Authorization Using Reverse Proxy Design Pattern in Cloud Environment
Learn about the implementation of the reverse proxy pattern to enhance security in cloud microservices acting as a gatekeeper for API calls.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeA persistent challenge within cloud solutions revolves around the necessity to segregate authentication patterns from microservices intricately tied to application code. This complexity arises from various factors, such as external applications utilizing diverse authentication schemes like OAuth2 and OpenID connect, with the potential for pattern changes over time. The objective is to ensure that modifications to these authentication patterns do not precipitate extensive cascading changes across all utilized microservices.
Additionally, addressing the broader demand for comprehensive multi-layered security mechanisms in the cloud poses a consistent and intricate aspect of this complex landscape. In this article, we will delve into the strategic implementation of the reverse proxy pattern to enhance the security of cloud microservices operating within Kubernetes (K8), concurrently ensuring the safeguarding of all communications to these microservices.
A reverse proxy operates as a pivotal gateway, mediating between clients initiating API calls and the hosting microservices. Functioning akin to a gatekeeper, it possesses the capability to either forward or reject incoming traffic directed towards the microservices. Administrators can further customize configurations for routing, policy implementation, throttling, and other critical parameters at this intermediary layer as well.
The robustness of security in cloud solutions is contingent upon the strength of the weakest link within the infrastructure. This article introduces a model cloud infrastructure designed to align with these security objectives.
Reverse Proxy-Based Authorization
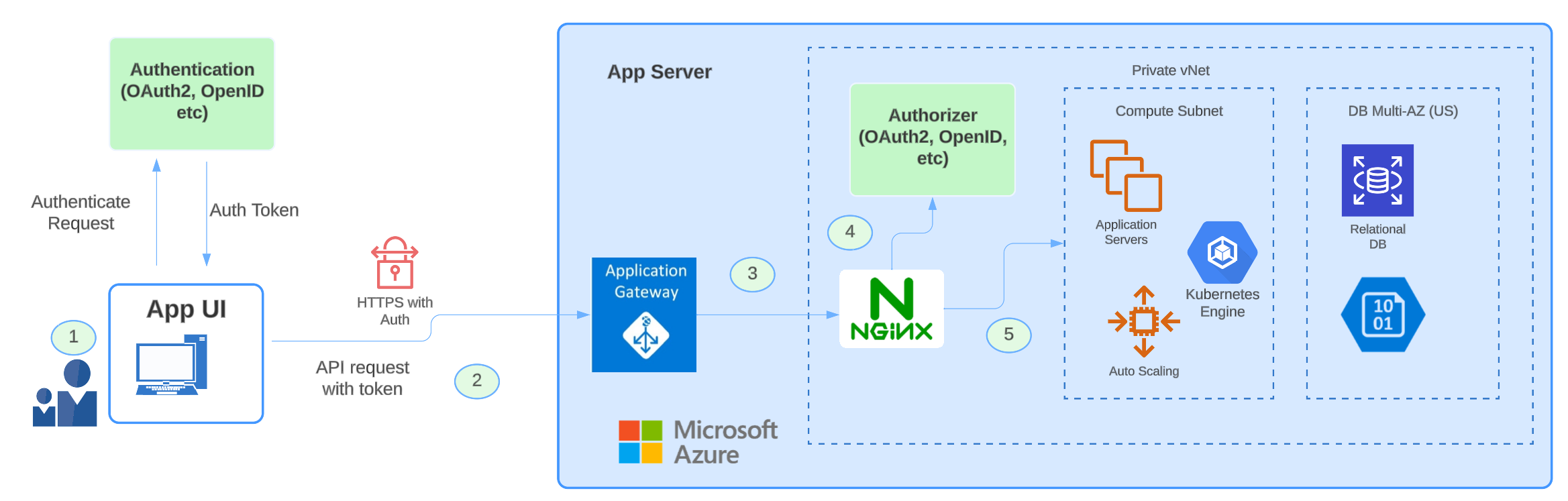
Let's explore the intricacies of the outlined cloud solutions infrastructure. Key details of this infrastructure include:
- Virtually all components, with the exception of the API gateway, are shielded within a private virtual network (VNET).
- Even if the entire environment with all of the cloud components is completely locked, a secondary level of access controls should be established for database access, blob storage access, etc.
- It is also assumed here all the secrets are saved in a vault and the services pull the secrets at run time from that environment’s secrets vault.
- Microservices APIs, databases, and blob storage are all confined to the private domain, inaccessible directly from the internet. Any external access necessitates traversal through the Gateway/NGINX layers, ensuring a controlled and secure environment.
Consider a scenario where a request originates from a User Interface (UI) Application, initiating communication with a server's API. The process unfolds as follows:
- User authentication: The user logs into the UI application using a supported authentication scheme, obtaining a token that is subsequently stored in local storage.
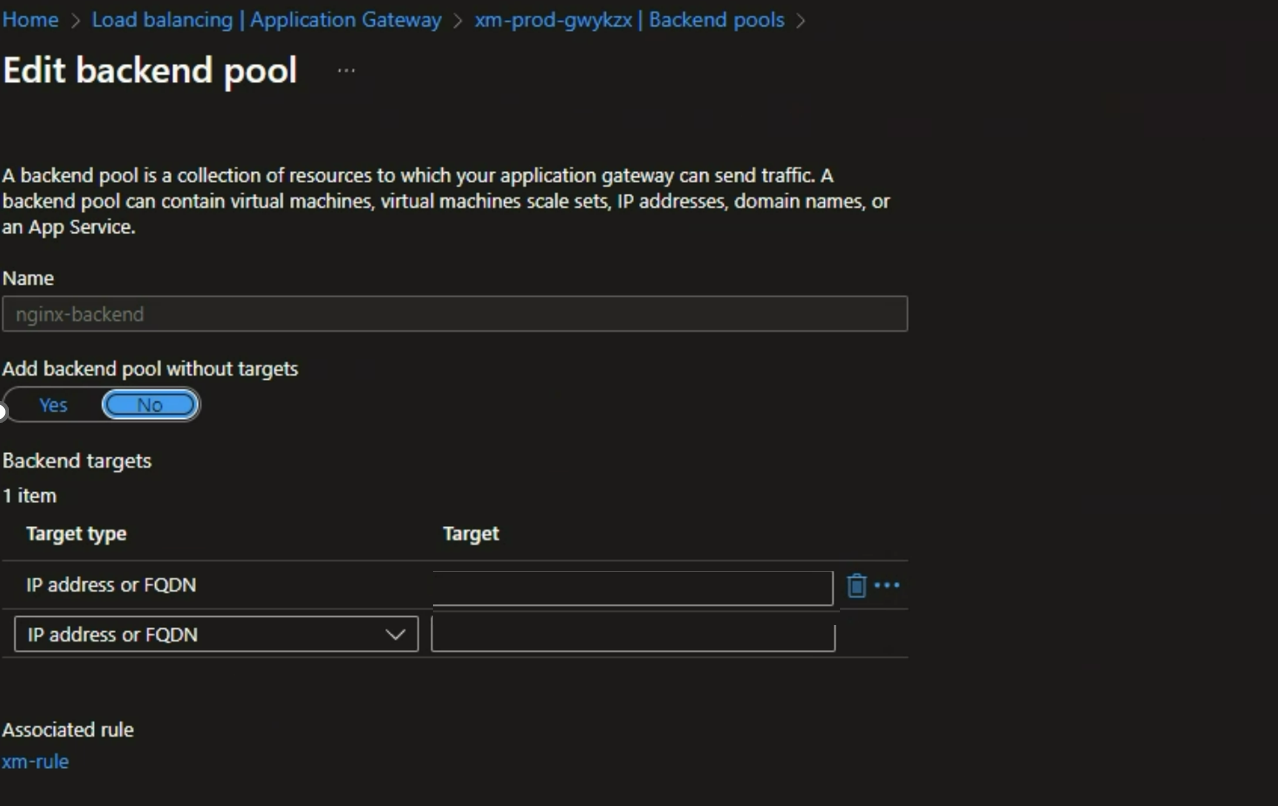
- API request initiation: The UI application triggers an API request with the authenticated token, reaching the public layer of the App Gateway. This gateway manages functions like rate limits, routing, and policy management. Importantly, it is configured to ensure that only the App Gateway can access the NGINX layer through a backend pool configuration.
![Edit backend pool]()
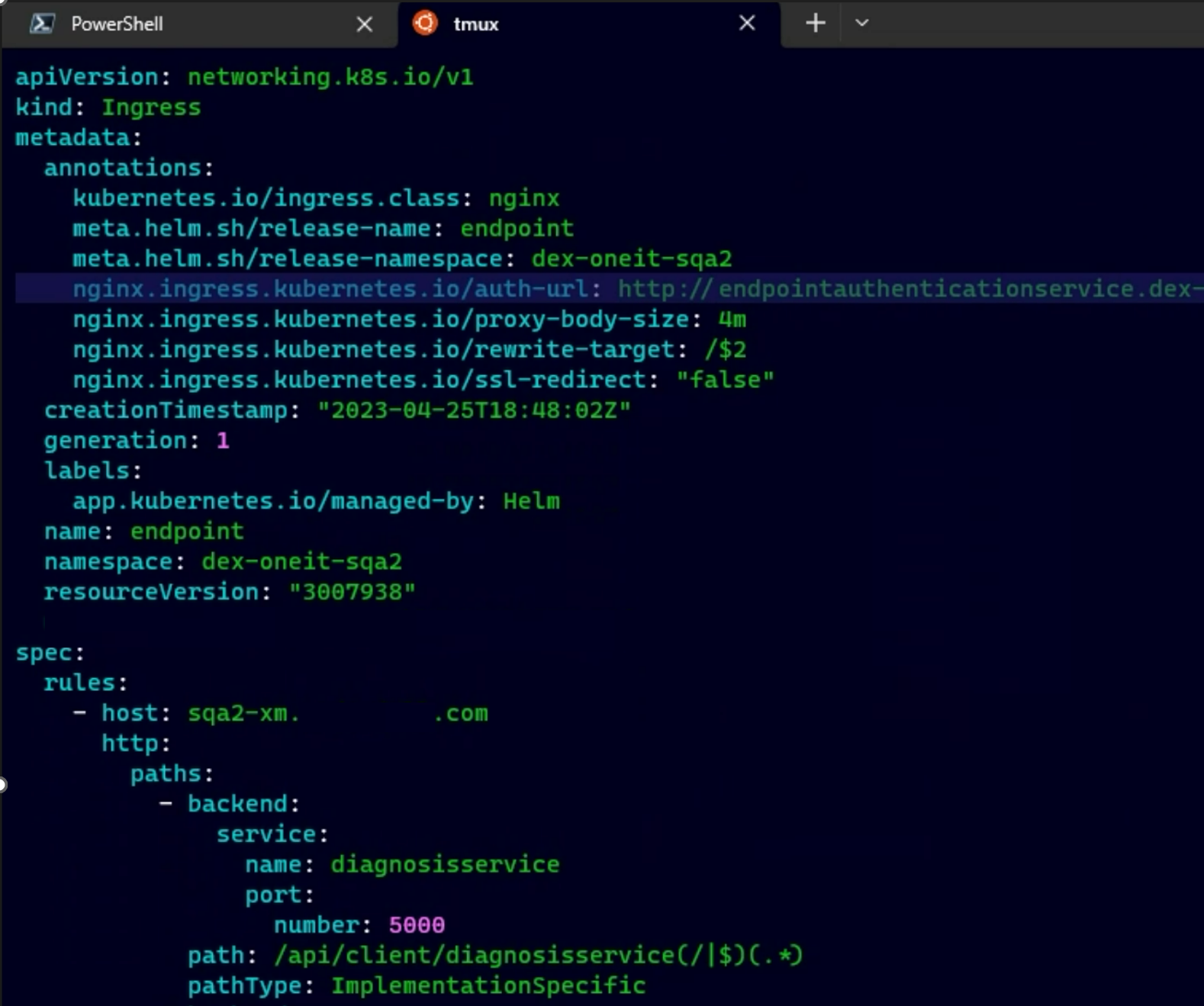
- NGINX proxy layer: App Gateway redirects the request to the NGINX Proxy layer, where crucial processes occur. NGINX identifies the token type and authentication method, utilizing thumbprints, certificate types, etc. It then invokes an appropriate authorization provider to validate the token in the authentication request. A typical configuration for NGINX with the authorizer endpoint and path forward URL will look like below:
![NGINX proxy layer]()
- Token validation: The Authorizer, responsible for token validation, uses public keys associated with the thumbprint to verify the token's signature. It communicates the validation status (valid or invalid) back to NGINX.
- Request handling: Based on the success or failure of the authorization request, NGINX Proxy either forwards the incoming API request or rejects it, ensuring a secure and controlled access mechanism.
Conclusion
In conclusion, employing the reverse proxy pattern within the illustrated model cloud infrastructure offers several distinct advantages:
- Seamless authentication scheme swapping: Facilitates the effortless interchange of authentication schemes without necessitating modifications to the underlying application code
- Granular backend server configuration: Enables the configuration of backend servers to exclusively accept traffic directly from the proxy, empowering the proxy to assume responsibility for detailed access control configurations
- Comprehensive cloud component protection: Affords complete black box protection for all components within the cloud environment, ensuring a heightened level of security
- Customized authorizationpPatterns: Permits distinct authorization patterns and URL configurations for different paths or microservices, enhancing flexibility in managing varied authentication requirements
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments