Comparing Ethereum Blockchain and Classical Java Enterprise Architecture
In this article, learn the difference between Ethereum blockchain solutions and classical enterprise applications.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeBlockchain and Java: Are They Comparable?
In simple terms, blockchain is a special distributed network and Java is a programming language. So how we can compare it? Does it seem that we can't?

Wait a Minute! There Are Still Many Similarities
They are different, but they have many things in common or that are similar between the two. Blockchain networks now have an embedded programming language. For example, Ethereum has Solidity. At the same time, Java has integration with a huge ecosystem and can create solutions similar to blockchain (in some way).
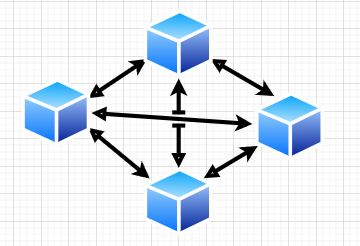
Blockchain Basic Architecture: Mesh Network
All blockchain-based solutions are based on single-rank networks. In such cases, mesh networks of each participant are equal to each other and replicate the same node with the same state, once any node commits a transaction. All other nodes (often half + 1) validate it and confirm or decline. After successful approval, all nodes save that transaction and became synchronized.
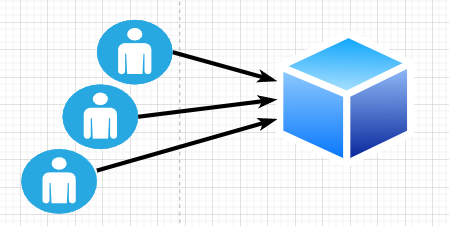
Enterprise Basic Architecture Client Server Network
Classical enterprise architecture is based on client-server architecture. Even having many server nodes doesn't make any difference. All clients don't have access to the server's data.
Ethereum and Java Comparison
Both languages live in significantly different ecosystems, but we still can compare them by some criteria. Let's review some of them:
Number of Reserved Keywords
Each language has reserved keywords. Such keywords can give a very rough estimation of language features and flexibility.
- Java has 67 reserved keywords, but some of them are outdated.
- Solidity has 31 keywords.
In general, Java is a significantly more flexible, general-purpose language that integrates with other languages with native calls. Solidity is a very specific language that focuses on consistency and security.
Variables Types
Java has 8 primitive types, from Boolean up to double (with floating point). The total number of possible object types is huge and covers the vast majority of developer's needs.
Solidity has 6 types and some of them are not fully supported. Among all of them, one type is very specific: address type. Reliable types are Boolean, integers (uint, int), and string.
Deploying Process
The deploying process depends on the ecosystem. Java applications are deployed to JVM, but in most of the cases, JVM is hidden inside something greater:
- Simple JVM
- Application Java EE servers like Tomcat, JBoss, etc.
- Lightweight containers like Spring, Google Guice, Dropwizard
Solidity compiled contracts can be deployed only to Ethereum networks or simply by saving to Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). The state of each EVM is synchronized between all EVMs in network.
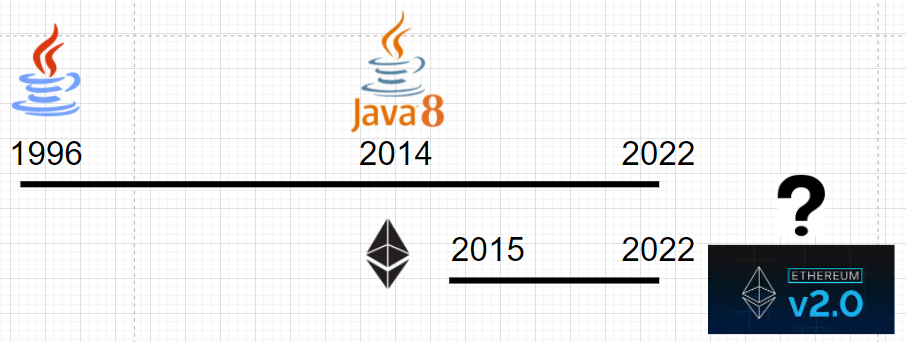
Language Age and Current Development
The first time Java was released was in 1996 and now has new releases every year. So after 26 years of Java, it is improving its features. There is a great difference between the first and the latest 17th version.
The first time Ethereum and Solidity were released was in 2015. Solidity also has constant development and it provides new minor changes every year. Soon Ethereum will release the new version 2, which is going to have significant changes.
IDE or Development Interfaces
As far as Java as a pretty old language, it has many options of development software such as:
- IntelliJ IDEA: The most powerful and popular with the paid version
- Eclipse: The previous leader, but it keeps losing its popularity
- NetBeans: I expect it's pretty dead software by now.
It is also worth mentioning that Java has many plugins due to its sizeable history and community.
Solidity has mainly one IDE, which is Remix. Remix is browser-based and is pretty limited. However, it doesn't require any desktop installations or any paid software. Such a Web Interface-based IDE is not even close to Java IDEs like IntelliJ IDEA.

Classical Architecture
Java conqured the enterprise world a long time ago. If we talk about the classical Java Web Application, then the client-server schema would look like this:
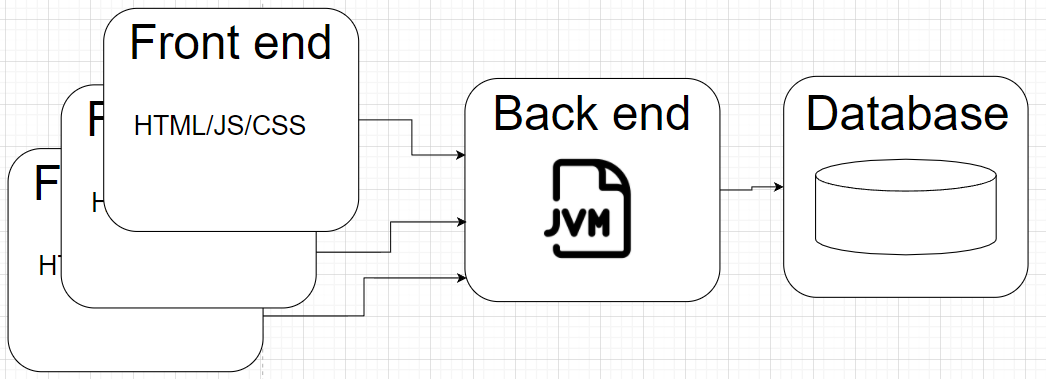
For the Ethereum network, each node is equal to the other. Inside each node we have our backend (EVM) and connector to connect it with the front end. Each EVM is constantly synchronizing its state with all other nodes.
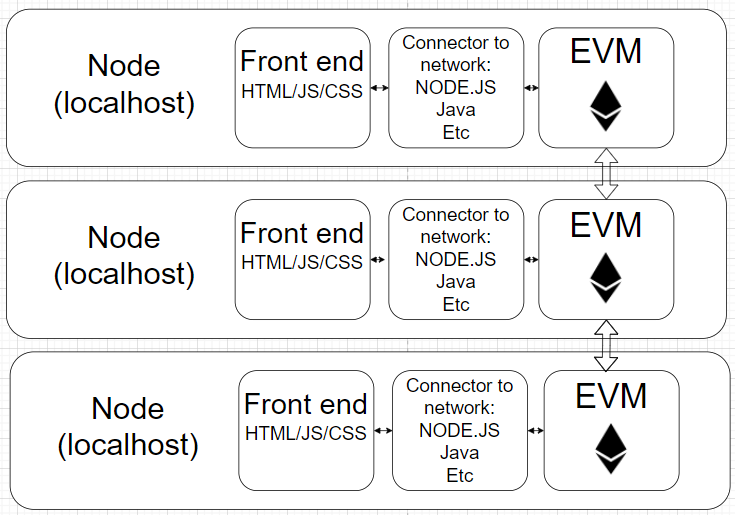
Stateless vs Stateful
In classical architecture, Java is a stateless layer and stores all the data in the database or in the filesystem. All data stored on the application layer disappears after a JVM restart.
In the Ethereum network, the EVM node is a rather stateful database and smart contracts live inside of it. The internal Ethereum storage is also known as blockchain. This means that any EVM restart won't affect its state and all data will be recovered after synchronization with other nodes in network.
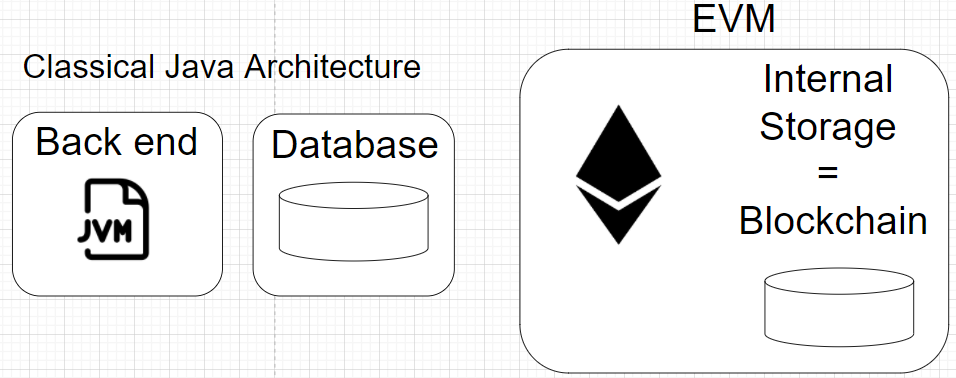
Instead of Conclusion
My main purpose of the article was to help classical developers to simplify learning of Ethereum blockchain. Today, blockchain solutions can only be used in a very small number of projects due to its original nature, but this does not underestimate the advantages of blockchain solutions.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments