Concepts of CQRS
Learn about the requirements and benefits of CQRS, or Command Query Responsibility Segregation, in application development.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn a previous blog, we learned what Event Sourcing is. Moving forward, we will dive into the concepts of CQRS, understanding its meaning, why it is required, and its advantages.
CQRS Pattern
CQRS stands for Command Query Responsibility Segregation. As the name suggests, we split the application into two parts: Command-Side and Query-Side. Now, one will ask, what do "command" and "query" mean?
- Commands change the state of the object or entity, also called modifiers or mutators.
- Queries return the state of the entity and do not change anything. Another term for them is "accessors."
Why Is It Required?
In traditional data management systems, both commands and queries are executed against the same set of entities, having a single representation, or view. CRUD operations are applied to a single datastore and the same entity or object is accessed to handle both read and write operations.
There are issues with having a single view for both read and write sides:
- Introduces the risk of data contention.
- Managing permissions and security become complex as the same objects are exposed to both read and write operations.
How CQRS Solves This Problem
The CQRS pattern holds the idea that the method should either change the state of the entity, or return the result, but not both. Segregating models for the read and write sides reduces the complexity that comes with having a single view for both of them.
Benefits of CQRS:
- Separate command and query models, resulting in simplified design and implementation of the system and overall reduction of complexity.
- One can easily optimize the read side of the system separately from the write side, allowing scaling of each differently as per the load on the side. For example, read datastores often encounter greater load, and hence can be scaled without affecting the write datastores.
- You can provide multiple views of your data for querying purposes depending on the use cases.
How CQRS Works
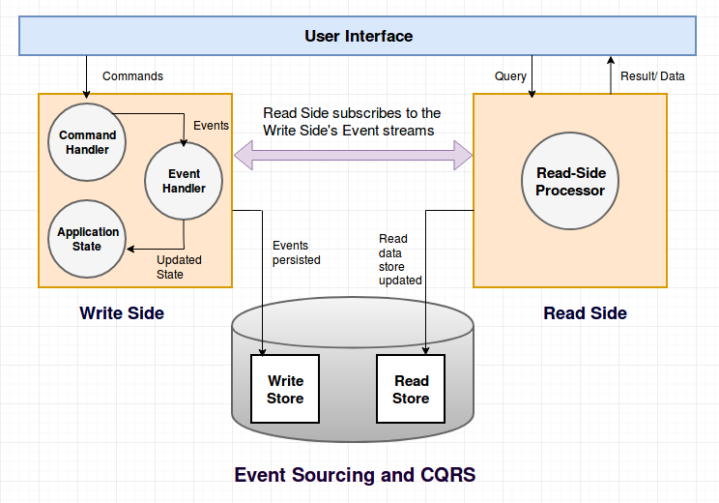
CQRS is mainly used in conjunction with Event Sourcing. The write side model of the CQRS-based system handles the events persistence, acting as a source of information for the read side. The read model of the system provides materialized views of the data, typically as highly denormalized views.
The diagram below provides the details of a CQRS-based system:
How to Implement Event Sourcing and CQRS
If you are using microservices architecture to build your applications and want to utilize the benefits of Event Sourcing and CQRS, various frameworks and platforms are available for developing asynchronous microservices.
Eventuate is one such example. It is an application platform consisting of two products, one of which is Eventuate ES, a microservices framework that implements an event sourcing-based programming and persistence model.
Lagom is an open-source microservice framework built on top of the Akka and Play frameworks. Lagom Persistence makes use of Event Sourcing and CQRS to help achieve decoupled architecture.
You can find real-life examples of how Lagom handles Event Sourcing and CQRS in the following blogs:
Axon is a lightweight framework that helps developers build scalable and extensible applications based on the CQRS principles by providing implementations of the most important building blocks, such as aggregates, repositories, and event buses.
Happy blogging!
Published at DZone with permission of Divya Dua, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments