A Guide to MySQL JOINs
This guide will demonstrate how to use each type of JOIN in MySQL, including INNER JOIN, OUTER JOIN (LEFT and RIGHT), and CROSS JOIN.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIntroduction
In a single query, JOINs are utilized to get data from several tables. In MySQL, JOINs aggregate data from several tables and get it as a single result. Each table in a relational database includes unique or common data, and each table is connected logically. JOINs are used to obtain data from tables that share a common field.
What Are JOINs in MySQL?
In MySQL, the JOIN statement is a technique of connecting data between several tables in a database based on the values of common fields in those tables. The same column name and data type are generally present in the tables being linked as common values. The join key or common key refers to the shared columns. SELECT, UPDATE, and DELETE commands can all employ JOINs.
Getting Started With JOINs
The MySQL JOIN type specifies how two tables in a query are linked. INNER JOIN, OUTER JOIN, and CROSS JOIN are the three types of JOIN clauses supported by MySQL. LEFT JOINs and RIGHT JOINs are two different types of OUTER JOINs. To show how the JOINs operate more visually, we need to create a new schema and insert some sample data.
CREATE TABLE Users (
UserID int,
UserName varchar(255),
Password varchar(255),
isActive boolean
);
CREATE TABLE Userprofile (
ProfileID int,
LastName varchar(255),
FirstName varchar(255),
Email varchar(255),
Phone varchar(255)
);The next thing we will do is insert some data into it. You can insert as many users into the tables as you like.
INSERT INTO Users
(UserID, UserName,Password, isActive)
VALUES
(1,'krofax','krofax1234', true);
INSERT INTO userprofile
(profileid, lastname, firstname, email, phone)
VALUES
(1,'Ada', 'George', 'adageorge@gmail.com','1290003456');MySQL INNER JOIN Clause
Only common matched records are retrieved using INNER JOINs. The INNER JOIN clause restricts records retrieval from Table A and Table B to those that satisfy the join requirement. It is the most often used JOIN type. Examine the Venn diagram below to acquire a better understanding of INNER JOINs.

Here is the syntax for MySQL INNER JOIN:
SELECT
columns
FROM
tableA
INNER JOIN tableB
ON tableA.column = tableB.column;
MySQL OUTER JOINs
OUTER JOINs, in contrast to INNER JOINs, yield non-matching records as well as matching rows. If rows in a connected table don't match, the NULL values will be shown.MySQL has two different forms of OUTER JOINs: MySQL LEFT JOIN and MySQL RIGHT JOIN. Let's look at each of them in more detail.
MySQL LEFT JOIN Clause
LEFT JOINs allow you to get all entries from Table A and those from Table B that meet the join criteria. NULL values are displayed for records from Table A that do not fit the criteria. Examine the Venn diagram below to have a better understanding of LEFT JOINs.

Here is the syntax for MySQL LEFT JOIN:
SELECT
columns
FROM
tableA
LEFT JOIN tableB
ON tableA.column = tableB.column;
Note: The LEFT JOIN keyword returns all records from the left table (Customers), even if there are no matches in the right table (Orders).
MySQL RIGHT JOIN Clause
As a result, RIGHT JOINs allow you to get all entries from Table B and those from Table A that meet the join criteria. The NULL values are presented for the records from Table B that do not fit the criteria. For a better understanding of RIGHT JOINs, see the Venn diagram below.

Here is the syntax for MySQL RIGHT JOIN:
SELECT
columns
FROM
tableA
RIGHT JOIN tableB
ON tableA.column = tableB.column;
Note: The RIGHT JOIN keyword returns all records from the right table (Employees), even if there are no matches in the left table (Orders).
MySQL CROSS JOIN Clause
The MySQL CROSS JOIN, commonly known as a cartesian join, returns all possible row combinations from each table. If no extra condition is provided, the result set is obtained by multiplying each row of table A with all rows in table B.Examine the Venn diagram below to learn more about CROSS JOINS.
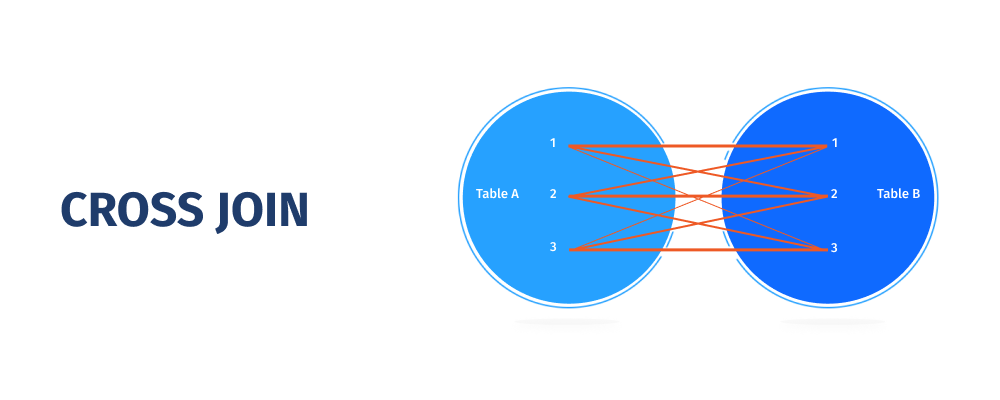
When do you think you'll need that kind of JOIN? Assume, for example, that you're tasked with finding all possible combinations of a product and a color. In that scenario, a CROSS JOIN would be quite useful.
Note: CROSS JOIN might result in quite huge result sets!
Here is the syntax for MySQL CROSS JOIN:
SELECT
columns
FROM
tableA
CROSS JOIN tableB;
Tips for JOINing
In MySQL, JOINs allow you to perform a single JOIN query rather than many simple queries. As a result, you'll get improved speed, lower server overhead, and fewer data transfers between MySQL and your application. Unlike SQL Server, MySQL does not have a distinct JOIN type for FULL OUTER JOIN. You may, however, combine LEFT OUTER JOIN and RIGHT OUTER JOIN to get the same effects as FULL OUTER JOIN.
SELECT
*
FROM
tableA
LEFT JOIN tableB
ON tableA.id = tableB.id
UNION
SELECT
*
FROM
tableA
RIGHT JOIN tableB
ON tableA.id = tableB.id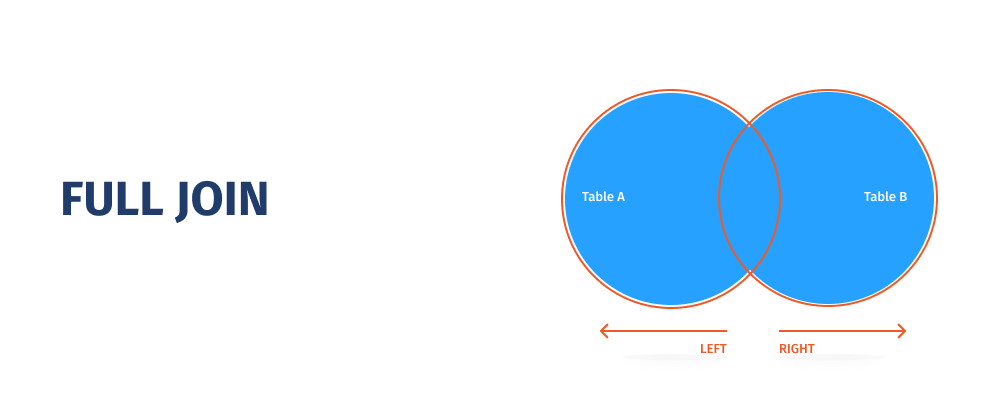
Using MySQL JOINs, you can also join more than two tables.
SELECT
*
FROM
tableA
LEFT JOIN tableB
ON tableA.id = tableB.id
LEFT JOIN tableC
ON tableC.id = tableA.id;
Why Are JOINS Useful?
- It's a lot quicker. In a single query, JOINS allows you to get data from two or more linked database tables. JOINS are very valuable since they save time over running queries one by one to achieve the same results.
- MySQL is more efficient. Another advantage of utilizing JOINS is that MySQL performs better since joins are performed via indexing.
- Using JOINS lowers server load. Because you execute one query, you get better and faster results.
Any analyst or DBA must have a solid grasp of JOINs and utilize them freely in their daily job. This is when Arctype for MySQL comes in handy. Even for complicated JOIN clauses, its sophisticated code completion works flawlessly. Arctype for MySQL will present you with a full JOIN clause, so you won't have to memorize hundreds of column names or aliases. Its feature-rich capability makes creating complicated queries and managing JOIN conditions a breeze.
Published at DZone with permission of Blessing Krofegha. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments