A Critical Detail About Kafka Partitioners
Understanding the role of a partitioner in the Kafka producer is important to understand to build effective Kafka applications.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeApache Kafka is the de facto standard for event streaming today. Part of what makes Kafka so successful is its ability to handle tremendous volumes of data, with a throughput of millions of records per second, not unheard of in production environments. One part of Kafka's design that makes this possible is partitioning.
Kafka uses partitions to spread the load of data across brokers in a cluster, and it's also the unit of parallelism; more partitions mean higher throughput. Since Kafka works with key-value pairs, getting records with the same key on the same partition is essential.
Think of a banking application that uses the customer ID for each transaction it produces to Kafka. It's critical to get all those events on the same partition; that way, consumer applications process records in the order they arrive. The mechanism to guarantee records with the same key land on the correct partition is a simple but effective process: take the hash of the key modulo the number of partitions. Here's an illustration showing this concept in action:
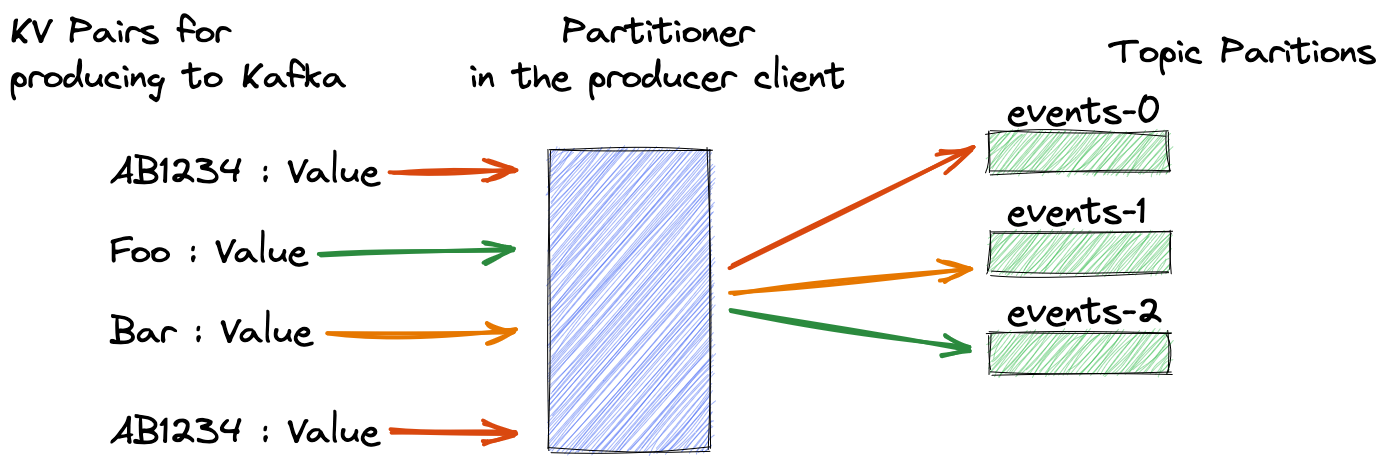
At a high level, a hash function such as CRC32 or Murmur2 takes an input and produces a fixed-size output such as a 64-bit number. The same input always produces the same output, whether implemented in Java, Python, or any other language. Partitioners use the hash result to choose a partition consistently, so the same record key will always map to the same Kafka partition. I won't go into more details in this blog, but it's enough to know that several hashing algorithms are available.
I want to talk today not about how partitions work but about the partitioner in Kafka producer clients. The producer uses a partitioner to determine the correct partition for a given key, so using the same partitioner strategy across your producer clients is critical.
Since producer clients have a default partitioner setting, this requirement shouldn't be an issue. For example, when using the Java producer client with the Apache Kafka distribution, the KafkaProducer class provides a default partitioner that uses the Murmur2 hash function to determine the partition for a given key.
But what about Kafka producer clients in other languages? The excellent librdkafka project is a C/C++ implementation of Kafka clients and is widely used for non-JVM Kafka applications. Additionally, Kafka clients in other languages (Python, C#) build on top of it. The default partitioner for librdkafka uses the CRC32 hash function to get the correct partition for a key.
This situation in and of itself is not an issue, but it easily could be. The Kafka broker is agnostic to the client's language; as long it follows the Kafka protocol, you can use clients in any language, and the broker happily accepts their produce and consume requests. Given today/s polyglot programming environments, you can have development teams within an organization working in different languages, say Python and Java. But without any changes, both groups will use different partitioning strategies in the form of different hashing algorithms: librdkafka producers with CRC32 and Java producers with Murmur2, so records with the same key will land in different partitions! So, what's the remedy to this situation?
The Java KafkaProducer only provides one hashing algorithm via a default partitioner; since implementing a partitioner is tricky, it's best to leave it at the default. But the librdkafka producer client provides multiple options. One of those options is the murmur2_random partitioner, which uses the murmur2 hash function and assigns null keys to a random partition, the equivalent behavior to the Java default partitioner.
For example, if you're using the Kafka producer client in C#, you can set the partitioning strategy with this line:
ProducerConfig.Partitioner = Partitioner.Murmur2Random;And now your C# and Java producer clients use compatible partitioning approaches!
When using a non-java Kafka client, enabling the identical partitioning strategy as the Java producer client is an excellent idea to ensure that all producers use consistent partitions for different keys.
Published at DZone with permission of Bill Bejeck, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments