Implementing and Deploying the Domain Project With MuleSoft
Shared resources allow multiple development teams to work in parallel using the same set of reusable connectors.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIntroduction
Domain Project is used to create shared resources that can be reused.
Mule can define selected connectors as common resources and expose them to all apps deployed under the same domain. These resources are known as shared resources. To host them, you must create a Mule Domain Project and then reference it from each of the projects that use the elements in it. Once defined, any Mule app associated with a particular domain can access resources in this file. Note that Mule apps can be associated with only one domain at a time.
You may also like: Mule Domain Project and Deploying Domain Project in Mule Standalone Server
Shared resources allow multiple development teams to work in parallel using the same set of reusable connectors. Defining these connectors as shared resources at the domain level allows the team to:
- Expose multiple services within the domain through the same port.
- Share the connection to persistent storage.
- Share services between apps through a well-defined interface.
- Ensure consistency between apps upon any changes because the configuration is only set in one place.
To share the metadata, keep the Mule domain project open in Anypoint Studio. Otherwise, you must enter the metadata manually on the linked Mule projects.
Use Case
Generally, when you deploy the application having HTTP Listener on mule standalone run time, each application needs to be deployed on different ports otherwise you will get an error.
To avoid this, you can implement the domain project and define HTTP Listener connection with some port (i.e. 8081) and that domain project can be referred across all the other projects or applications so you can run all the applications on the same port (i.e. 8081).
Creating Domain Project
To create domain projects using Anypoint Studio, Go To File -> New -> Mule Domain Project.
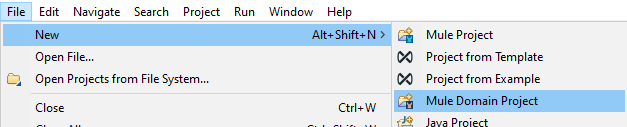
Provide the Project Name, Select Mule Runtime, and Finish.
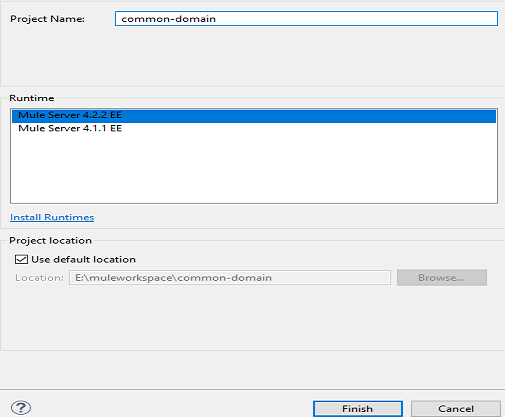
After Finish, we will define the HTTP Listener with port 8081 in mule-domain.config.xml.
Under Global Configuration Elements, Select Create -> Connector Configuration -> HTTP Listener config.
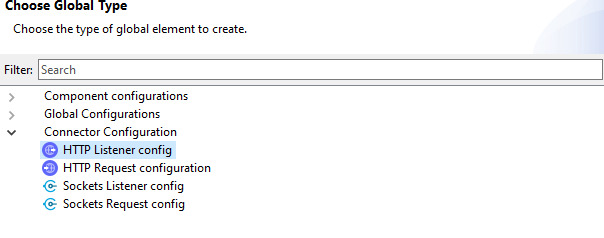
Under HTTP Listener config, set Port to 8081. Click OK.
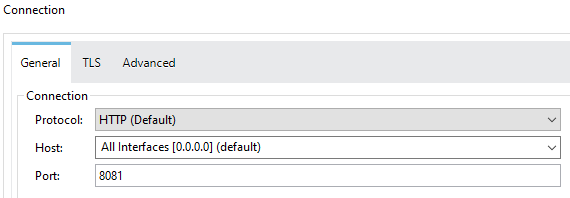
mule-domain-config.xml
<domain:mule-domain
xmlns:http="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http"
xmlns="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core"
xmlns:domain="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/ee/domain"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:doc="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/documentation" xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core/current/mule.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/ee/domain http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/ee/domain/current/mule-domain-ee.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http/current/mule-http.xsd">
<http:listener-config name="HTTP_Listener_config" doc:name="HTTP Listener config" doc:id="713eacdb-c363-48a7-88e6-08191fd34541" >
<http:listener-connection host="0.0.0.0" port="8081" ></http:listener>
</http:listener-config>
<!-- configure here resource to be shared within the domain -->
</domain:mule-domain>
Building Domain Project
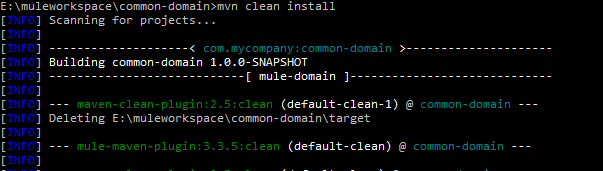
To build a domain project, use command mvn clean install.
Go to the path where domain project exists on command prompt and run maven command to build it. It will generate a jar file at the target folder in your domain project (i.e. common-domain-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT-mule-domain.jar).
Deploying the Domain Project
To deploy a domain project, copy the jar file which has been built above at $MULE_HOME/domains and as soon you copy the file to that location, it will automatically unzip the jar file.
Before copying the jar file, you need to make sure your mule runtime is running.
Referring to the Mule Domain Project in Mule Application
To Refer domain project in Mule Application, you need to make sure domain project and mule application both exist in Anypoint Studio.
Right, Click on Mule Application -> Properties -> Mule Project, Select Domain project and Apply and Close.

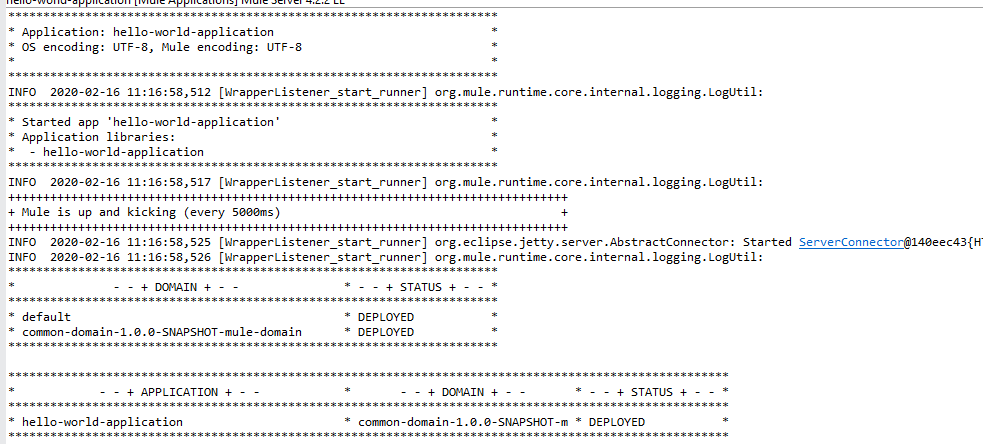
Now you can see HTTP Listener config defined in the domain project can be used in Mule Application (i.e. hello-world-application).

HTTP_Listener_config populated from domain project. This is how you can refer domain projects to multiple mule applications to reuse HTTP Listener Config for port 8081.
You need to make sure the domain project is deployed on Mule Runtime before deploying Mule application otherwise it will fail the deployment.
Now you can run all your applications having HTTP Listener on port 8081 by referring to domain project HTTP Listener Config.
Running Mule Application and Domain Project With Anypoint Studio
Once you start running the Mule Application, the domain project will automatically start with Mule Application. You don't need to start a domain project explicitly.
Now, you know how to implement and deploy Domain Project With MuleSoft.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments