Deep Dive Into JMS Integration Patterns With MuleSoft and JMS Behavior With Anypoint Clustering and Server Groups
A DZone Core member gives a tutorial on how to use JMS integration patterns in Mulesoft applications and how to avoid common errors in the process.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeJMS (Java Messaging Service) is mostly used with APIs, enabling the application to communicate through the exchange of messages. JMS connector is capable of sending and receiving messages to and from topics and queues.
JMS supports two models for messaging:
- Queue (point to point).
- Topic (publish-subscribe).
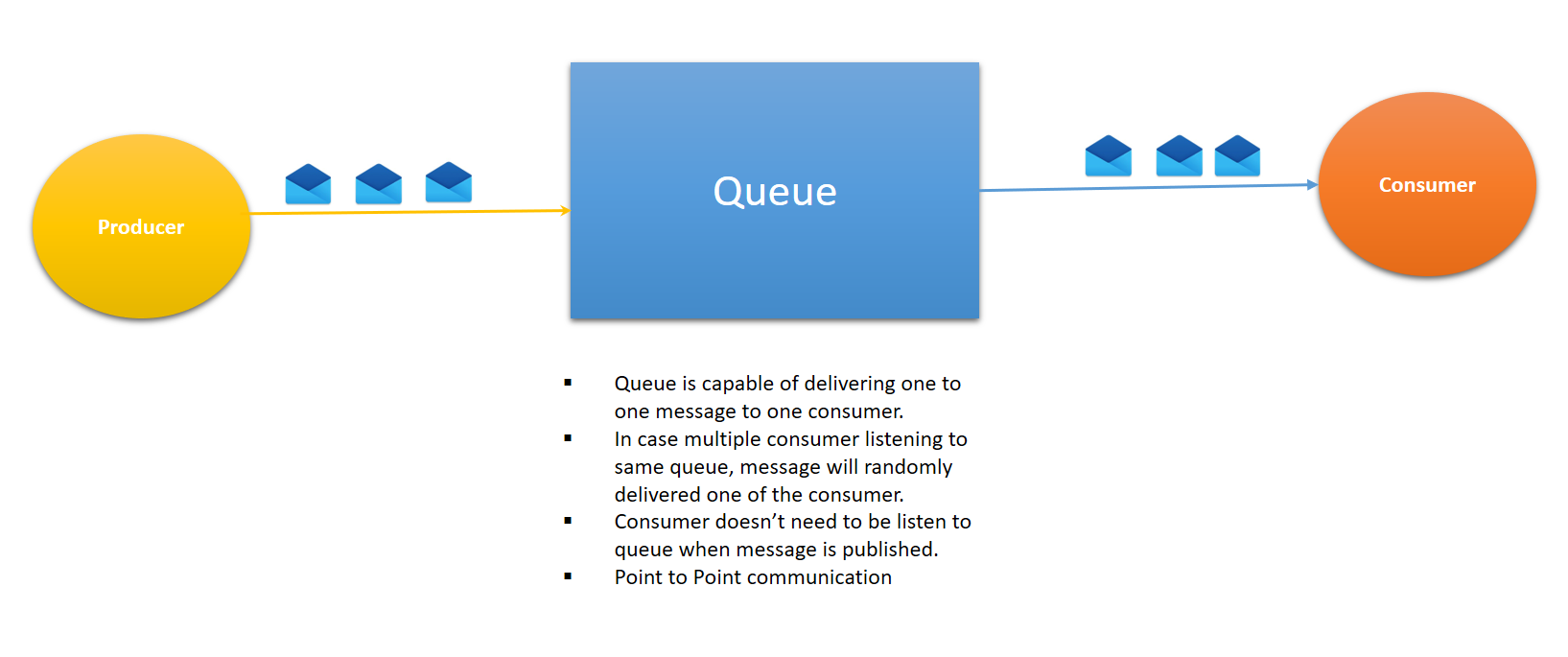
Queue
- It enables one-to-one communication. It is also called point-to-point communication.
- The sender will deliver a message to the queue and single receivers will pick the message from the queue.
- The receiver doesn't need to listen to the queue at the time the message is sent to the queue.
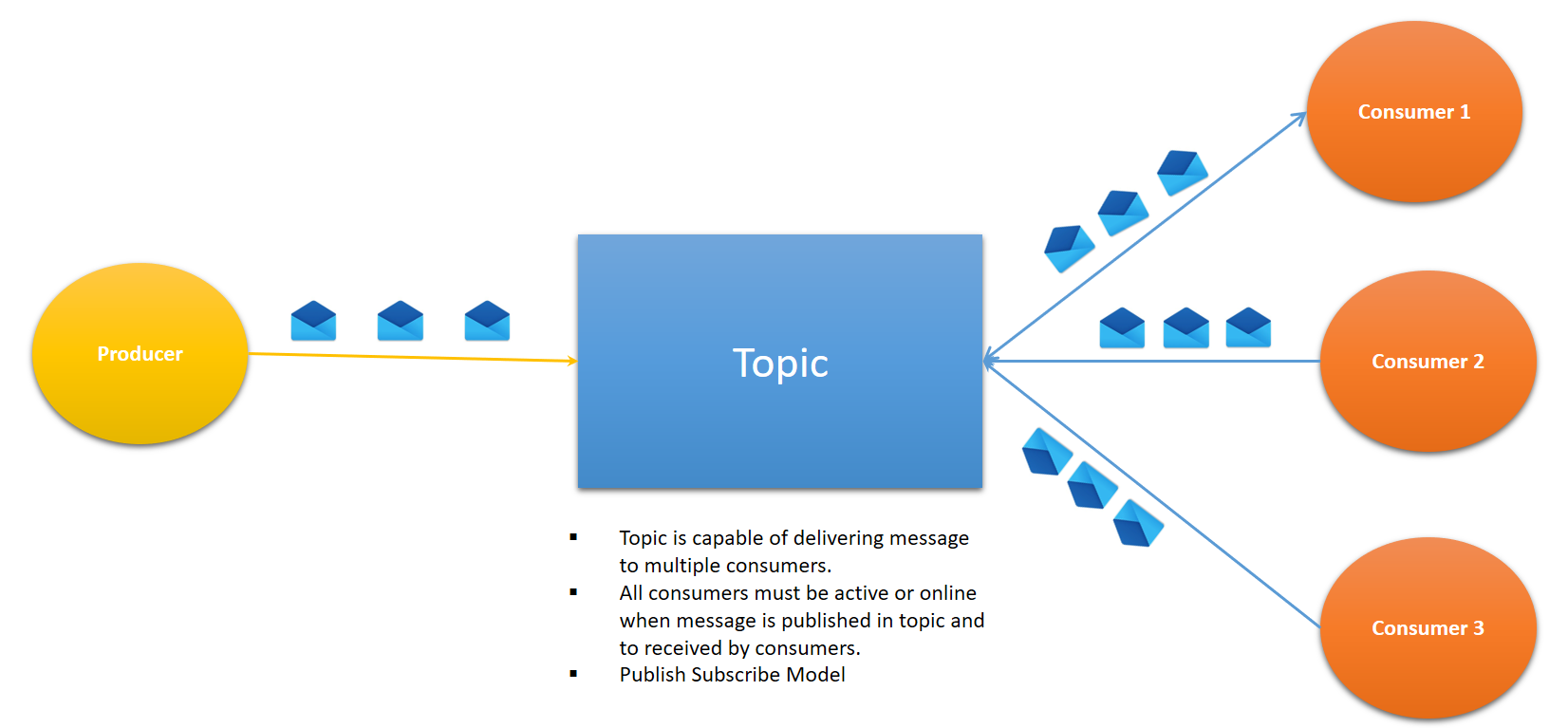
Topic
- It enables one-to-many communication. It is also called publish-subscribe communication.
- The publisher will deliver the message to a topic and it will be received by all subscribers who are actively listening to the topic.
- A subscriber will miss the published message if it is not actively listening to the topic, unless messages are made durable.
We will walk through how to use Anypoint JMS Connector for receiving and sending messages to a topic.
MuleSoft provides a JMS connector to connect any JMS supported MQ (e.g. Apache ActiveMQ). JMS Connector provides various operations, such as:
- Ack
- Consume
- On New Message
- Publish
- Publish consume
- Recover session
This video tutorial will explain how to configure the JMS connection with MuleSoft as well as go over some of the basics of Queues and Topics.
Request Reply Pattern
The MuleSoft JMS connector provides a publish-consume operation to implement a request-reply pattern. In this pattern, the requestor publishes the message to the Queue and the consumer subscribes to the message from the Queue and performs the processing. Once the processing is completed, the consumer will send a response back to the queue and the requestor will subscribe to the message from the reply queue. This is called synchronous communication.
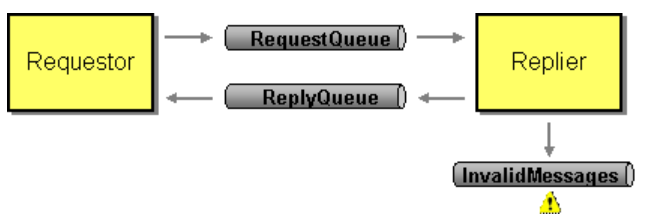
Here is a video tutorial explaining how to implement the request-reply pattern.
Guaranteed Delivery/Persistent Delivery
In persistent delivery, the JMS provider has to make sure that no message is lost in the case of a JMS provider failure or that message can be recovered easily in the case of any failures. In the case of any failures, JMS will make sure that the message can be sent to the Dead Letter Queue.
Here are two video tutorials that explain how to achieve persistent delivery with JMS and MuleSoft.
Durable Topic Subscription
Durable Topic subscription allows you to receive a message when its published to the topic, even when the consumer is offline. Once a durable subscription is registered, each time a consumer is available it will receive all the messages published before the connection was established.
By default, Mule's subscription to a topic is non-durable.
Here is video tutorial explaining how to implement durable topic subscription with JMS and MuleSoft.
Transaction With JMS and MuleSoft
MuleSoft supports the transaction for the three connectors that are listed below:
- Database
- VM
- JMS
The transaction will ensure the atomicity and consistency. It is very useful when you want to make sure that the series of operation executes successfully when the transaction is committed. In case of any failures in any of the operations, the whole transaction needs to be rolled back and all the systems must be in the same state they were in before the transaction started.
Here is ta video tutorial explaining how to perform transactions with JMS and MuleSoft.
Until Successful With JMS and MuleSoft
Until successful is a MuleSoft component which allows you to configure a retry option for any connector in MuleSoft. Basically, you need to wrap up any connector for which you need to implement retry logic with the until successful component.
Here is a video tutorial explaining how to configure until successfulfor a JMS Connector.
Behavior of JMS Queues and Topics on the Clustering and Server Group
Here a the video tutorial explaining how JMS Queue and Topic will behave when deployed on a Clustering or Server Group.
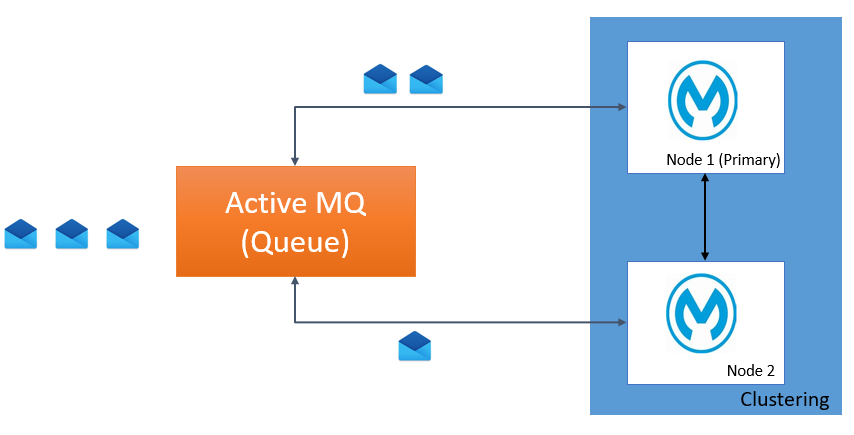
Use Case 1: Application Deployed on a Cluster With a Queue Listener (primaryNodeOnly=false)
Clustering is a group of nodes that acts as an single unit.
In JMS connector configuration, use can configure attribute primaryNodeOnly to define whether a message will be only picked by the primary node or any node in the cluster. By default, the primaryNodeOnly attribute is false.
In other words:
- if
primaryNodeOnlyattribute is false, the clustering works in active-active mode. - if
primaryNodeOnlyattribute is true, then clustering works in active-passive mode.
xxxxxxxxxx
<jms:config name="JMS_Config" doc:name="JMS Config" doc:id="9989650e-6587-457d-a5d9-270357141697" primaryNodeOnly="false">
<jms:active-mq-connection username="admin" password="admin" >
<jms:factory-configuration brokerUrl="tcp://localhost:61616" />
</jms:active-mq-connection>
</jms:config>
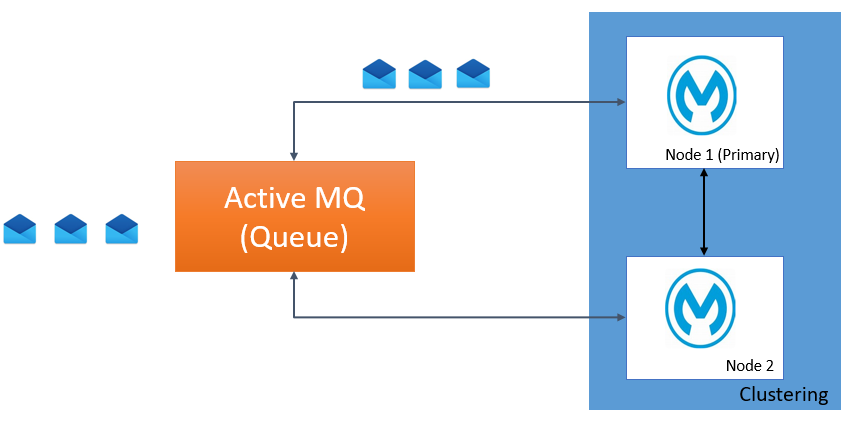
Use Case 2: Application Deployed on a Cluster With Queue Listener (primaryNodeOnly=true)
When primaryNodeOnly is true, all messages will be delivered to the primary node in the cluster. If the primary node goes down, any one of the other nodes in the cluster will become primary and the message will be delivered to that node.
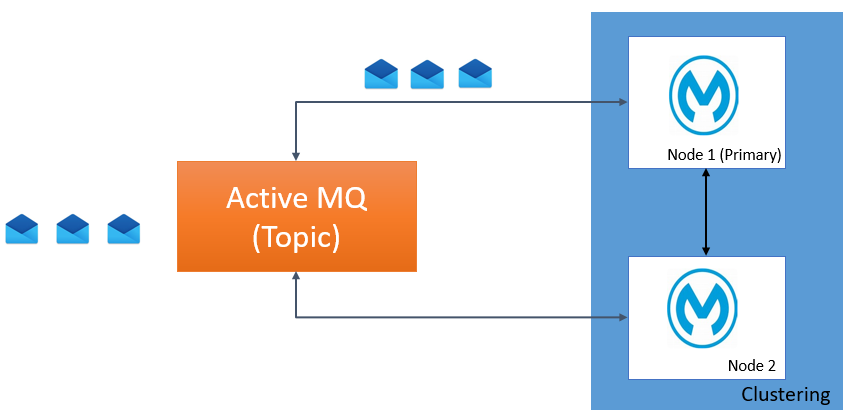
Use Case 3: Application Deployed on a Cluster With Topic Listener (primaryNodeOnly=true)
In case of the Topic listener, you need to make sure that if a message needs to be delivered to only one node that both nodes don't process the same message. To do this, make sure that primaryNodeOnly attribute is true on JMS connector configuration.
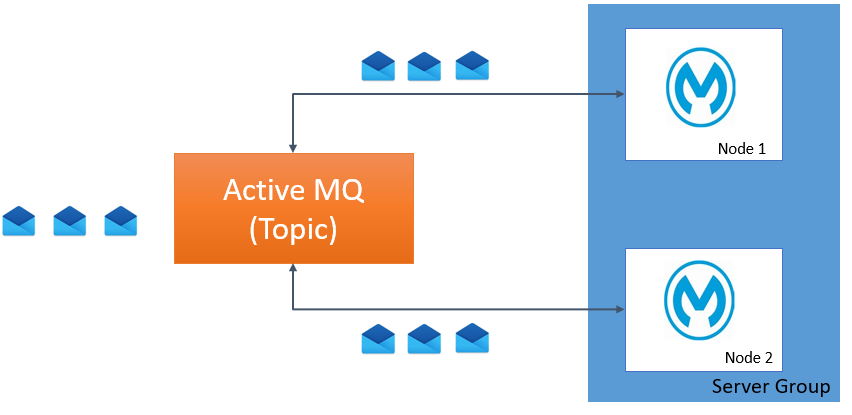
Use Case 4: Application Deployed on a Server Group With a Topic Listener
A server group is basically a group of nodes that are isolated from each other and work independently.
If an application is deployed to a server group with a topic listener, then all the nodes in the server group receive the same messages. The topic has a multicast property that sends the same message to multiple consumers.
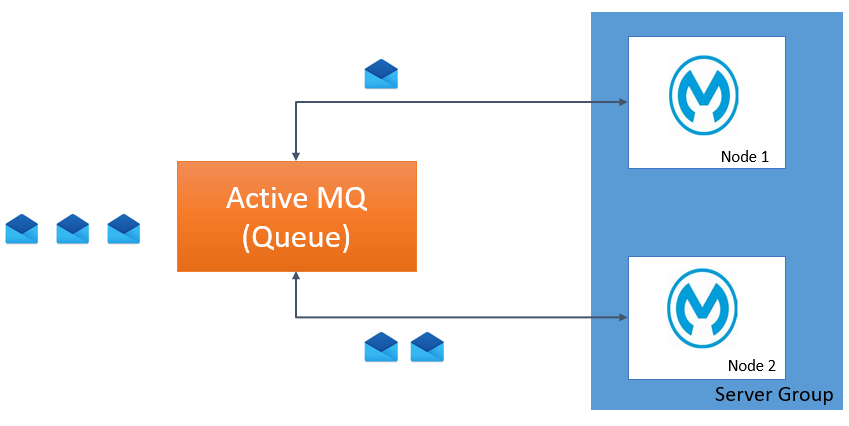
Use Case 5: Application Deployed on a Server Group With a Queue Listener
In the case of a server group with a queue listener, the message will be only delivered to one of the nodesin the server group as the queue has a property whereby its delivers one message to one consumer, even if multiple consumers are listening to the same queue. It will send message randomly to one of the consumer.
It is very important to understand the use cases before you decide to perform clustering or server group implementation.
From the above use cases, we understand one thing: in the case of a topic listener, the server group will not work, as this leads to processing the same message with multiple consumers. In such cases, you need to implement clustering which will avoid concurrency issues.
For more details on clustering and server group, check below references.
- https://dzone.com/articles/implementing-clustering-with-mulesoft-runtime-mana
- https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PL5GwZHHgKcuCB2Zy7ApKBIFDbyWqKVqZV
- https://docs.mulesoft.com/runtime-manager/managing-servers
Now you know what are the different operations can be implemented with JMS Connector and MuleSoft.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments