Create Clusters in MuleSoft Runtime Manager Using APIs
Learn how to create clusters of a group of servers in MuleSoft, using either the Anypoint Platform console, or the RunTime Manager API.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn the case of MuleSoft, we can create clusters of a group of servers either using the Anypoint Platform console, or by using the RunTime Manager API. The following list of APIs should be used sequentially in order to create a cluster in Runtime through the API.
We mainly go for the cluster concept in MuleSoft to ensure high availability of the Mule applications running on the server, which means that all the servers that belong to a cluster will have one single application running on the top of it.
Note: Mulesoft API's are by default REST API so all the output will be in JSON Format.
Step 1: Get the Authorization Token
The first step is to authenticate our AnyPoint Platform account in order to get access to it. The following API is used to get the authorization token by passing our Anypoint Platform login credentials.
API: https://anypoint.mulesoft.com/accounts/login
Method: POST
Parameters: username=
password=
Output:
From the above output, we can make use of the access token as our authentication-id to perform the further actions.
Note:This token will be valid only a shorter duration after which you have to generate a new token.
Step 2: Get the Organization ID
After generating the access token, pass that access token value as a header in order the get the organization ID.
As in Anypoint Platform, all the APIs, Clusters, Mule applications, and servers fall under the organization. We can have multiple organization and sub-organizations under one Anypoint Platform account.
API: https://anypoint.mulesoft.com/accounts/api/me
Method: GET
Headers:
Authorization= ‘access_token’
OUTPUT:
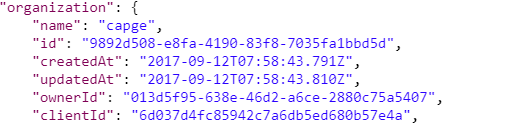
From the above output in JSON format, obtain the id of the organization class, as this will be passed as a parameter in the upcoming API.
STE 3: Get the Environment ID
After obtaining the organization id, we have to filter the environment under which the cluster should be created. Under each organization, we can create multiple environments; the default one would be the sandbox environment.
API: https://anypoint.mulesoft.com/accounts/api/organizations/{org-id}/environments
Method: GET
Headers: Authorization= bearer ‘access_token’
OUTPUT:
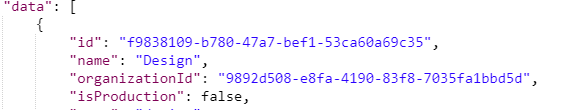
Step 4: Get the List of Servers
After getting the desired environment id and organization id, we have to be aware of the list of the servers available in the environment, and we have to fetch the id assigned to the particular server that has to be added to the cluster. In order to obtain that, we make use of the below API.
API: https://anypoint.mulesoft.com/hybrid/api/v1/servers
Method: GET
Headers: Authorization= bearer ‘access_token’
X-ANYPNT-ORG-ID= ‘org-id’
X-ANYPNT-ENV-ID= ‘env-id’
Here we pass the headers of token org-id and env-id that are obtained from the previous API's.
OUTPUT:
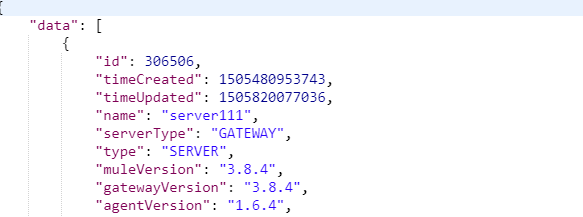
From the output, we obtain the server id of the servers that are present in that particular environment that should be formed as a cluster.
Step 5: Create Clusters
After obtaining all the details, we can go ahead and pass the same set of headers that we have sent for the previous API along, which you should pass as a message body in JSON format that provides the name of a cluster that we are going to create along with the server id's field (mandatory).
Apart from this, we can also pass the Server IP and a few other fields as a field in the JSON body.
API: https://anypoint.mulesoft.com/hybrid/api/v1/clusters
Method: POST
Headers: Authorization= bearer ‘access_token’
X-ANYPNT-ORG-ID= ‘org-id’
X-ANYPNT-ENV-ID= ‘env-id’
Body:
{ "name": "cluster1",
"multicastEnabled": "true",
"servers": [ {"serverId" : 30433433}]
}Finally, the cluster will be created with either a single or a group of servers; provided that the servers are of multi-cast, then the servers should be up and running, whereas in uni-cast, the server can even be in disconnected mode.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments