What Does a Java Array Look Like in Memory?
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Freearrays in java store one of two things: either primitive values (int, char, …) or references (a.k.a pointers).
when an object is creating by using “new”, memory is allocated on the heap and a reference is returned. this is also true for arrays.
1. single-dimension array
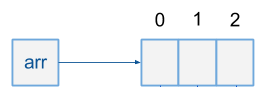
int arr[] = new int[3];
the int[] arr is just the reference to the array of 3 integer. if you create an array with 10 integer, it is the same – an array is allocated and a reference is returned.
2. two-dimensional array
how about 2-dimensional array? actually, we can only have one dimensional arrays in java. 2d arrays are basically just one dimensional arrays of one dimensional arrays.
int[ ][ ] arr = new int[3][ ]; arr[0] = new int[3]; arr[1] = new int[5]; arr[2] = new int[4];
multi-dimensional arrays use the name rules.
3. where are they located in memory?
from the above, there are arrays and reference variables in memory. as we know that jvm runtime data areas include heap, jvm stack, and others. for a simple example as follows, let’s see where the array and its reference are stored.
class a {
int x;
int y;
}
...
public void m1() {
int i = 0;
m2();
}
public void m2() {
a a = new a();
}
...
- when m1 is invoked, a new frame (frame-1) is pushed into the stack, and local variable i is also created in frame-1.
- when m2 is invoked inside of m1, another new frame (frame-2) is pushed into the stack. in m2, an object of class a is created in the heap and reference variable is put in frame-2. now, at this point, the stack and heap looks like the following:
arrays are treated the same way like objects, so how array locates in memory is straight-forward.
Published at DZone with permission of Ryan Wang. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.



Comments