ActiveMQ JMS (Java Messaging Service) vs. Data Streaming Kafka With Camel Code Sample
While ActiveMQ JMS and Kafka are used for message queuing and real-time data processing, they have significant differences.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeActiveMQ and Kafka are both messaging systems used for real-time data processing and streaming. Both of these systems are open-source and offer different features that cater to specific use cases. While ActiveMQ JMS and Kafka are both used for message queuing and real-time data processing, there are significant differences between them.
ActiveMQ JMS is a traditional message broker that supports multiple messaging protocols such as JMS, AMQP, and MQTT. It is designed to provide reliable message delivery and offers features such as message persistence, clustering, and transaction support. ActiveMQ JMS is commonly used in enterprise systems for mission-critical applications where reliability is of utmost importance.
Sample Example for consuming message from rest API and Writing to AMQ queues:
import org.apache.camel.CamelContext;
import org.apache.camel.builder.RouteBuilder;
import org.apache.camel.impl.DefaultCamelContext;
public class RestApiToActiveMq {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CamelContext context = new DefaultCamelContext();
// define a route to consume messages from REST API and write them to ActiveMQ
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() {
public void configure() {
from("rest:get:/api/messages")
.to("activemq:queue:myQueue");
}
};
// add the route to the Camel context
context.addRoutes(builder);
// start the Camel context
context.start();
// keep the program running to continue consuming messages
Thread.sleep(Long.MAX_VALUE);
// stop the Camel context
context.stop();
}
}
Sample Example for consuming message AMQ queues and writing to snowflakes Data warehouse:
import org.apache.camel.CamelContext;
import org.apache.camel.builder.RouteBuilder;
import org.apache.camel.impl.DefaultCamelContext;
public class AmqToSnowflake {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CamelContext context = new DefaultCamelContext();
// define a route to consume messages from AMQ and write them to Snowflake
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() {
public void configure() {
from("activemq:queue:myQueue")
.to("snowflake-jdbc:myDatabase?query=INSERT INTO myTable (message) VALUES (:?message)");
}
};
// add the route to the Camel context
context.addRoutes(builder);
// start the Camel context
context.start();
// keep the program running to continue consuming messages
Thread.sleep(Long.MAX_VALUE);
// stop the Camel context
context.stop();
}
}
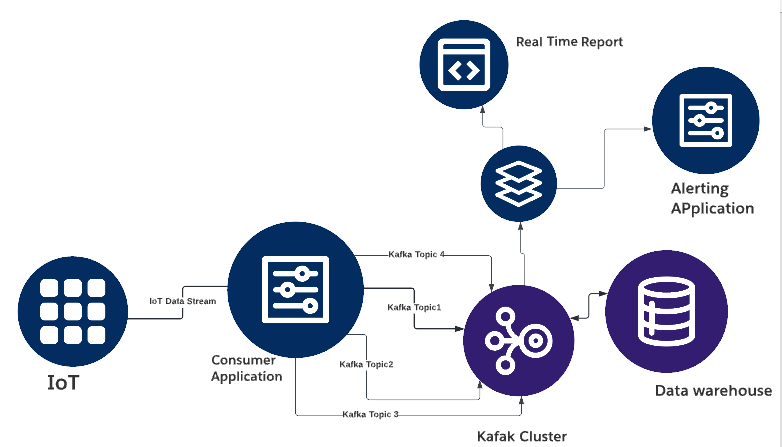
On the other hand, Kafka is a distributed streaming platform designed for handling large-scale data streaming. It is optimized for horizontal scalability, fault tolerance, and high throughput, making it an excellent choice for big data applications. In addition, Kafka offers features such as real-time data streaming, high-performance messaging, and distributed data storage.
Sample Example for consuming message from rest API and Writing to Kafak Topic:
import org.apache.camel.CamelContext;
import org.apache.camel.builder.RouteBuilder;
import org.apache.camel.impl.DefaultCamelContext;
public class RestApiToKafka {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CamelContext context = new DefaultCamelContext();
// define a route to consume messages from REST API and write them to Kafka
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() {
public void configure() {
from("rest:get:/api/messages")
.to("kafka:myTopic?brokers=localhost:9092");
}
};
// add the route to the Camel context
context.addRoutes(builder);
// start the Camel context
context.start();
// keep the program running to continue consuming messages
Thread.sleep(Long.MAX_VALUE);
// stop the Camel context
context.stop();
}
}
Sample Example for consuming message Kafka Topic and writing to snowflakes Data warehouse:
import org.apache.camel.CamelContext;
import org.apache.camel.builder.RouteBuilder;
import org.apache.camel.impl.DefaultCamelContext;
public class KafkaToSnowflake {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CamelContext context = new DefaultCamelContext();
// define a route to consume messages from Kafka and write them to Snowflake
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() {
public void configure() {
from("kafka:myTopic?brokers=localhost:9092")
.to("snowflake-jdbc:myDatabase?query=INSERT INTO myTable (message) VALUES (:?message)");
}
};
// add the route to the Camel context
context.addRoutes(builder);
// start the Camel context
context.start();
// keep the program running to continue consuming messages
Thread.sleep(Long.MAX_VALUE);
// stop the Camel context
context.stop();
}
}
One of the key differences between ActiveMQ JMS and Kafka is their architecture. ActiveMQ JMS is a traditional messaging system that is based on a hub-and-spoke model, where the message broker acts as a centralized hub for all message exchanges. On the other hand, Kafka is designed as a distributed system that uses a publish-subscribe model, where messages are published to a topic, and subscribers consume the messages from that topic. Kafka's distributed architecture provides fault tolerance and high availability, making it an ideal choice for mission-critical applications.
Another difference between ActiveMQ JMS and Kafka is their performance. ActiveMQ JMS is designed to provide reliable message delivery with features such as message persistence and transaction support. While this provides a high level of reliability, it can also impact performance. In contrast, Kafka's architecture is designed for high throughput and low latency, making it an excellent choice for real-time data processing and analysis.
In terms of use cases, ActiveMQ JMS is an excellent choice for traditional messaging applications where reliability and message ordering are more important than speed. It is commonly used in enterprise systems for mission-critical applications where reliability is of utmost importance. On the other hand, Kafka is an excellent choice for real-time data processing and analysis. It is commonly used for big data applications where high throughput and low latency are critical.
In conclusion, both ActiveMQ JMS and Kafka are excellent messaging systems that offer different features for different use cases. ActiveMQ JMS is an excellent choice for traditional messaging applications where reliability is of utmost importance, while Kafka is an excellent choice for real-time data processing and analysis. Therefore, it is important to consider the specific requirements of your application when choosing between ActiveMQ JMS and Kafka.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments