Batch Processing in Mule 4 vs. Mule 3
Learn about the improvements to batch jobs from Mule 3 to Mule 4, and how to to run batch jobs with these new capabilities.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn the Mule Batch series, we looked at the batch processing capabilities of Mule ESB 3. At the time of writing this post, Mule 4 was already available as a Release Candidate version.
Mule 4 offers huge improvements and changes to Mule 3, such as the introduction of DataWeave 2.0, Reusable Streaming, improved processing strategies, operation based connectors, and much more. Mule 4 also has some changes to the way batch jobs were implemented in Mule 3. In this post, we will look at batch processing in Mule 4.
If you have missed the batch processing capabilities in Mule 3, then I recommend reading below articles from earlier series -
Part 1: Mule Batch Processing - Introduction
Part 2: Mule Batch Processing - MUnit Testing
Part 3: Mule Batch Processing - MUnit Testing (The Conclusion)
Refreshing Memory - Batch in Mule 3.x
Batch processing in Mule 3 is divided into four phases - Input, Load and Dispatch, Process, and On Complete. A special scoped variable set, called Record Variables is used to store any variables at the record level. These are different than flow variables, which in Mule 3, could not be used during record processing.
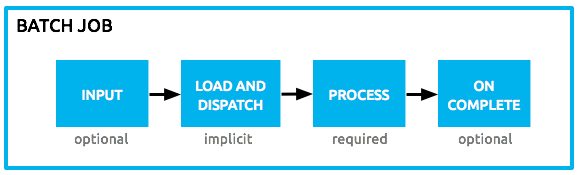
Figure 1.A: Mule Batch Phases [Source: Mule Docs].
Input Phase: This is an optional part of the batch job that can be used to retrieve the source data using any inbound connector.
Load and Dispatch: This is an implicit phase and Mule runtime takes care of it. In this phase, the payload generated in the Input phase or provided to the Batch from the Caller flow is turned into a collection of records.
Process: This is the required phase where actual processing of every record occurs asynchronously. Records are processed through each step while they move back-and-forth between steps and the intermediate queue.
On Complete: In this final but optional phase, a summary of batch execution is made available to possibly generate reports or any other statistics. The payload in this phase is available as an instance of BatchJobResult object. It holds information such as the number of records loaded, processed, failed, succeeded. It can also provide details of exceptions occurring in the steps.
Batch Job in Mule 4
In Mule 3.x, a Batch Job was a top-level element and existed independent of flows/subflows. It could be called inside a flow using the Batch Execute (similar to flow-ref) component.
In Mule 4, this is changed. Batch is now a Scope like for-each, transactional, and async, and it can be added into the flow itself. No more having different elements!
This is how a batch job looks Mule 4 -
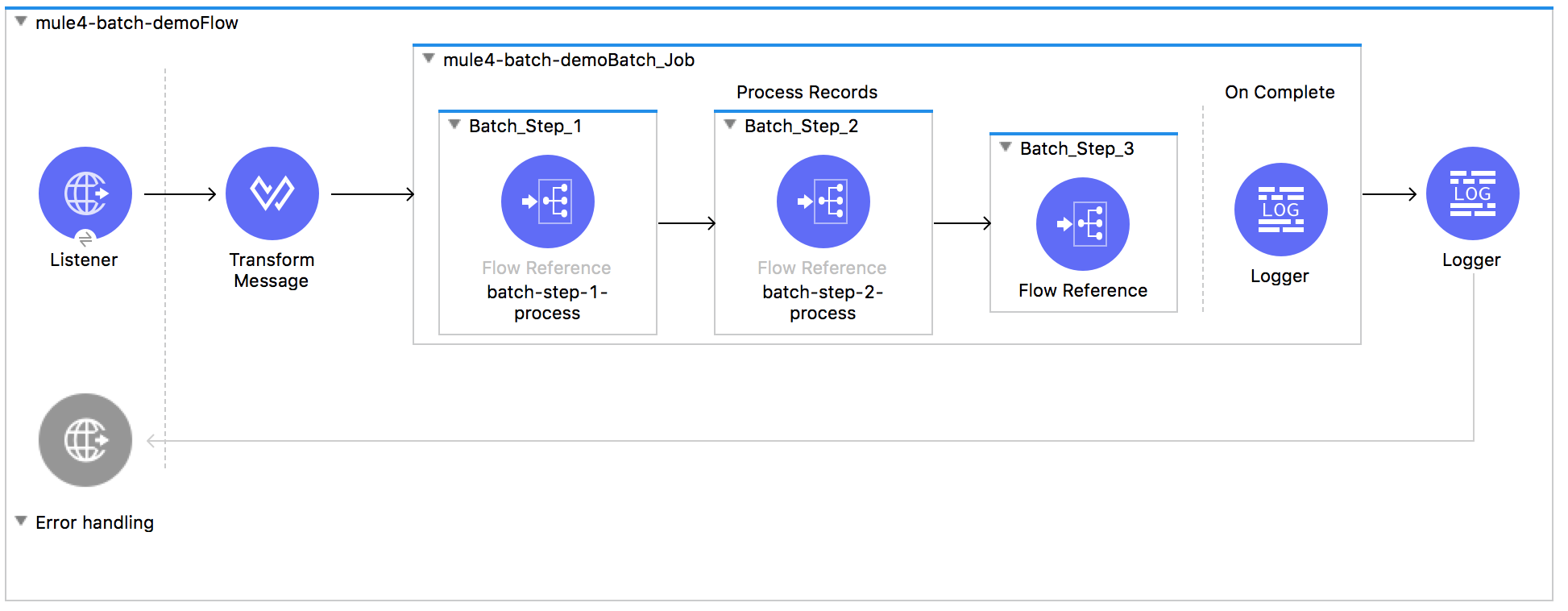
Let’s compare the Mule 4 Batch with Mule 3 Batch and learn about the changes.
Batch Phases
There are only 3 phases in a Mule 4 Batch job compared to 4 phases in Mule 3 Batch job. Input phase does not exist in Mule 4. Since Batch is a scope and it does not need any special Input phase. The payload of the flow is passed to the batch.
Load and Dispatch: This is still there, Implicit and does the same thing as in Mule 3. It will create job instance, covert payload into the collection of records and then split the collection into individual records for processing.
Process: This is still a required phase and essentially same as it was in Mule 3. It will process all records asynchronously. Batch steps in this phase, still allow you to filter records using acceptExpression and/or acceptPolicy configurations.
OnComplete: The last and optional phase in batch functions same as in Mule 3. That means, you still do not get the processed results back in calling flow and they are available as an instance of BatchJobResult in this phase only.
Flow Variables Instead of Record Variables
Batch jobs in Mule 3 have a special variable set called as Record Variables. These variables, unlike flow variables, only existed during the process phase.
In Mule 4, flow variables have been enhanced to work efficiently during batch processing, just like the record variables. Flow variables created in batch steps are now automatically tied to the processing record and stays with it throughout the processing phase. No longer record variables are needed.
This also removes all special treatment we had to give to record variables during MUnit testing.
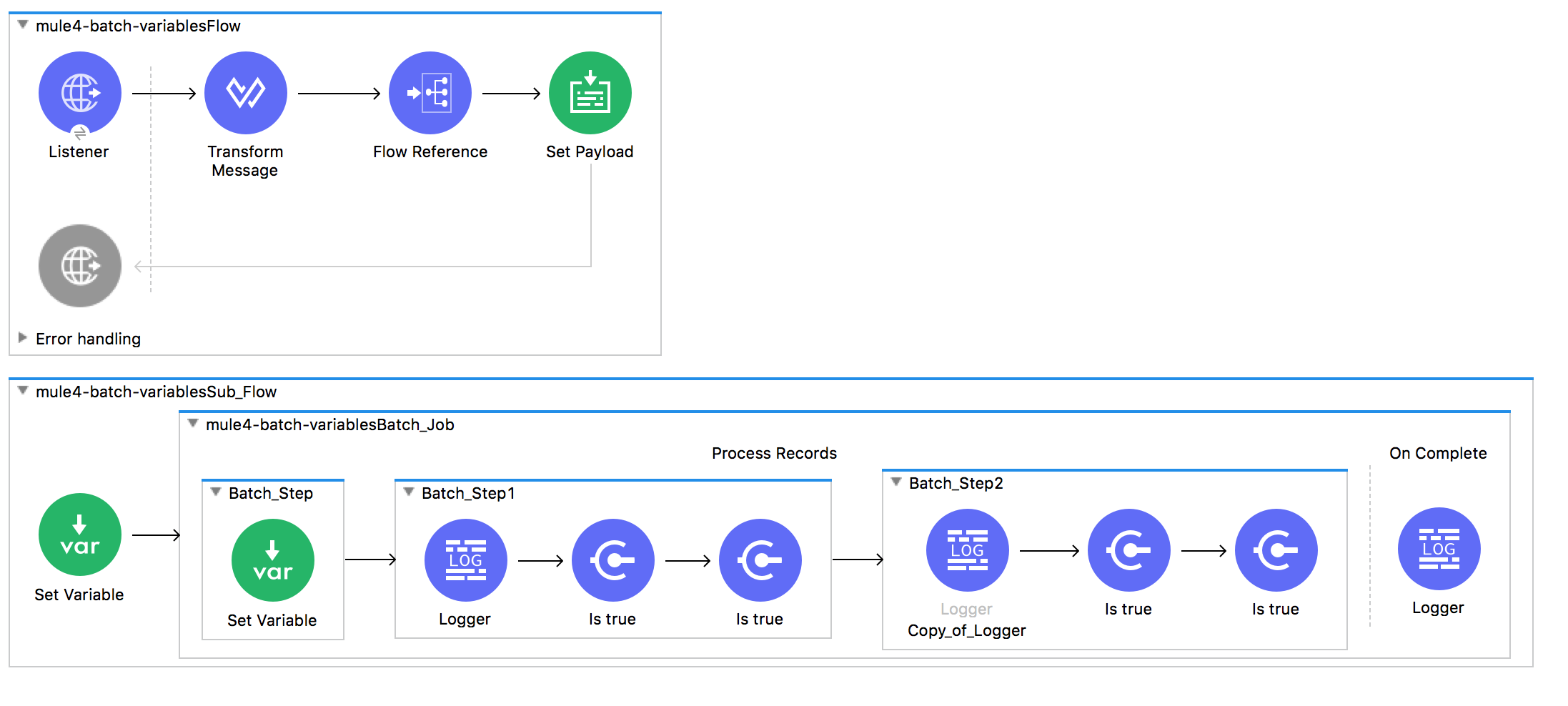
In this test batch application, the 100K objects are created with DataWeave 2.0 and then passed to the batch job for processing.
%dw 2.0
output application/java
---
(1 to 100000) map {
id: $,
"Name": "Name-" ++ $
}In batch step 1, it sets a flow variable recordId with value of id.
<set-variable variableName="recordId" value="#[payload.id]" doc:name="Set Variable" />Step 2 and Step 3 then have a validation component that compares the flow variable value with payload.id. If you run this application, not a single record fails due to validation, which means all 100K flow variables stayed with their records!
Any flow variables created during process phase, exist during the Process phase only. Flow variables that existed before and outside the batch scope are available throughout process phase as well as in on complete phase.
Batch Aggregator Instead of Batch Commit
In a Mule 3 Batch Job, you would be using Batch Commit to group records to send over the outbound connector such as a database, Salesforce, etc. Instead of calling database insert for each record, you can specify the group size to perform a batch commit.
In Mule 4 Batch job, this has been replaced with the Batch Aggregator component. The underlying behavior and functionality of Batch Aggregator is the same as Batch Commit.
A grouped collection in the batch aggregator is a mutable collection, i.e. it allows you to modify individual records in groups or variables associated with those. You can aggregate records to process in two ways -
- Aggregate fixed amount of records
- Streaming all records
The important difference about mutability in both options is, streaming provides one-read forward-only iterator of records, while the other one allows you randomly as well as sequentially access records.
Conclusion
Mule 4 comes with lots of improvements and enhancements. Batch processing in Mule 3 was already powerful, in Mule 4 it has been simplified for developers and thus easy to implement.
Source code is available on Github.
References
- Mule 3 Documentation for Batch Processing
- Mule 4 Documentation for Batch Processing
- Mule 3 Batch Series with MUnit Testing on Mule Batch Jobs
Published at DZone with permission of Manik Magar, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments