WeakHashMap in Java With Class Example
Let's take a closer look at the WeakHashMap implementation in Java.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn this article, we will learn WeakHashMap class from the java.util package with examples.
What Will We Learn?
WeakHashMapClass OverviewWeakHashMapClass Constructor SummaryWeakHashMapClass Constructor MethodsWeakHashMapClass Example
1. WeakHashMap Class Overview
WeakHashMap is a Hash table-based implementation of the Map interface with weak keys. An entry in a WeakHashMap will automatically be removed when its key is no longer in ordinary use. Both null values and the null key are supported. This class has performance characteristics similar to those of the HashMap class and has the same efficiency parameters of initial capacity and load factor. Like most collection classes, this class is not synchronized. A synchronized WeakHashMap may be constructed using the Collections.synchronizedMap method. Weak Reference − if the only references to an object are weak references, the garbage collector can reclaim the object's memory at any time. It doesn't have to wait until the system runs out of memory. Usually, it will be freed the next time the garbage collector runs. This class is a member of the Java Collections Framework.
2. WeakHashMap Class Constructors
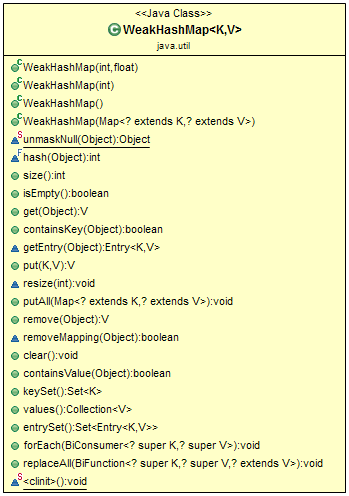
WeakHashMap()— Constructs a new, emptyWeakHashMapwith the default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).WeakHashMap(int initialCapacity)— Constructs a new, emptyWeakHashMapwith the given initial capacity and the default load factor (0.75).-
WeakHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)— Constructs a new, emptyWeakHashMapwith the given initial capacity and the given load factor. WeakHashMap(Map< ?extends K,? extends V> m)— Constructs a newWeakHashMapwith the same mappings as the specified map.
3. WeakHashMap Class Methods
-
void clear()— Removes all of the mappings from this map. boolean containsKey(Object key)— Returns true if this map contains a mapping for the specified key.-
boolean containsValue(Object value)— Returns true if this map maps one or more keys to the specified value. -
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>>entrySet()— Returns a Set view of the mappings contained in this map. void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K,? super V> action)— Performs the given action for each entry in this map until all entries have been processed or the action throws an exception.-
V get(Object key)— Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or null if this map contains no mapping for the key. boolean isEmpty()— Returns true if this map contains no key-value mappings.-
Set keySet()— Returns a Set view of the keys contained in this map. V put(K key, V value)— Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.-
void putAll(Map<? extends K,? extends V> m)— Copies all of the mappings from the specified map to this map. -
V remove(Object key)— Removes the mapping for a key from this weak hash map if it is present. -
void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V>function)— Replaces each entry's value with the result of invoking the given function on that entry until all entries have been processed or the function throws an exception. -
int size()— Returns the number of key-value mappings in this map. Collection values()— Returns a Collection view of the values contained in this map.
4. WeakHashMap Class Example
As we know, an entry in a WeakHashMapwill automatically be removed when its key is no longer externally referenced and the key is due for garbage collection. In this example, we created two keys — key1 and key2 — with values "ACTIVE" and "INACTIVE." Now, make key1 null and run the program. The output should be a single entry:
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.WeakHashMap;
public class WeakHashMapExample {
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final Map<Key, Project> map = new WeakHashMap<>();
Key key1 = new Key("ACTIVE");
final Key key2 = new Key("INACTIVE");
map.put(key1, new Project(100, "Customer Management System", "Customer Management System"));
map.put(key2, new Project(200, "Employee Management System", "Employee Management System"));
key1 = null;
System.gc();
for (final Entry<Key, Project> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey().getKey() + " " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
class Key {
private String key;
public Key(final String key) {
super();
this.key = key;
}
public String getKey() {
return key;
}
public void setKey(final String key) {
this.key = key;
}
}Output:
INACTIVE [project id : 200, project name : Employee Management System,
project desc : Employee Management System ]
Note that the key1 is null and its entry is removed and garbage collected. Happy coding!
Further Learning
Collections Framework - EnumMap
Collections Framework - IdentityHashMap
Collections Framework - CopyOnWriteArraySet
Collections Framework - EnumSet
Collections Framework - CopyOnWriteArrayList
Reference
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/WeakHashMap.html
Published at DZone with permission of Ramesh Fadatare. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments