Coordinating an Apache Ignite Cluster With GridGain Control Center
GridGain simplifies the complex architectures by managing Apache Ignite clustered environments. This article shows Ignite cluster configuration to work with GridGain.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeBundling various data sources, APIs, services, applications, and several data streams while managing application data integration can become cumbersome. It’s so complex that it typically results in application performance loss. So, database administrators use Apache Ignite, a distributed database that provides high-performance computing capabilities using in-memory speed. Integrating Apache Ignite as an in-memory caching or distributed database solution helps improve the velocity and performance of complex architecture.
But, at the same time, this solution presents new challenges: we’re integrating yet another component into our already complex architecture. GridGain provides a solution to this challenge enabling monitoring, managing, and troubleshooting Apache Ignite clustered environments, whether they’re running as an on-premises solution or as a SaaS offering in the cloud.
This article shows how to configure an Ignite cluster to work with GridGain Control Center and what we can do with it.
Apache Ignite Setup
Before setting up the GridGain Control Center, you need to have your Apache Ignite cluster up and running. The article won’t go into too much detail about installing this software but instead will provide the basic steps.
The sample scenario we use in this article runs on a cluster of two Apache Ignite nodes running on Windows Server 2016. You can manage the cluster’s orchestration using the SaaS-hosted version of the GridGain Control Center.
Once you download the binary files from the Ignite website, extract them to a directory on your server. Next, run ignite.bat from within the bin directory. This script starts an Ignite node, and the node prints out diagnostics and logging information related to the run-time.
Running GridGain Control Center
You can install the GridGain Control Center in several ways, including a complete software installation on a Linux machine, a Docker Container stand-alone, a Kubernetes-based scenario, or using the SaaS-hosted alternative. There’s no functionality or feature difference between the various topologies. For this article, we use the hosted SaaS trial version.
Create a GridGain account if you don’t have one yet. Once authenticated, you must choose either GridGain Nebula or Existing Cluster. Choose Existing Cluster by clicking Attach Cluster.
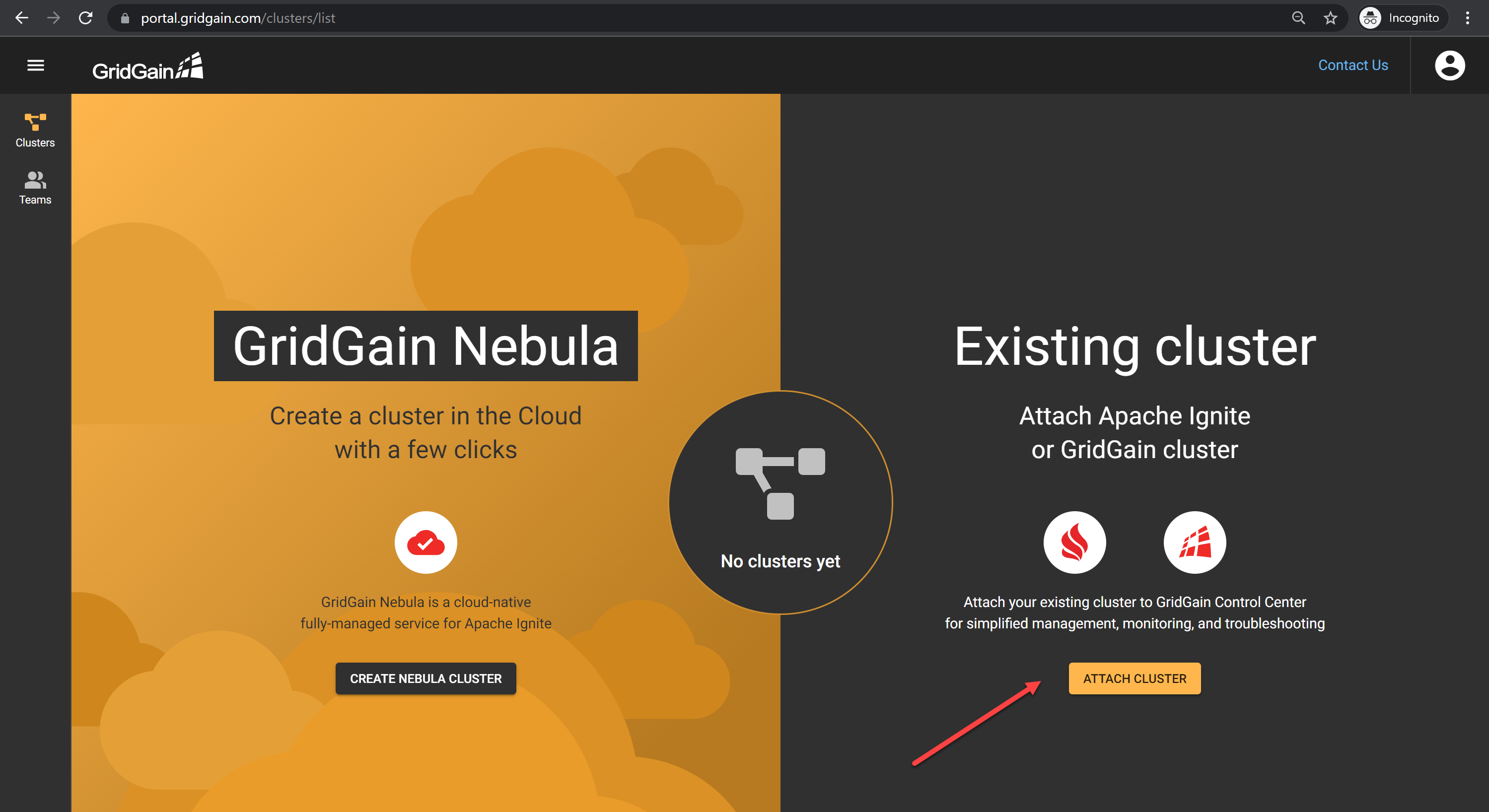
To add your Apache Ignite clusters, click Download the Agent in the Apache Ignite Users Should section. This redirects you to the GridGain download web page.

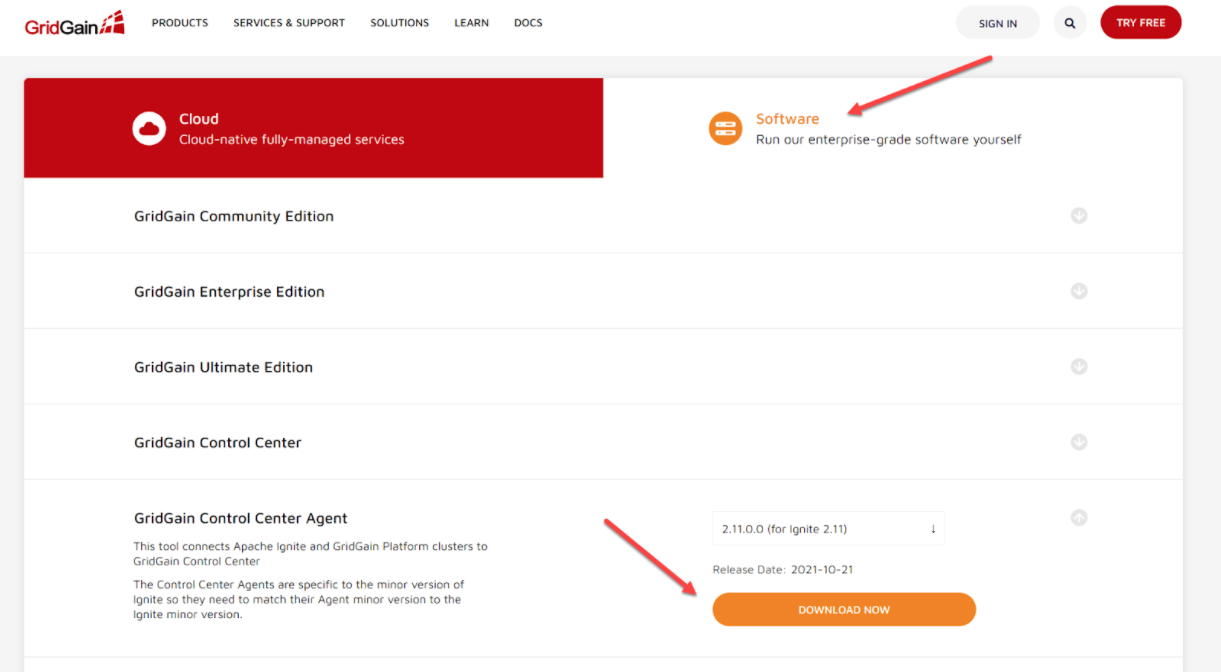
On the GridGain's Downloads page, select Software, then select GridGain Control Center Agent from the list of downloads.
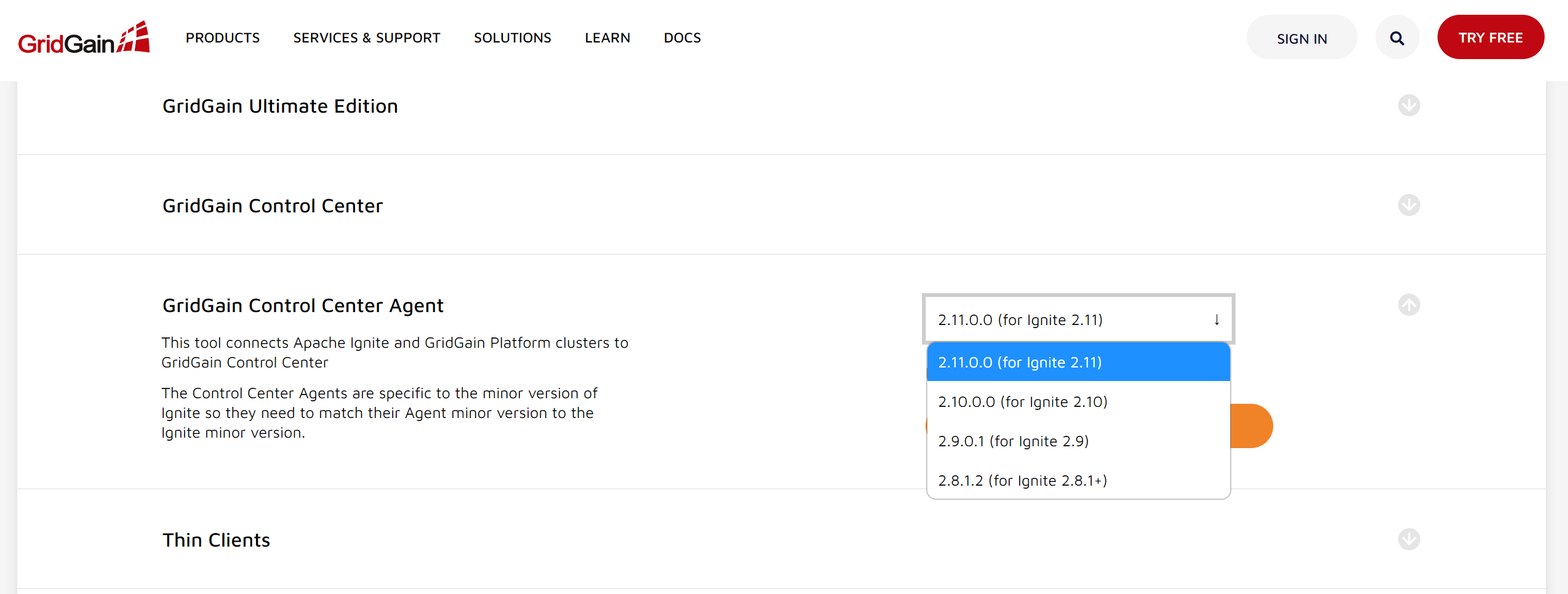
Now select the agent for your Ignite platform. Ensure the agent version corresponds to the Ignite version you’re running.
Download and extract the Agent archive to your machine, and extract the ZIP file into its own Ignite folder.
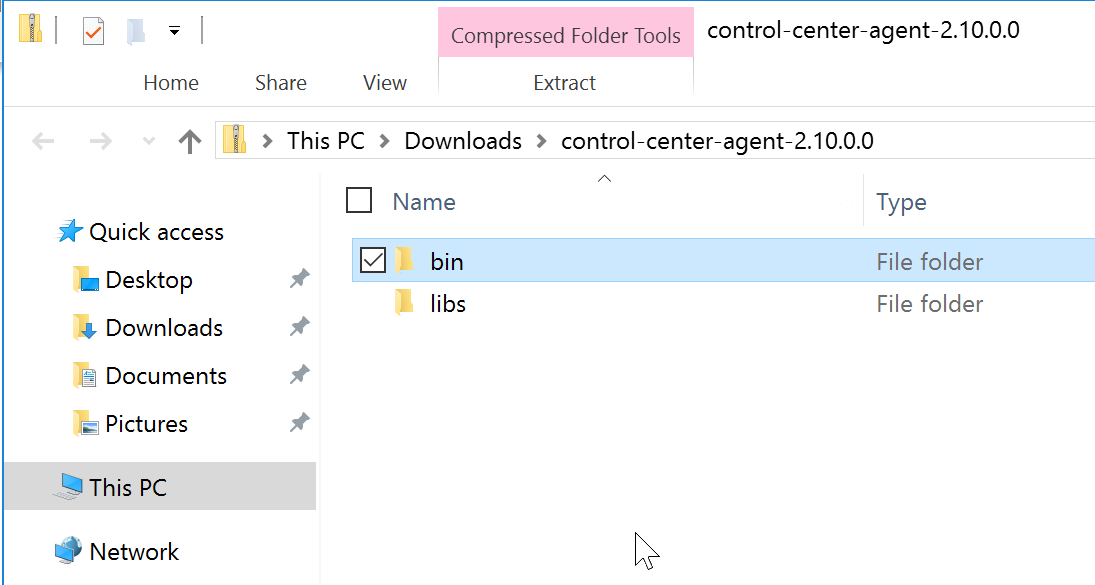
Your running Ignite instance contains the same folders in the Program Files folder (on Windows Server). Copy the content of the Control Center's bin and libs folders into similar folders located under the Ignite Program Files folder:
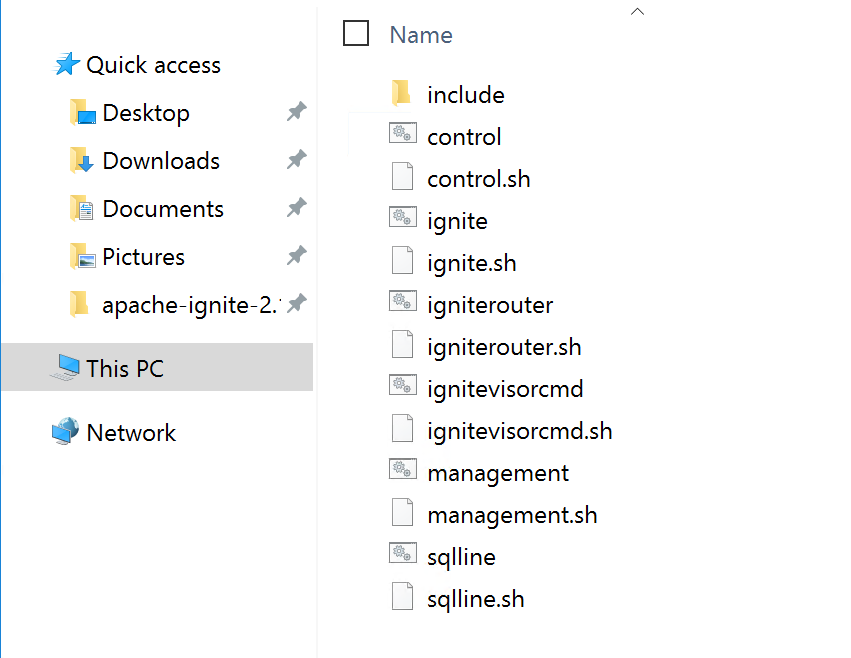
Restart the Ignite nodes, and check the startup logs. They contain a reference to the control-center-agent module and provide a unique token and direct URL to connect to the GridGain Control Center.
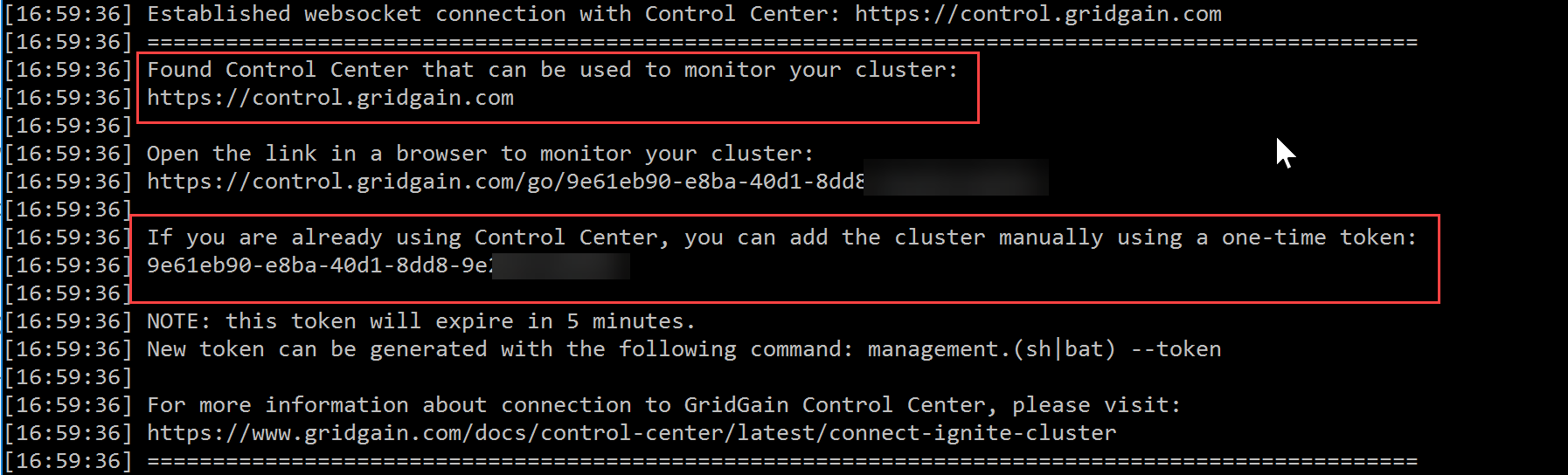
Copy the token, return to Control Center and Add Cluster by providing the token:
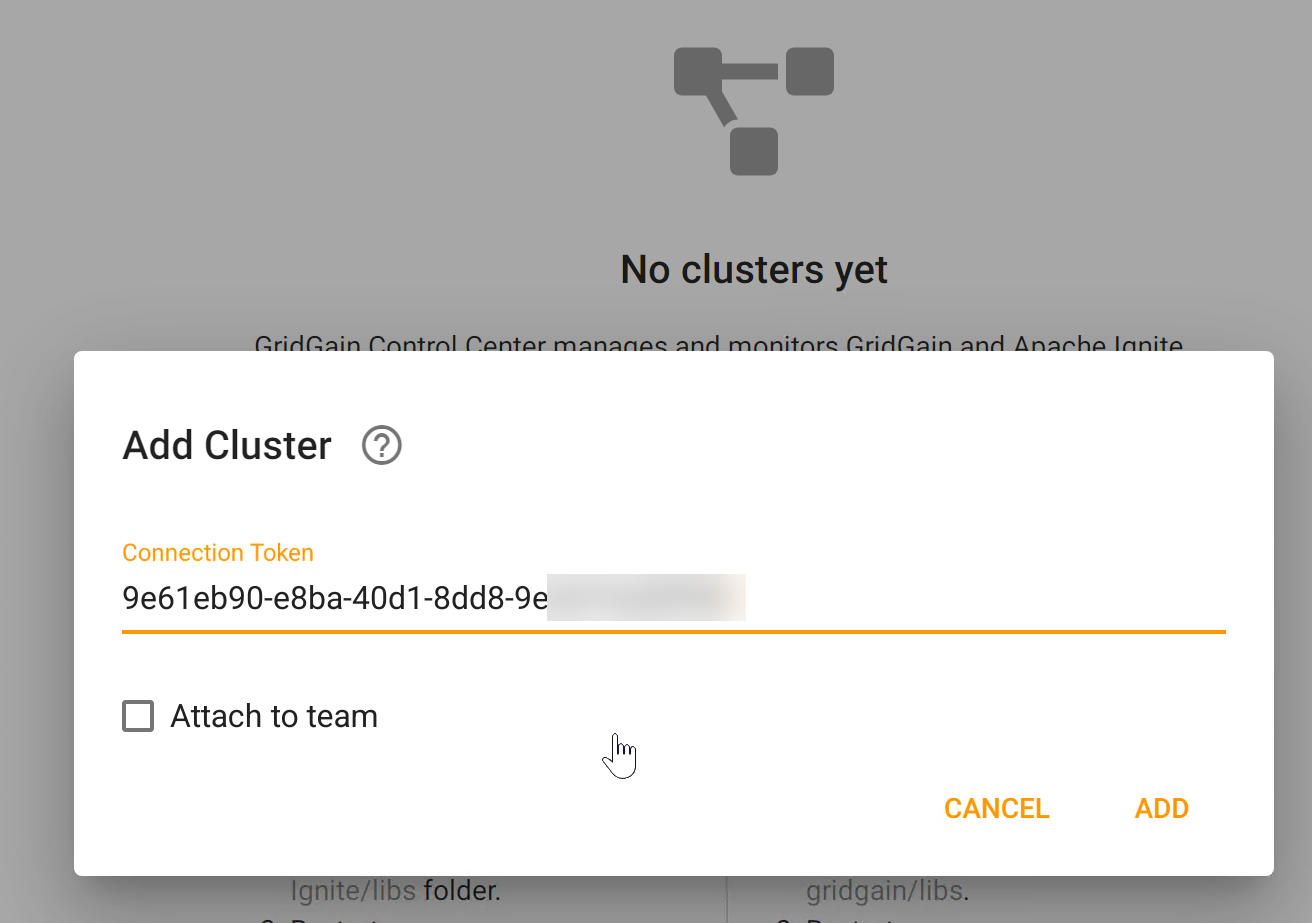
Clicking Add Cluster adds the cluster to the Control Center Dashboard, listing the different nodes in the cluster. The dashboard displays each node’s health, CPU, memory, heap size, and heat map in real-time.
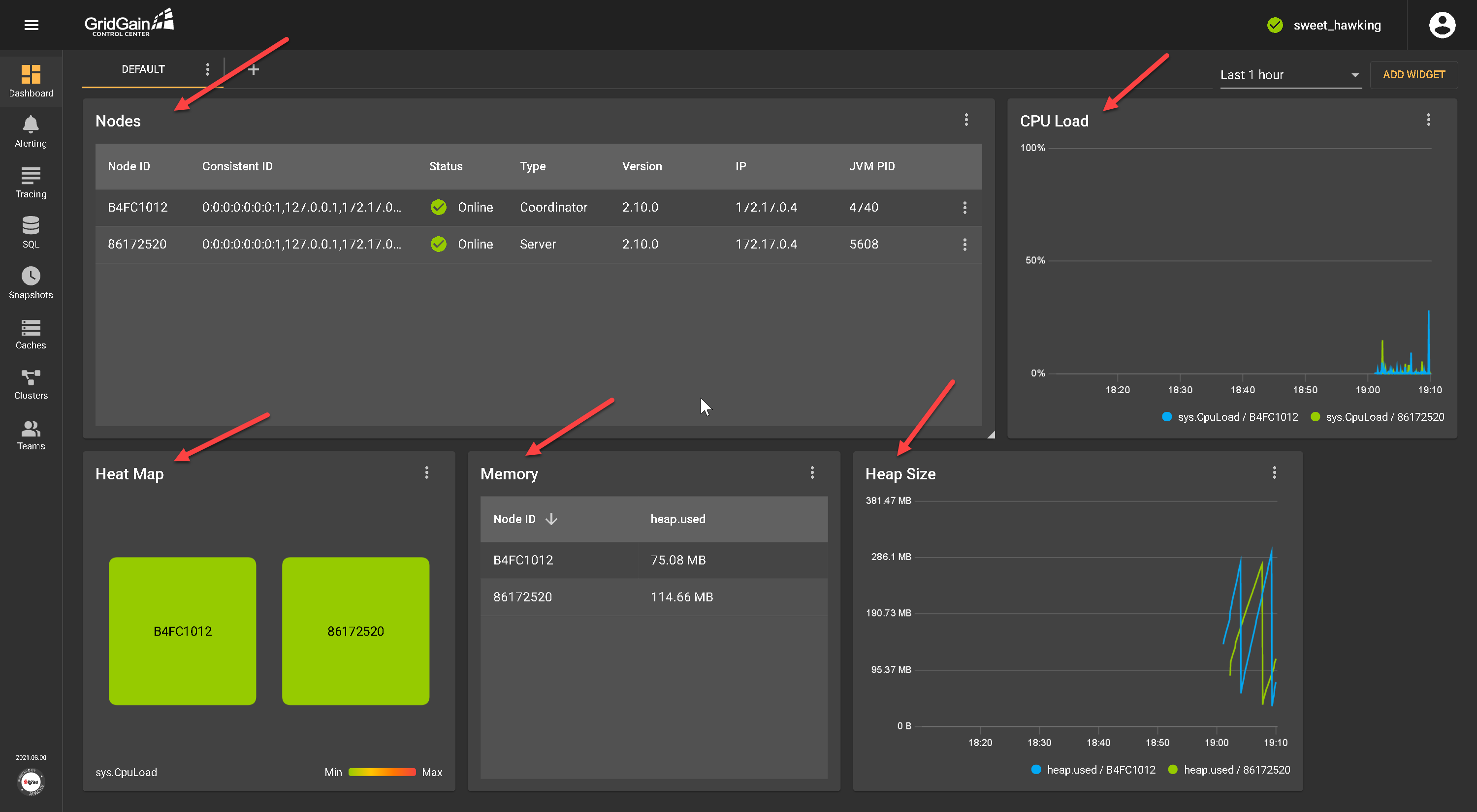
We’re set up now and ready to dig into some of the core Control Center capabilities and features.
Using the GridGain Control Center
Control Center offers a multitude of features for typical administrative tasks when managing, monitoring, or troubleshooting Apache Ignite. Let’s briefly touch on some of them.
Receive Alerts
The Alert feature enables you to define notifications (email or text messages) for more than 150 customizable metrics. Let’s quickly set up an alert for losing a node in our monitored cluster.
On the toolbar on the left, click Alerts. Then, click Add Configuration.
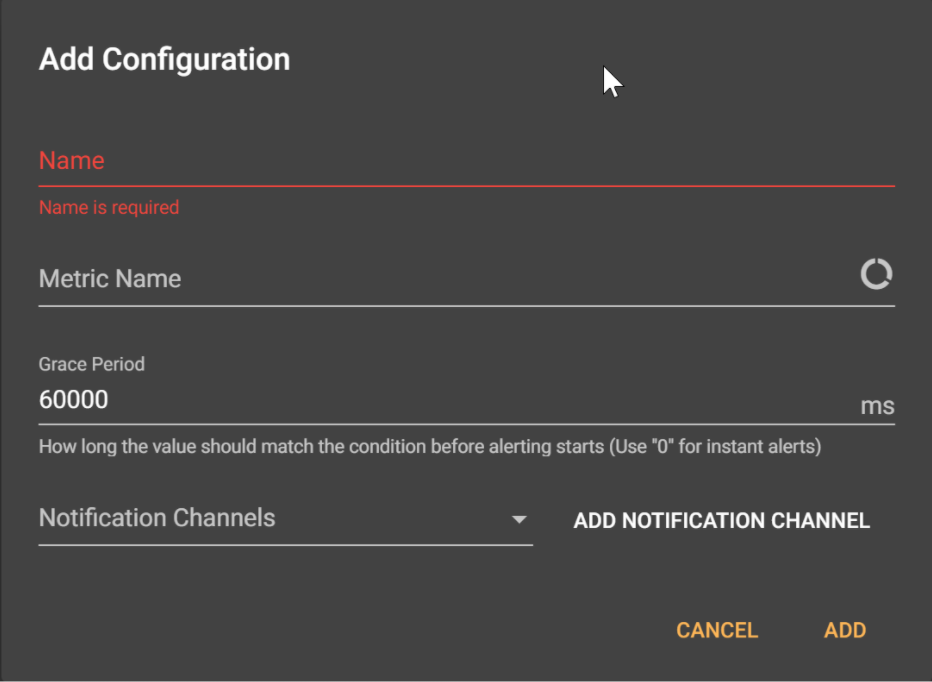
Complete the necessary parameters, using the following sample data:
- Name: Provide a clear name for the alert — for example, lost_node.
- Metric Name: From the pop-up window listing metrics, select the cluster metric option, then choose ServerNodesCount as the metric.
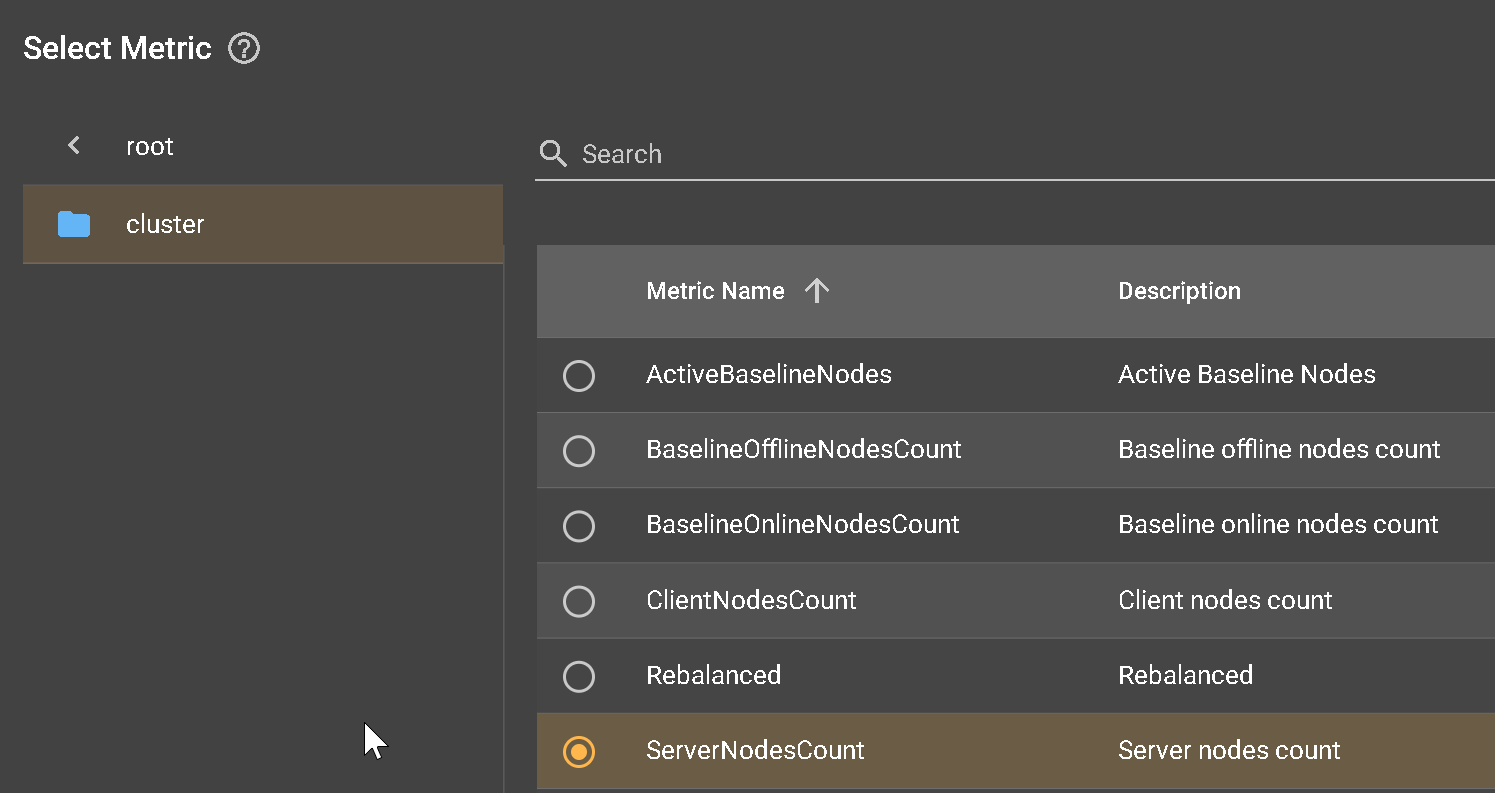
- Save the metric setting by clicking OK.
- Notice that the Add Configuration window now has a Condition field.
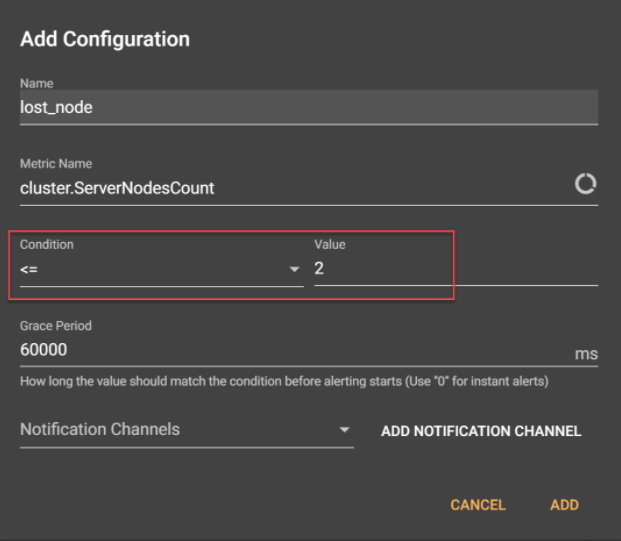
- Condition: This means we get an alert once we have fewer than the set number of nodes. Specify <= with a value of 2.
- Grace Period: This is the length of time before the alert kicks in. The default is 60,000ms. To see immediate alerts, change this value to 0.
- Notification Channels: This is how you’re receiving alerts. Click Add Notification Channel, select the notification channel type of email and provide a valid email address. Save the channel setting by giving a name — for example, helpdesk.
The completed Configuration window looks like this now:
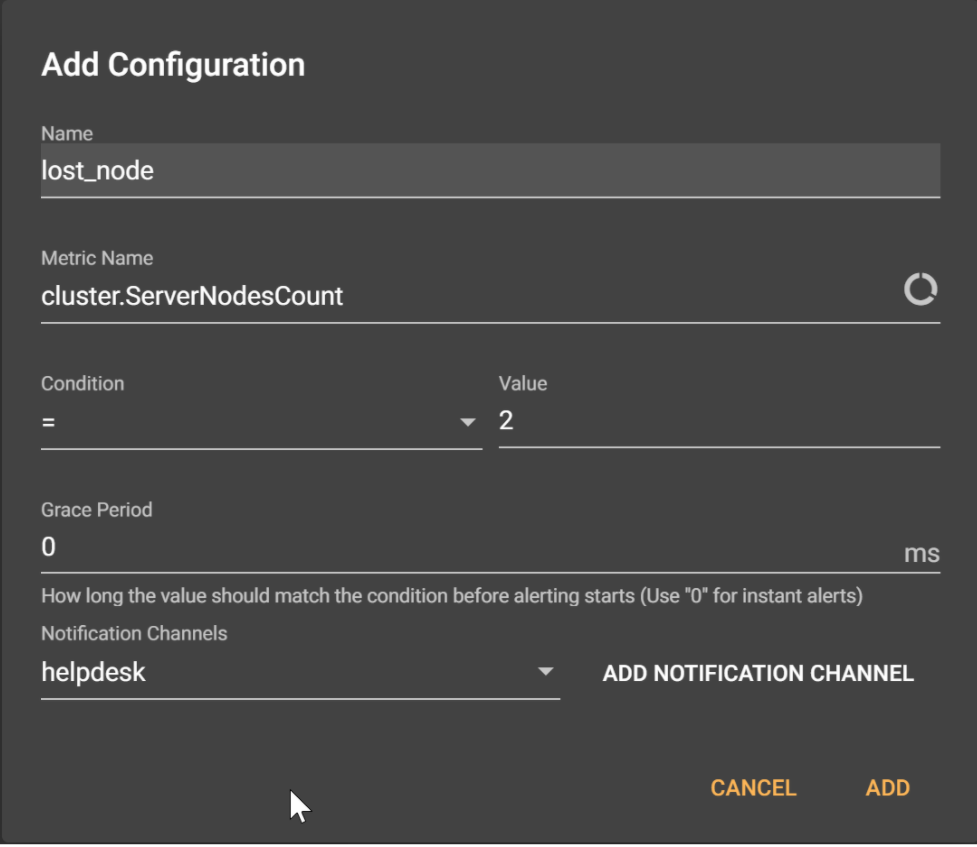
After defining this alert and saving the configuration, you can test the alert configuration by shutting down one of your Ignite nodes. As long as you meet the condition of less than or equal to two, you are fine.
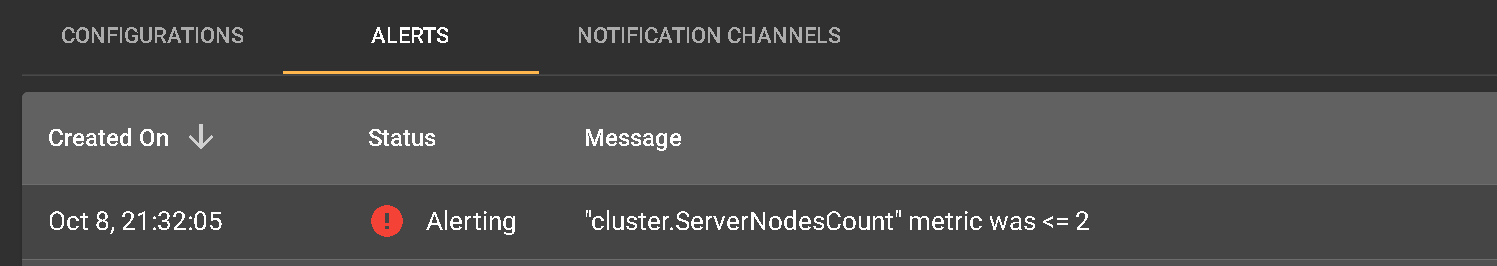
Check the results of the alert condition by clicking the Alerts tab.
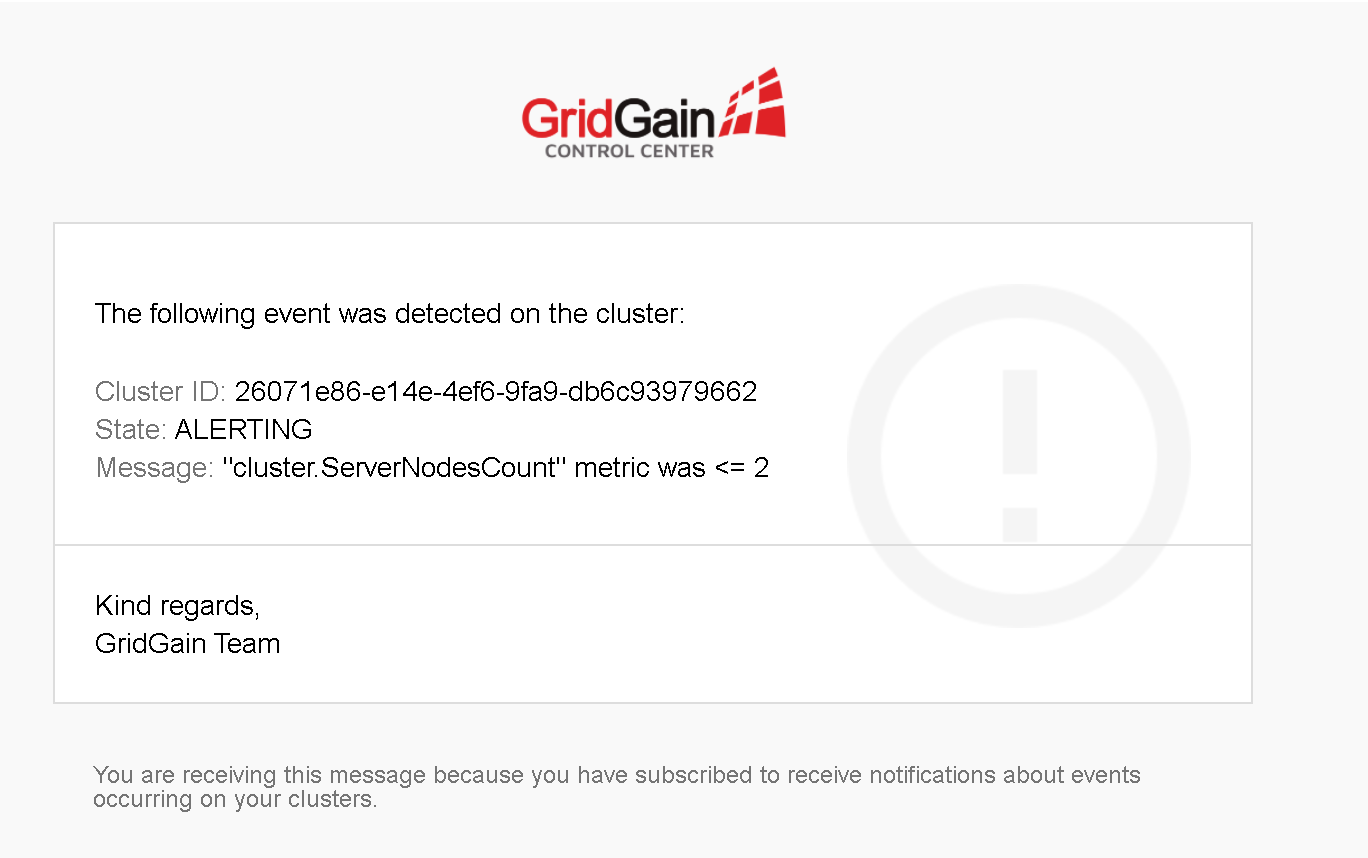
The email message the GridGain Control Center sends summarizes the alert condition.
SQL Execution and Optimization
SQL optimization is one of the GridGain Control Center’s most popular and potent features. It helps us run SQL scripts, like using SQL Management Studio or the like, directly from within the Control Center.
On the main GridGain page, on the left-side toolbar, click SQL, then select Queries List. Here, you can run any SQL query operation. The sample below creates a new table called Person with two fields, ID and Name, and some corresponding data.
Execute the following queries:
CREATE TABLE Person(ID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, NAME VARCHAR(100));
INSERT INTO Person(ID, NAME) VALUES (1,’Ed’), (2, ‘Ann’), (3, ‘Emma);
SELECT * FROM Person;
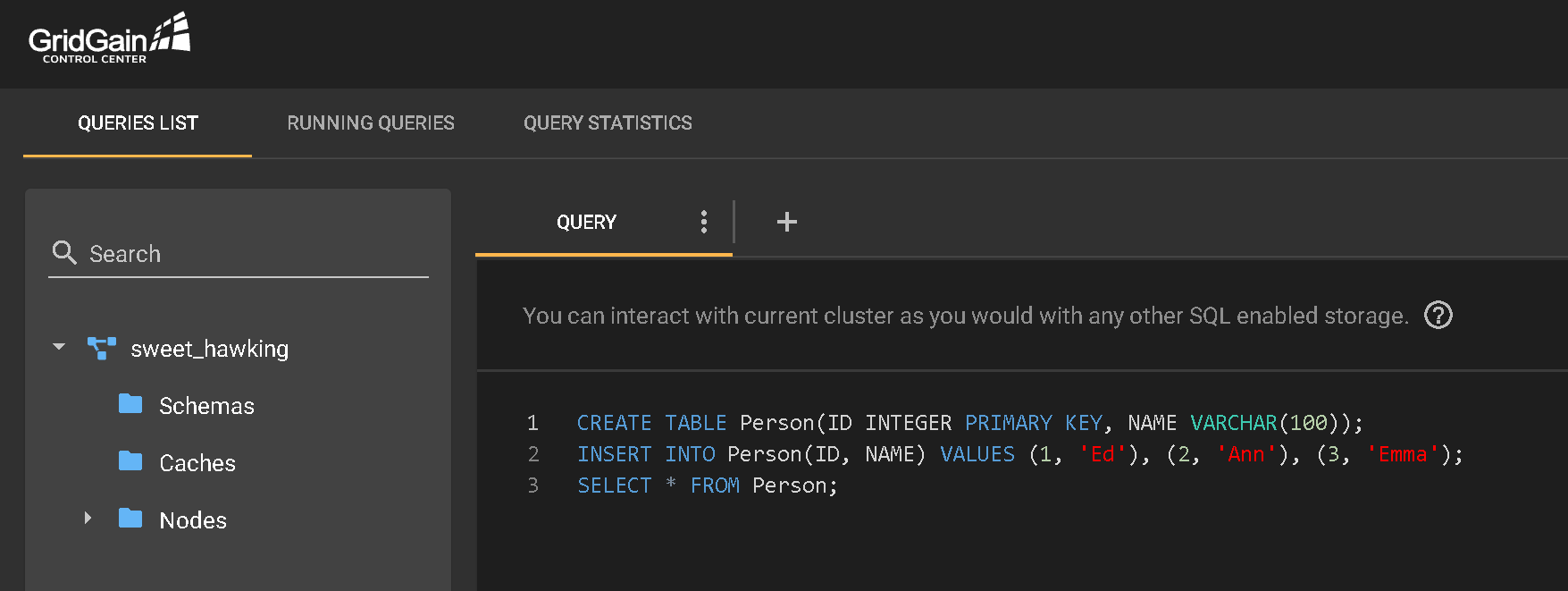
Control Center produces the following result set:
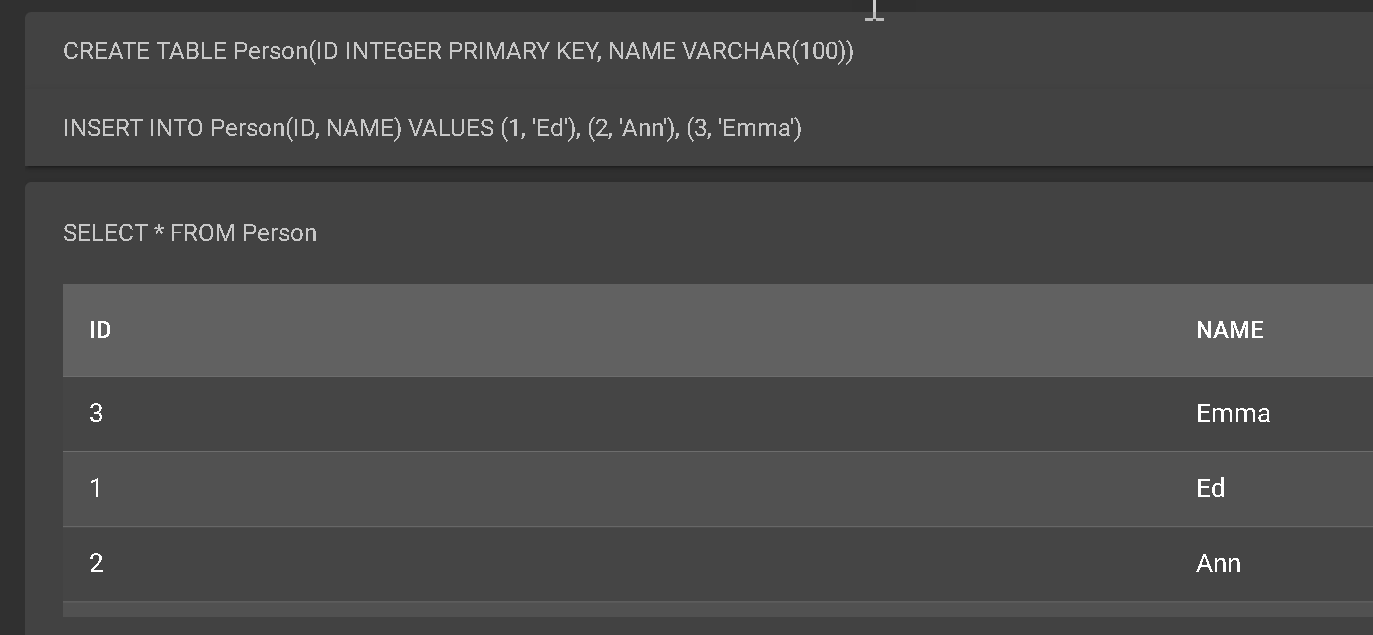
Let’s update the query a little bit to add additional records to the table. Here’s a sample query to trigger updates:
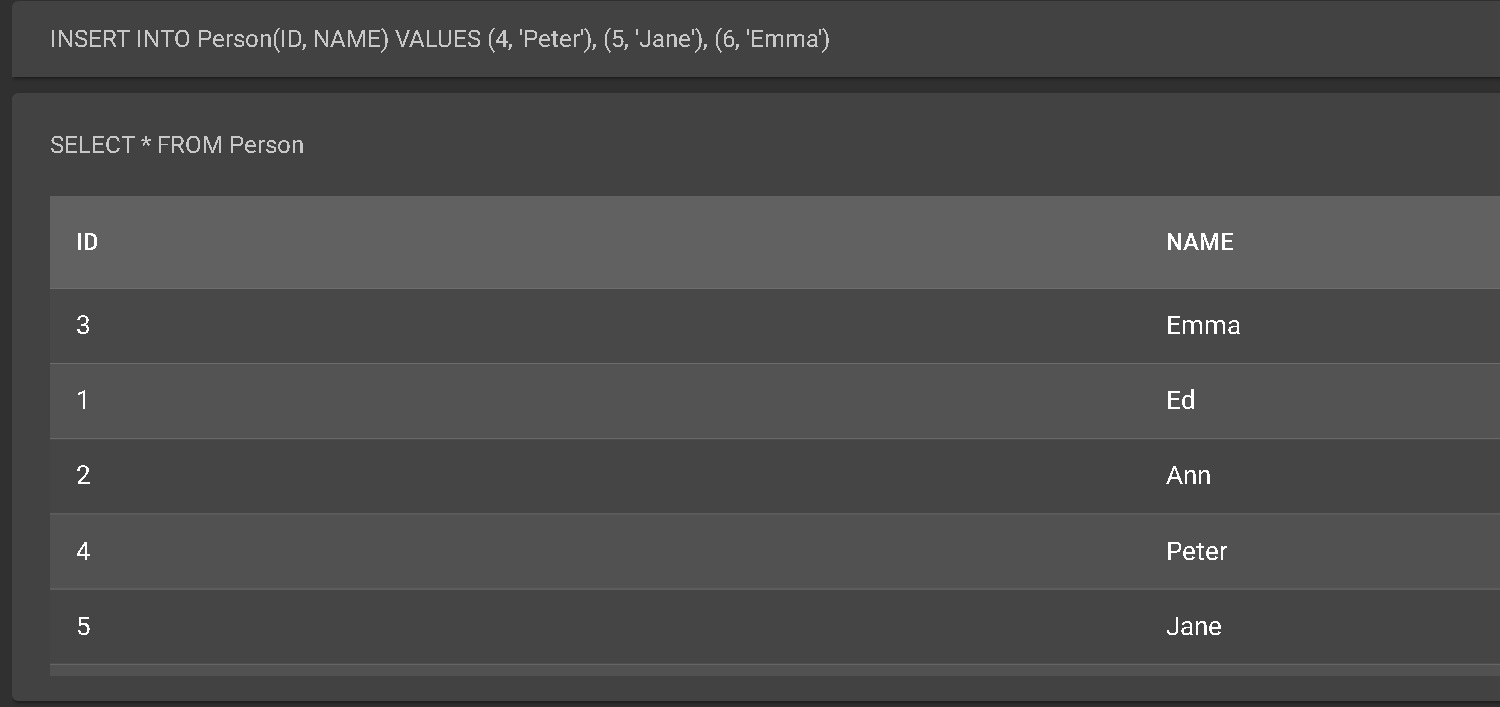
INSERT INTO Person(ID, NAME) VALUES (4,’Peter’), (5, ‘Jane’), (6, ‘Emma);
SELECT * FROM Person;
The result looks like this:
Even more powerful are the built-in Query Statistics and Query Analyzer features. First, navigate to Query Statistics.
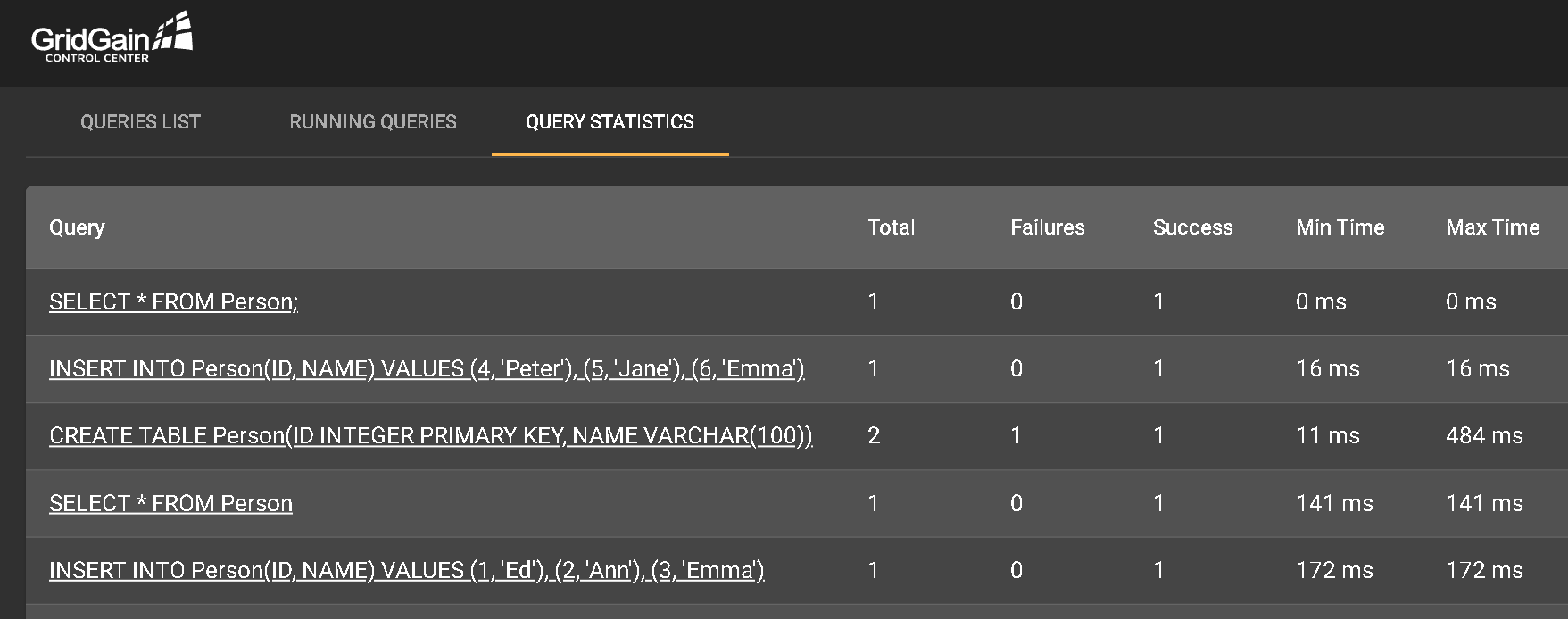
This tab shows a list of the most recent query actions performed. At the right end of a query line, click <…> and select Explain Query. This action opens a new tab that shows the query job's analytics and details of how the data was composed. For example, run a select query to find all duplicates in the Name column with the value Emma.
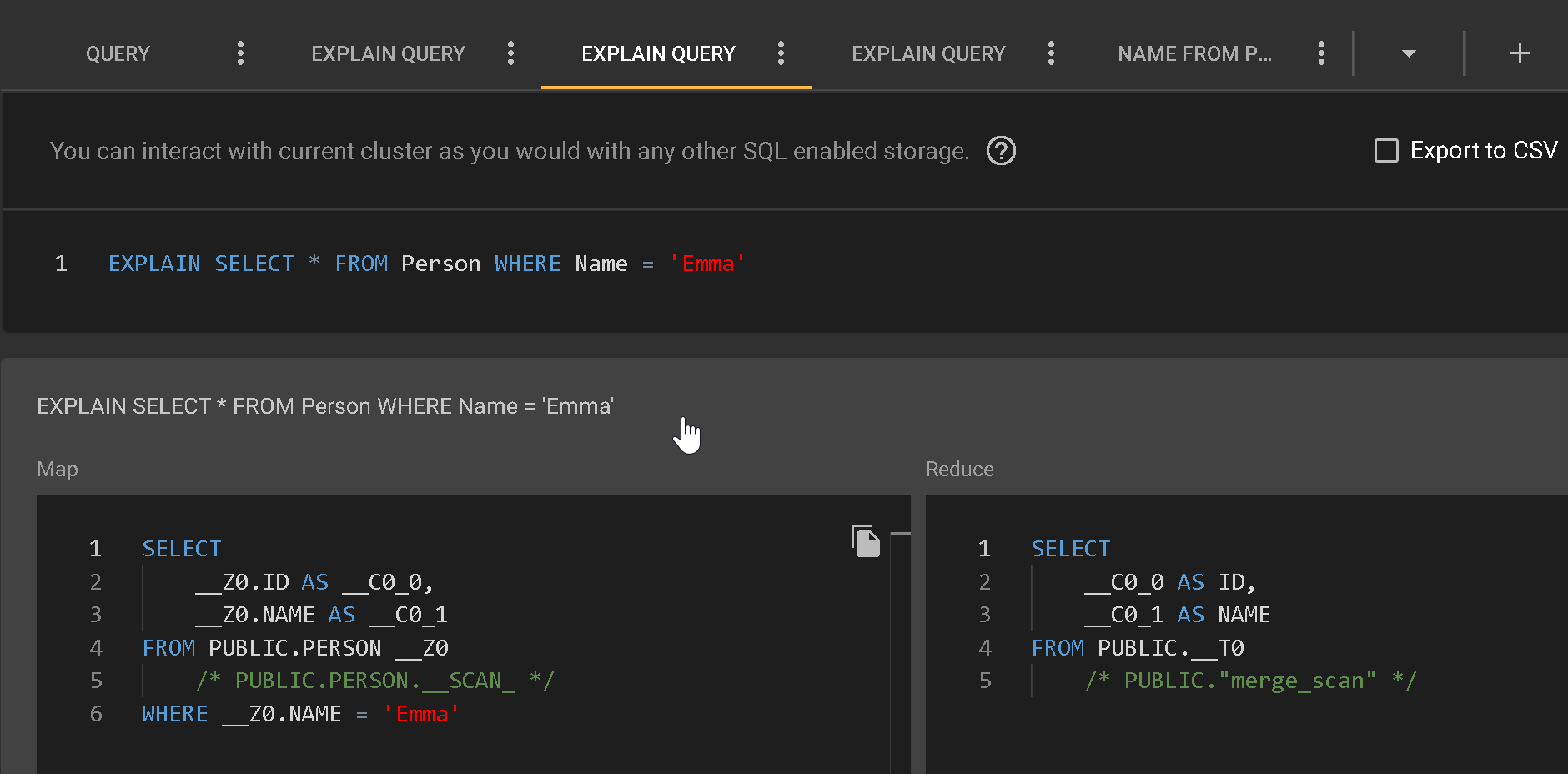
You can make this query perform better by creating an index for the Name table, as you would with a traditional SQL database. Then, re-run the same query afterward, and it runs much faster.
Backup and Recover
This option is available in the GridGain Ultimate Edition by clicking Snapshots in the toolbar on the main page. This feature allows taking snapshots of your clusters and running restores in case of a disaster. You can see snapshots as traditional diagrams of relational databases to learn more.
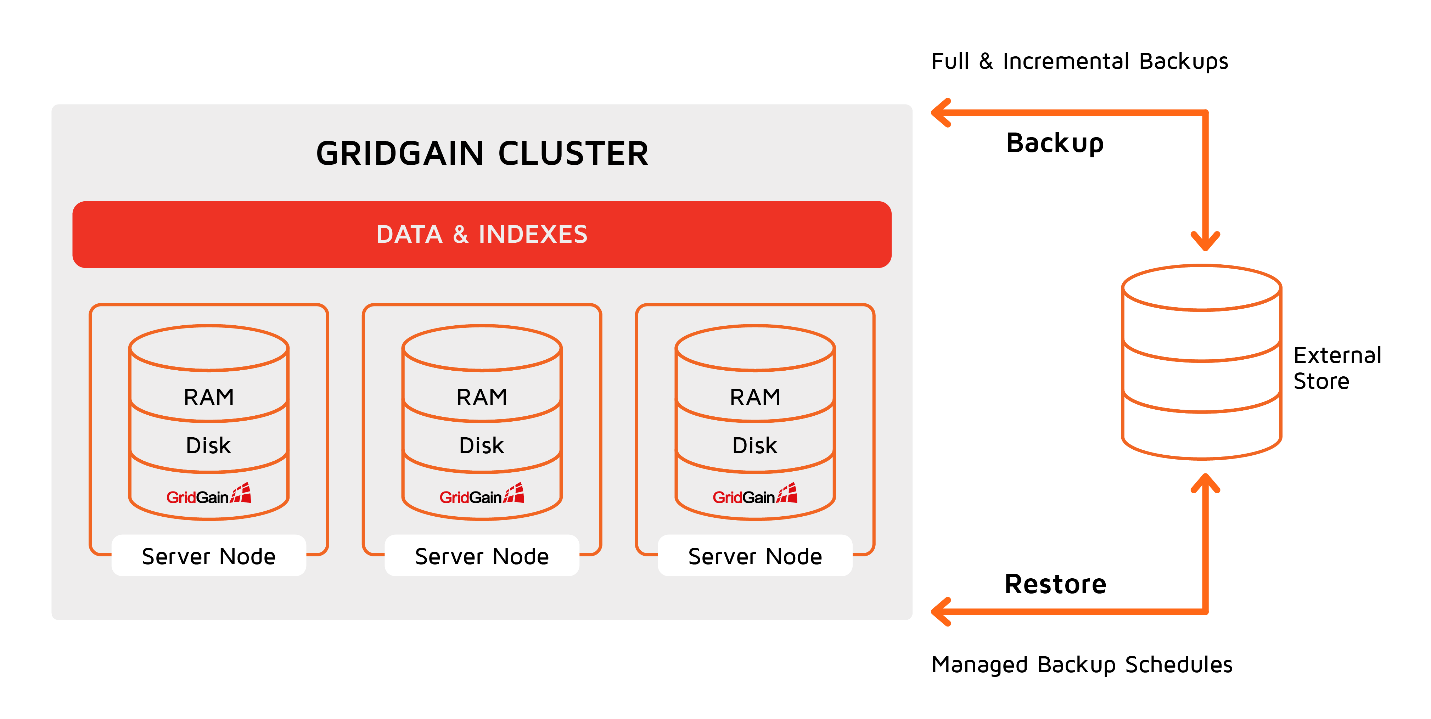
Conclusion
Managing Apache Ignite can be cumbersome without proper tools. GridGain Control Center simplifies Apache Ignite administration, troubleshooting and optimization with a visual interface to your cluster. Its capabilities help developers and administrators understand Apache Ignite clusters' health and performance states. It also has powerful, customizable alerting, intelligent SQL query analytics, and detailed node metrics views.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments