AngularJS: How to Handle XSS Vulnerability Scenarios
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free- escape html completely
- insert html in secure way while ignoring elements such as “script”. this is as well dangerous and could deface your website, if not taken care, especially with “img” tag.
- trust and insert entire html; this is dangerous and could easily end-up defacing your website
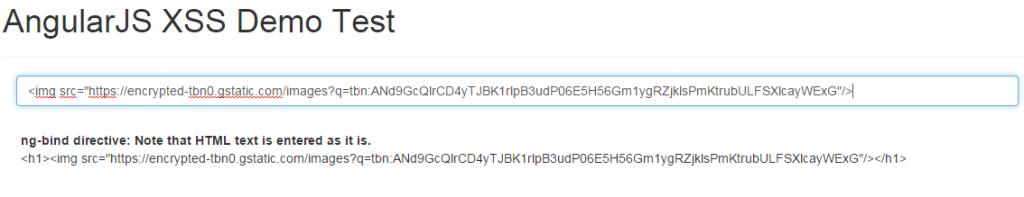
escape html using ng-bind directive
in case you want to escape html in entireity, you may want to use ng-bind directive. all it does is escape the html elements and print it as it is. following code demonstrates the ng-bind directive usage.
<div>
<form>
<h1>angularjs xss demo test</h1>
<hr/>
<div class="col-md-12">
<input type="text" ng-model="name" class="form-control col-md-12" ng-change="processhtmlcode()" placeholder="enter some html text..."/>
</div>
</form>
</div>
<hr/>
<div style="padding:20px">
<span><strong>ng-bind directive: note that html text is entered as it is.</strong></span><br/>
<span ng-bind="hellomessage">{{hellomessage}}</span>
</div>
following diagram demonstrates the above. pay attention to the html code entered in the text field. it is printed as it is, on to the html page.
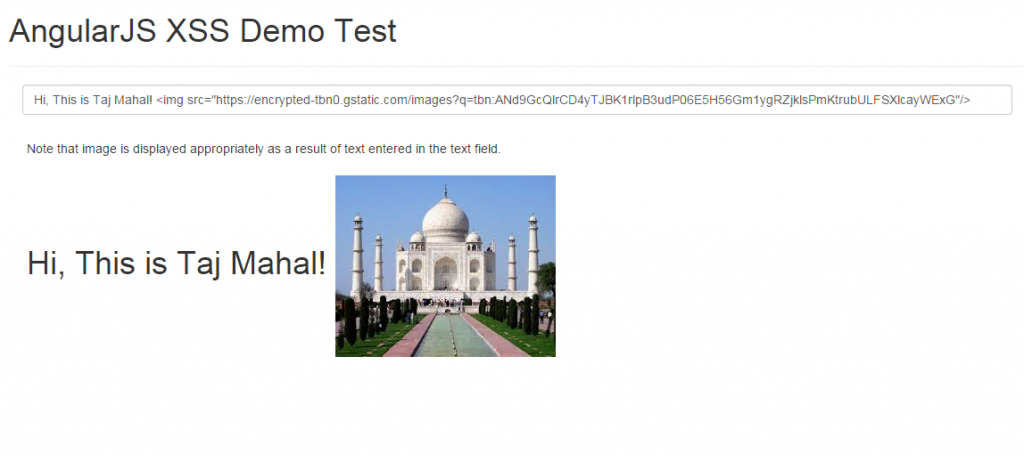
insert html in secure way, while ignoring elements such as “script”, using ng-bind-html directive
this is key to solving xss attacks. that said, one should still take care of elements such as “img” ( included as part of white-list; void elements) as it could display any image (including illegal ones) on your webpage, thus, defacing your webpage . using ng-bind-html directive, javascript script tag such as “script” could be ignored straight-away. ng-bind-html directive evaluates the expression and inserts the resulting html into the element in a secure way. for cases where user inputs could consist of html (such as comments), the inclusion of ng-bind-html directive would ensure that the text is sanitize against a white-list of safe html tokens. the whitelist of safe tokens is coded as part of $sanitize module and mentioned below. following is included in the safe list (taken directly from the source code):
- void elements : area,br,col,hr,img,wbr. the details of same could be found at http://dev.w3.org/html5/spec/overview.html#void-elements
- block element : address,article,aside,blockquote,caption,center,del,dir,div,dl,figure,figcaption,footer,h1,h2,h3,h4, h5,h6,header,hgroup,hr,ins,map,menu,nav,ol,pre,script,section,table,ul
- inline elements : a,abbr,acronym,b,bdi,bdo,big,br,cite,code,del,dfn,em,font,i,img,ins,kbd,label,map,mark,q,ruby, rp,rt,s,samp,small,span,strike,strong,sub,sup,time,tt,u,var
- end tag elements : colgroup,dd,dt,li,p,tbody,td,tfoot,th,thead,tr,rp,rt. the details of same could be found at http://dev.w3.org/html5/spec/overview.html#optional-tags
following are two elements which are escaped as it is in untrusted category . in case, you want to show it, you would have to use $sce service and call trustashtml method for angular to execute below-mentioned elements.
- script
- style
following represents code sample demonstrating the ng-bind-html directive usage.
<div> <form> <h1>angularjs xss demo test</h1> <hr/> <div class="col-md-12"> <input type="text" ng-model="name" class="form-control col-md-12" ng-change="processhtmlcode()" placeholder="enter some html text..."/> </div> </form> </div> <hr/> <div style="padding:20px"> <span>ng-bind-html directive: note that image is displayed appropriately as a result of text entered in the text field.</span> <span ng-bind-html="hellomessage"></span> </div>
following image demonstrates how it looks like when entering html code in textfield that is inserted into dom in a secure way. pay attention to “img” element which is a part of void elements in above list. as the code is entered in the textfield, the image appeared as “img” is in trusted list (white-list)
trust and insert entire html
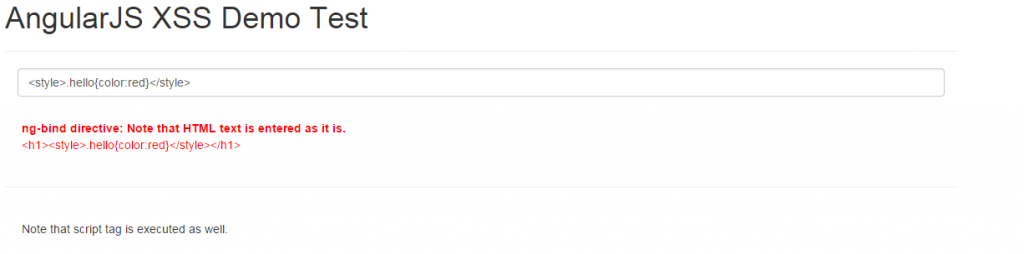
warning: this is dangerous and could easily end-up defacing your website . only when you know and are doubly sure, you should use trustashtml. in case, you are confident that the text content could be trusted, you could use $sce service and call trustashtml method which then inserts entire html into the dom. pay attention to the html and javascript code snippet where $sce service is used to invoke trustashtml method to trust the html code. in that case, one code such as “<style>.hello{color:red}</style>” is inserted, it ended up painting already existing html element. this may not be healthy. one could change the background images with illegal images that way.
<script type="text/javascript">
angular.module('helloapp', ["ngsanitize"])
.controller('helloctrl', ['$scope', '$sce', function($scope, $sce){
$scope.name="";
$scope.processhtmlcode=function() {
$scope.hellomessage = "<h1>" + $scope.name + "</h1>";
$scope.trustedmessage = $sce.trustashtml( $scope.name );
}
}])
</script>
<!-- pay attention to class hello which is coded in ui and as a result, element is painted in red-->
<div style="padding:20px">
<span class="hello"><strong>ng-bind directive: note that html text is entered as it is.</strong></span><br/>
<span class="hello" ng-bind="hellomessage">{{hellomessage}}</span>
</div>
<hr/>
<div style="padding:20px">
<span>note that script tag is executed as well.</span>
<span ng-bind-html="trustedmessage"></span>
</div>
following image demonstrates how it looks like when entering html style code in textfield that is inserted into dom . as a result, the other html element is painted in red as shown below. in scenarios where a hacker could insert an style element with background, this could show-up unwanted background and bring bad experience for the end users.
entire code – cut/copy and paste and play
<html>
<head>
<title>hello angularjs</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="http://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.2.0/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<script type="text/javascript" src="http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.3.3/angular.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.3.3/angular-sanitize.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body class="container" ng-app="helloapp" ng-controller="helloctrl">
<div>
<form>
<h1>angularjs xss demo test</h1>
<hr/>
<div class="col-md-12">
<input type="text" ng-model="name" class="form-control col-md-12" ng-change="processhtmlcode()" placeholder="enter some html text..."/>
</div>
</form>
<hr/>
</div>
<hr/>
<div style="padding:20px">
<span class="hello"><strong>ng-bind directive: note that html text is entered as it is.</strong></span><br/>
<span class="hello" ng-bind="hellomessage">{{hellomessage}}</span>
</div>
<hr/>
<div style="padding:20px">
<span>note that script tag is executed as well.</span>
<span ng-bind-html="trustedmessage"></span>
</div>
<hr/>
<div style="padding:20px">
<span>ng-bind-html directive: note that image is displayed appropriately as a result of text entered in the text field.</span>
<span ng-bind-html="hellomessage"></span>
</div>
<hr/>
<script type="text/javascript">
angular.module('helloapp', ["ngsanitize"])
.controller('helloctrl', ['$scope', '$sce', function($scope, $sce){
$scope.name="";
$scope.processhtmlcode=function() {
$scope.hellomessage = "<h1>" + $scope.name + "</h1>";
$scope.trustedmessage = $sce.trustashtml( $scope.name );
}
}])
</script>
</body>
</html>Published at DZone with permission of Ajitesh Kumar, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments