Automate Your Development Workflow With Github Actions
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeHi everybody. My name is Hacene. I am a software developer and interested in DevOps. Today, I will show you how to automate a development workflow life cycle using Github Actions.

On November 13, 2019, Github engineers revealed some news: GitHub Actions is supporting CI/CD now, and it's free for public repositories! We can manage and automate our development workflows right in our repository using GitHub Actions. The API supports multiple Operating Systems (Linux, Windows, MacOS…) and different languages.
In this article, I will give you an example of a CI/CD pipeline using Github Actions for Spring boot 2.x (java 8) web service.
Introduction
The idea is to automate the development workflow by building a CI/CD pipeline using Github Actions. The aim is to deploy a Spring Boot web service on a remote server. We will use a succession of jobs to build, test, generate code coverage report, and deploy our code right from GitHub. The generated package will be deployed on the remote server.
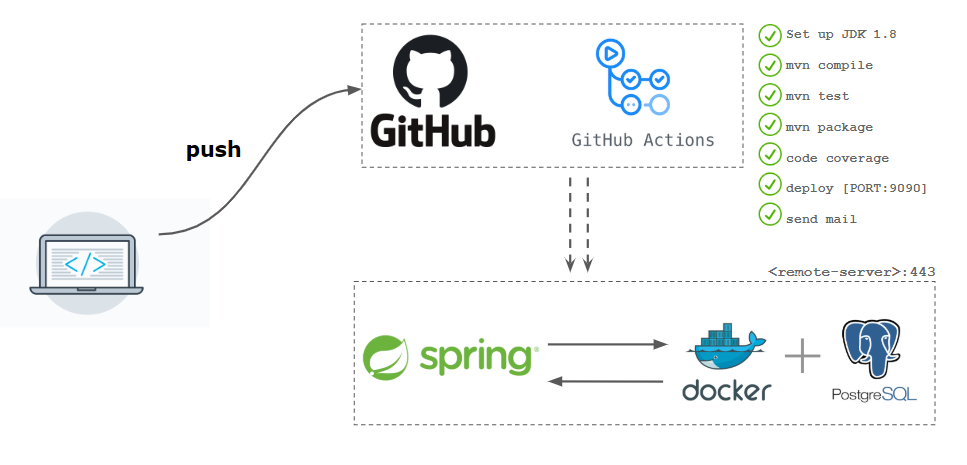
There are two ways to create a required workflow file :
We can create a workflow in our Github repository. The YAML file must be stored in the .github/workflows directory in the root of our Github repository. The workflow must have at least one job that contains a set of steps that perform individual tasks. Steps can run commands or use an action. Our workflow file should respect a YAML syntax and must have either a .yml or .yaml file extension. If you want to learn more about YAML, see "Learn YAML in five minutes."
By creating a workflow file in the Actions section on GitHub repository, we choose maven workflow :
When we click on Set up this workflow, we will see the pre-filled maven workflow below:
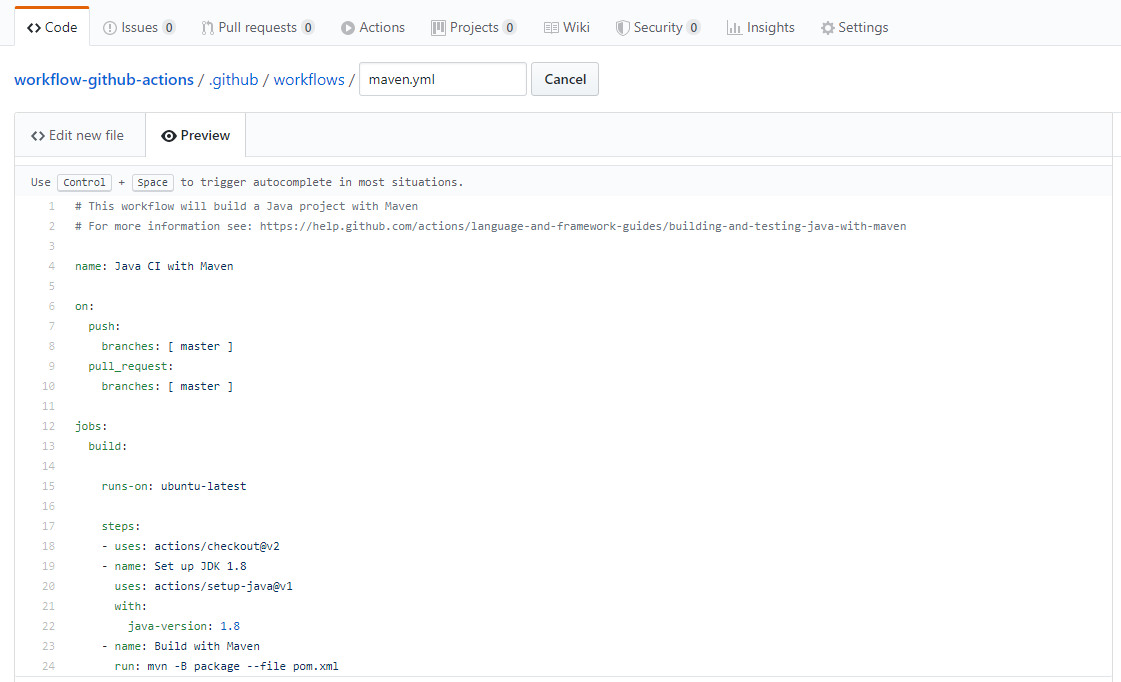
The jobs are based on Matrix builds. A matrix build can generate at most 256 jobs per workflow run.
We configure a workflow to start when a GitHub event occurs. The jobs will be triggered after pushing code or making a pull request on the master branch. The main job in this example is the launching mvn package command. As it's specified in the YAML file, we have to commit the changes to the master branch.
Testing the Workflow
Let’s test it and see what happens …
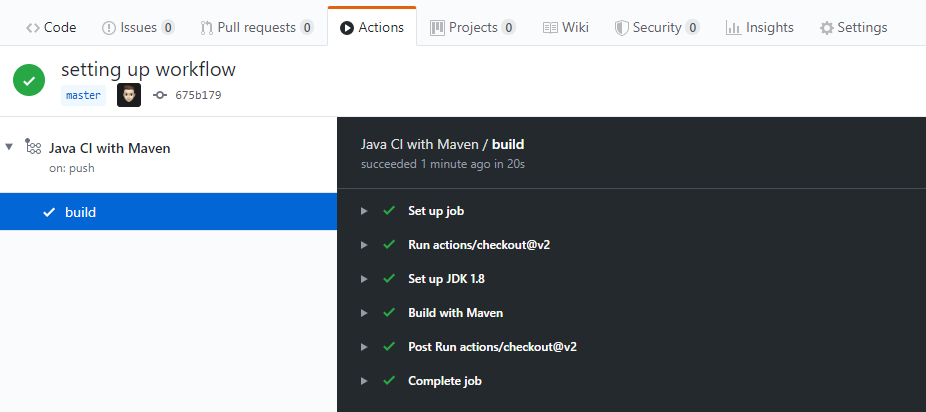
After launching the workflow process, the configuration executed will define some actions that should be performed inside the Ubuntu container. The job makes a checkout of my git repository on the master branch and sets up a JDK 1.8. Then, it starts the mvn build command and puts up the required Maven packages included in my pom.xml. Finally, it runs the tests and generates the JAR file.
Here are some limits about using Github Actions, check this link.
Enhancing the Workflow
Now, we will divide our workflow into different jobs:
compile job: checks out the Github source code and compiles it.
test job: runs unit tests (it requires a compile job).
build job: runs the mvn build command and generates the code coverage report, which will be sent to codecov.io.
Below is the complete file:
xxxxxxxxxx
nameJava CI with Maven
on
push
branches master
pull_request
branches master
jobs
compile
runs-onubuntu-latest
nameRunning Java $ matrix.java compile
steps
usesactions/checkout@v2
nameSet up JDK 1.8
usesactions/setup-java@v1
with
java-version1.8
nameCompile code
runmvn compile
test
runs-onubuntu-latest
nameRunning tests
needscompile
steps
usesactions/checkout@v2
nameSet up JDK 1.8
usesactions/setup-java@v1
with
java-version1.8
nameRun unit tests
runmvn test
build
runs-onubuntu-latest
nameRun mvn build and generate coverage report
needstest
steps
usesactions/checkout@v2
nameSet up JDK 1.8
usesactions/setup-java@v1
with
java-version1.8
nameBuild with Maven
runmvn -B package --file pom.xml -Dmaven.test.skip=true
namegenerate report codecov
runmvn coberturacobertura
nameUpload coverage
ifsuccess()
run
curl -s https://codecov.io/bash | bash
env
CODECOV_TOKEN$ secrets.CODECOV_TOKEN
shellbash
We use encrypted secrets that allow us to store sensitive information. A field CODECOV_TOKEN, is a token retrieved from codecov.io. It's persisted as a secret in the Github environment.
Once the actions have been performed, we can see the result in the Actions tab:
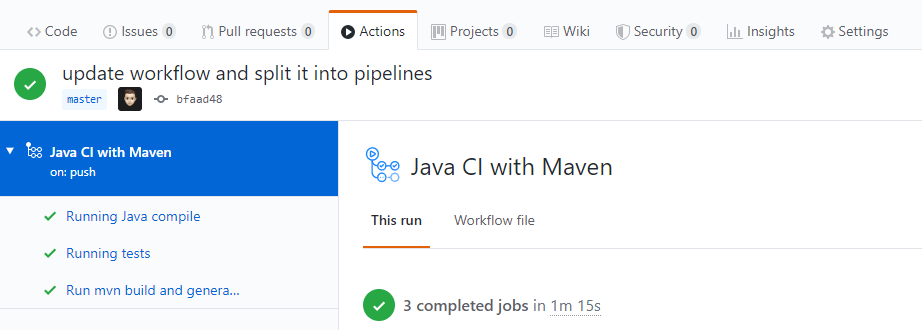
In the last step, we need to add a job to deploy the jar file on the remote server. This job is pretty much the same as the preceding ones. We have to copy the executable file to the remote server; this operation is based on SFTP protocol.
To get this working, we will use actions shared by the GitHub community, and we will customize them as needed, garygrossgarten/github-action-scp@release and fifsky/ssh-action@master. Then, we have to add the secrets (environment variables for ssh connection) on the Github secrets section of our repository.
These variables will be available in the container that was started with Github Actions:
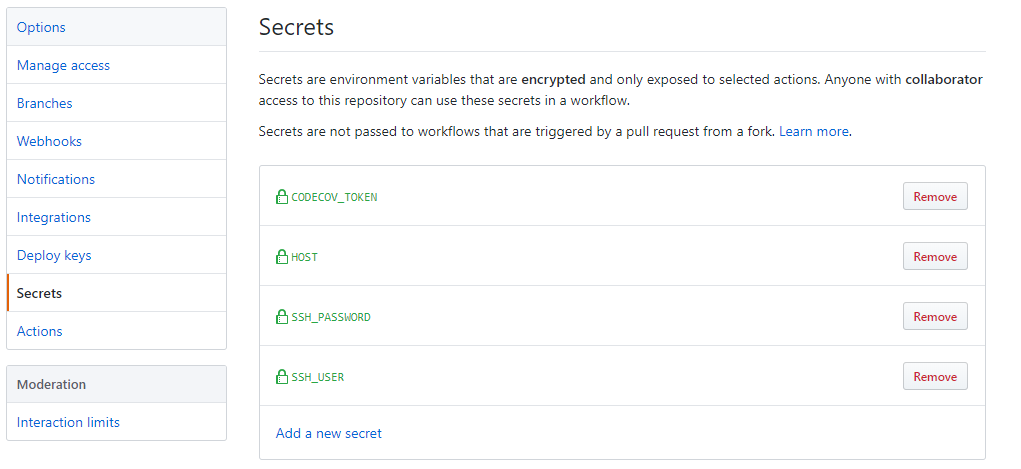
Adding a job to deploy the executable file:
xxxxxxxxxx
deploy
runs-onubuntu-latest
nameDeploy the JAR file to the remote server
needsbuild
steps
usesactions/checkout@v2
nameSet up JDK 1.8
usesactions/setup-java@v1
with
java-version1.8
nameGenerate the package
runmvn -B package --file pom.xml -Dmaven.test.skip=true
nameDeploy the package to the remote server
usesgarygrossgarten/github-action-scp@release
with
localtarget/workflow-github-actions-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar
remotehacene/demo/actions/workflow-github-actions.jar # My remote directory
host$ secrets.HOST
username$ secrets.SSH_USER
password$ secrets.SSH_PASSWORD
nameRun a script on remote server (start the application)
ifalways()
usesfifsky/ssh-action@master
with
command
cd hacene/demo/actions/ && java -jar workflow-github-actions.jar &
host$ secrets.HOST
user$ secrets.SSH_USER
pass$ secrets.SSH_PASSWORD
args"-tt"
# The & in the command runs the process on background
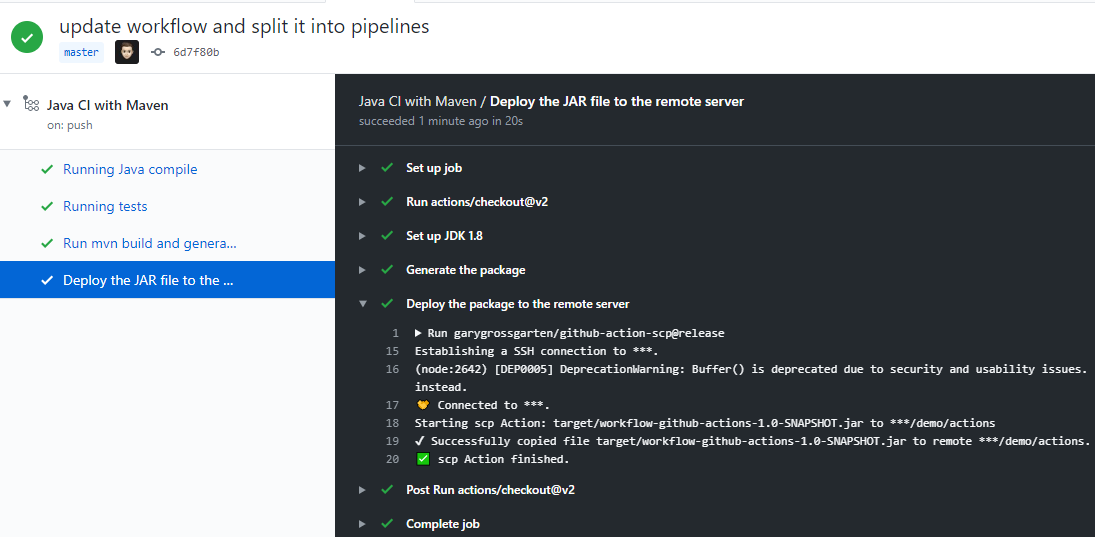
The result looks like this :
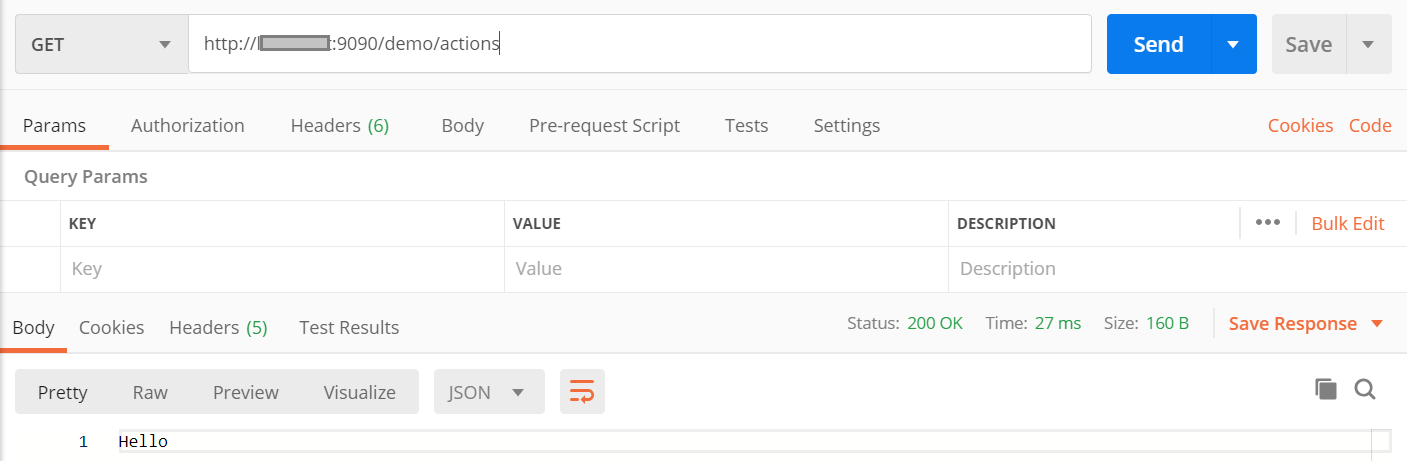
After deploying and running the container using Postman, we call an exposed endpoint:
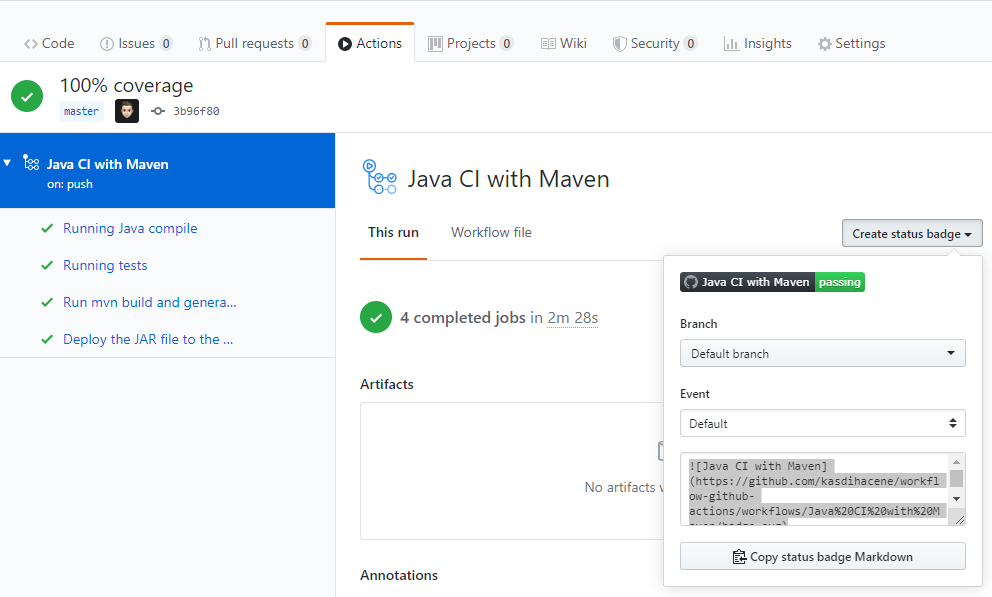
Everything seems to be working. Now, we add the well-deserved badge markdown on our README.md.
xxxxxxxxxx

In the README.md file, the result looks promising :
Conclusion
I hope that you have enjoyed the post and learned how to use Github actions to automate your CI/CD workflow.
Personally, I used to work on a CI platform with Jenkins that required a lot of prerequisites to set up the workflow. So, I’m pretty surprised how well the CI/CD pipeline is working, flawlessly, and quickly using Github Actions. We can take advantage of this flexibility to create and maintain customized development workflows to automate the software development lifecycle processes.
You can find the mentioned project on GitHub, you can also ask me your questions on my blog.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments