Demystifying Machine Learning: Unveiling Algorithms, Models, and Applications
Discover various algorithms, models, and practical applications to unlock the transformative potential of this technology.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeMachine learning is a rapidly evolving field within the broader field of artificial intelligence (AI). It involves the development of algorithms and models that enable computers to learn from and make predictions or decisions based on data. Machine learning has become increasingly popular in recent years due to its wide range of applications and its ability to automate complex tasks.

What Is Machine Learning?
At its core, machine learning is about creating mathematical models and algorithms that can learn from data. Instead of explicitly programming a computer to perform a specific task, machine learning algorithms learn from examples and patterns in the data to make predictions or take actions. This ability to learn and adapt makes machine learning particularly useful in handling complex and unstructured data.
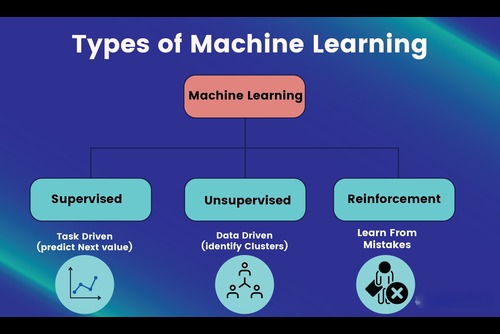
Types of Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine learning algorithms can be broadly categorized into three types: Supervised learning, Unsupervised learning, and Reinforcement learning.
1. Supervised Learning
The algorithm in supervised learning learns from labeled samples when the intended output is known. Supervised learning algorithms are classified into two types:
Classification: This algorithm predicts discrete class labels. For example, given a set of emails, a classification algorithm can be trained to predict whether each email is spam or not.
Examples: Logistic Regression, Support Vector Machines (SVM), Decision Trees, Random Forests, and Naive Bayes are some of the techniques used. These algorithms are used to detect email spam, analyze sentiment, and classify images, among other things.Regression: Regression techniques forecast continuous numerical values. For example, estimating the price of a property based on its characteristics such as size, location, and number of rooms.
Examples: Regression methods that are widely employed include linear regression, polynomial regression, support vector regression (SVR), and random forest regression (RFR). They can be used to forecast house prices, stock market movements, or sales.
2. Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning involves finding patterns and relationships in unlabeled data. These algorithms aim to discover patterns, relationships, or structures in the data. Unsupervised learning can be further divided into two main types:
Clustering: Clustering algorithms group similar data points together based on their characteristics or features. The goal is to find inherent patterns or clusters within the data. An example is clustering customer data to identify different market segments.
Examples: Popular clustering techniques include K-means, Hierarchical Clustering, and DBSCAN (Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise). They're utilized for things like customer segmentation, picture segmentation, and anomaly detection.Dimensionality reduction: These algorithms aim to reduce the number of features in a dataset while preserving important information. It helps in visualizing and understanding complex data by representing it in a lower-dimensional space.
Example: Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and t-SNE (t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbour Embedding) are two techniques that are often used to reduce the dimensionality of a dataset while retaining crucial information. They are useful for visualizing high-dimensional data and extracting features.
3. Reinforcement Learning
It focuses on training an agent to interact with an environment and learn through trial and error. The algorithm receives feedback in the form of rewards or penalties based on its actions, enabling it to optimize its decision-making process. It is commonly used in applications like game-playing, robotics, and autonomous driving.
- Q-Learning: It is a popular reinforcement learning algorithm. It employs a table (Q-table) to learn optimum behaviors based on environmental status and matching rewards. It has been used to solve difficulties like game playing (chess, Go) and control systems (autonomous cars).
- Deep Q-Network (DQN): DQN is a Q-learning extension that uses deep neural networks as function approximators. It has been successfully used to play Atari games and does complicated control duties.
Model Selection and Applications
Different algorithms have different strengths and weaknesses, and selecting the appropriate model requires an understanding of the problem domain and the characteristics of the data.
Model selection involves evaluating various factors such as the complexity of the problem, the size of the dataset, the interpretability of the model, and the computational resources available. Commonly used machine learning models include decision trees, support vector machines, neural networks, and ensemble methods like random forests.
Here are some common machine learning models and their applications with examples:
Linear Regression
- Application: Predicting house prices based on features like area, number of bedrooms, and location.
- Example: A real estate company uses historical data of house sales to build a linear regression model that predicts the price of a new house given its features.
Logistic Regression
- Application: Email spam detection, where the model classifies emails as spam or non-spam.
- Example: An email service provider trains a logistic regression model using labeled data to automatically filter out spam emails from users' inboxes.
Decision Trees
- Application: Credit scoring, where the model predicts the creditworthiness of a customer based on various factors.
- Example: A bank uses a decision tree model to determine whether a loan applicant will likely default or repay based on their income, credit history, and other relevant information.
Random Forests
- Application: Medical diagnosis, where the model classifies patients into different disease categories based on symptoms and medical test results.
- Example: A hospital uses a random forest model to analyze patient data and assist doctors in diagnosing diseases such as cancer, diabetes, or heart conditions.
Support Vector Machines (SVM)
- Application: Image classification, where the model classifies images into different categories.
- Example: An online image hosting platform employs an SVM model to automatically categorize uploaded images as landscapes, animals, or people.
K-means Clustering
- Application: Customer segmentation for targeted marketing campaigns.
- Example: An e-commerce company applies k-means clustering to group customers based on their purchasing behavior and preferences, allowing them to tailor marketing strategies for each segment.
Neural Networks (Deep Learning)
- Application: Natural Language Processing (NLP), such as sentiment analysis or language translation.
- Example: A social media platform utilizes a deep learning model, like a recurrent neural network (RNN) or transformer, to analyze user comments and classify their sentiment as positive, negative, or neutral.
Reinforcement Learning
- Application: Game playing, where an agent learns to play games and improves its performance over time.
- Example: DeepMind's AlphaGo used reinforcement learning techniques to defeat human champions in the complex board game of Go.
That's all there is to it for now!
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments