of time to load the account or home page. This page is dynamic — it means that sometimes it takes 10 seconds to load the homepage, and sometimes, it’s 15 seconds and so on. In such situations, explicit wait helps us to wait until a specific page is not present.
Condition 2 – You are working on a travel application and have filled a web form and clicked on the submit button. Now, you have to wait until the specific data is no longer displayed. In this case, again, you can use the explicit wait, which can give waits until a specific or set of elements are not displayed.
Syntax: WebDriverWait wait=new WebDriverWait(WebDriveReference,TimeOut);In the above syntax, I have created an object of WebDriver wait and passed the driver reference and timeout as parameters. This is how you need to write explicit waits. Now, let’s take an example and understand how explicit wait works. Let’s take a look at the code below.
package Edureka;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;importorg.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;importorg.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.ExpectedConditions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.WebDriverWait; publicclassLocators {publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args) throwsInterruptedException {System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "C:\\Selenium-java-edureka\\chromedriver_win32\\chromedriver.exe");
WebDriver driver = newChromeDriver();
driver.manage().window().maximize();
driver.manage().deleteAllCookies();
driver.manage().timeouts().pageLoadTimeout(40, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
driver.get("https://www.facebook.com/");WebElement firstname= driver.findElement(By.name("firstname"));
WebElement lastname= driver.findElement(By.name("lastname"));
sendKeys(driver, firstname, 10, "Edureka");
sendKeys(driver, lastname, 20, "Edureka");WebElement forgotAccount= driver.findElement(By.linkText("Forgotten account?"));
clickOn(driver,forgotAccount, 10);driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}publicstaticvoidsendKeys(WebDriver driver1, WebElement element, inttimeout, String value){newWebDriverWait(driver1, timeout).until(ExpectedConditions.visibilityOf(element));element.sendKeys(value);}
publicstaticvoidclickOn(WebDriver driver1, WebElement element, inttimeout){newWebDriverWait(driver1, timeout).until(ExpectedConditions.elementToBeClickable(element));element.click();}}</pre><pre>In the above example, I used the Facebook sign-up credentials and located them using name locators. Furthermore, I have created a utility or one generic function that will be available for all elements to provide explicitly wait. In the above example, I have written my own sendKeys() method. This method will enter the value in a particular text field, but internally, it will provide an explicit wait also. Inside the sendKeys() method, I have given the expected conditions for visibility of the element. Basically, I am asking the driver to wait for 20 seconds until the expected condition visibility of the element. Furthermore, if the condition is satisfied, then you can apply sendKeys() to the method. Now, say I want to enter my first and last name. What I will do is use this sendKeys() method and pass the driver, first name, timeout, etc. for 10 seconds and value as edureka. The same goes for the last name as well.
When you execute the program, the Chrome driver will launch Google Chrome and navigate through facebook.com and enter the values mentioned in the code. It’s not mandatory to set the explicit wait for a timeout of a particular value. Based on your requirement, you can change it. This is the major advantage of using explicit wait, but for implicitly wait, once you have defined 10 seconds, it will be applicable to all the elements on the webpage and cannot be modified. The same goes with clickOn() method as well. But, this method is useful only for links on the webpage. This is how you can use explicit waits.
Let’s move further and differentiate between implicit and explicit Waits.
Implicit Vs. Explicit Waits
| Implicit Waits | Explicit Waits |
| 1. Implicit wait time is applied to all the elements in the script | 1. Explicit wait time is applied only to those elements that are specified by the user |
| 2. In implicit wait, we need not specify “ExpectedConditions” on the element to be located | 2. In explicit wait, we need to specify the “ExpectedConditions” on the element to be located |
| 3. It is recommended to use when the elements are located with the time frame specified in implicit wait | 3. It is recommended to use when the elements are taking a long time to load and also for verifying the property of the element like(visibilityOfElementLocated, elementToBeClickable,elementToBeSelected) |
I hope you understood the difference between implicit and explicit waits. This brings us to the end of the this blog. Please let us know what you think in the comments below!
Published at DZone with permission of Neha Vaidya, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments