What is JSON? How Do I Use It? Does It Beat BSON?
If you’ve ever wondered about JSON—what it is, how to use it or what it has to do with BSON—then you’ve come to the right place. In this article I’ll explore what these acronyms stand for and what these formats do in the world of programming and databases.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
TL;DR: If you’ve ever wondered about JSON—what it is, how to use it or what it has to do with BSON—then you’ve come to the right place. In this article I’ll explore what these acronyms stand for and what these formats do in the world of programming and databases.
What is JSON?
JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation. Basically, it uses syntax derived from JavaScript to represent data in a way that is readable to both humans and machines. For instance, an example used on the JSON website describes a glossary in JavaScript Object Notation, as shown in the figure below.
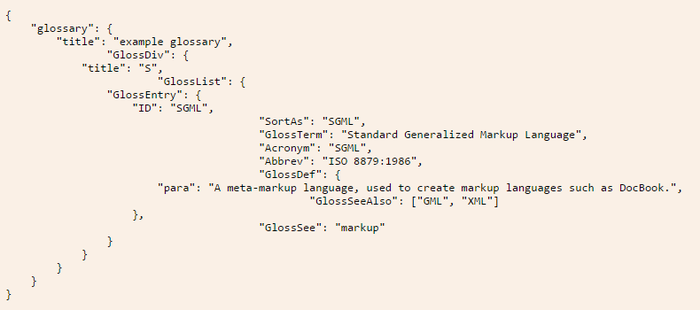
How to Use JSON
As you can see, a hierarchy is created that encloses each level within a set of curly braces ({}). At each level, you have name/value pairs, such as “title”: “example glossary”. In the same way that JavaScript objects work, the value part of the pair can open yet another level by starting a new set of curly braces. This creates a well-structured layout of the data that can be scanned easily for information by machines, as well as be looked at by humans to find what is needed.
This notation allows a number of data types to be represented—numbers, strings, and Booleans, hashes (enclosed by {}) and arrays (enclosed by []) all can be used in this format.
Once data is represented in this notation, a JSON parser can be used in most any programming language to turn this notation into the native data types for that language, thus allowing programmers to access the data using that language’s natural syntax. Since this notation is so prevalent, most programmers have a great deal of experience in storing and retrieving this type of data.
Does It Get Used in Databases?
Document databases typically store data in JSON format or something based upon that format. Rather than the tables and rows used by a relational database, a document database will store and query information through the use of the JSON format.
These databases refer to each set of JSON data as a document. Since the structure is hierarchical, each document can have subdocuments on any of its keys. This setup makes it very easy for a programmer familiar with the language to both store and query the data within the database.
What is BSON?
BSON stands for Binary JSON. This format is specifically used by MongoDB for its document database. The idea behind it is to provide the utility of the JSON format, but also be able to use that format with the speed that comes with a binary format.
JSON vs. BSON
While JSON simply represents a data structure, MongoDB can use BSON to build database indexes on keys at any level, thus helping improve speed in that area. MongoDB also provides a specification called GridFS that can be used in conjunction with BSON to store data over BSON’s 16MB document size limit. This can be useful to store large files, as it divides them into “chunks” to allow the storage to work properly in the database.
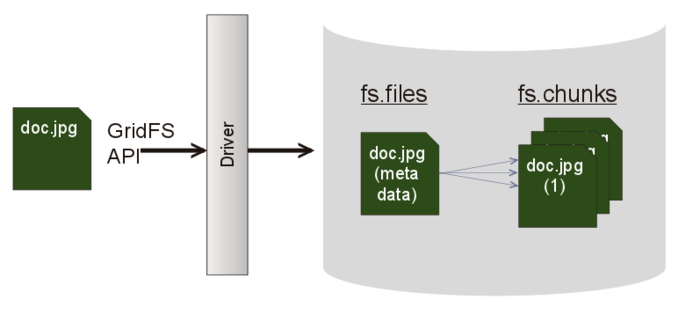
For the most part, JSON and BSON are very similar, but BSON can provide an extra punch of speed as well. Both are certainly very handy ways of storing and retrieving data for applications.
Related Refcard:
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments