Deploy Node Express App on Heroku: 8 Easy Steps
Deploy your Heroku app including nodejs buildpacks and environment variables with step-by-step explanation and code snippets.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
With so many deploying interfaces on the web like firebase, netlify, AWS….none have an effective way to deploy a node app server except Heroku.
Deploying a node app on Heroku using CLI is not difficult if you follow my steps. Otherwise, they pose one or other problems especially when it comes to adding build packs and config vars. Here is a quick guide to deploying a node app with environments variables too.
Before you follow the following steps I believe your project is running well on your localhost.
Step 1: Setting Port Number
In root file like app.js/index.js you must have specified a local PORT, for example, 8000, on which your app runs. To run the app on the Heroku server it gives its global port.
Add the following line:-
app.listen(process.env.PORT || 3000);
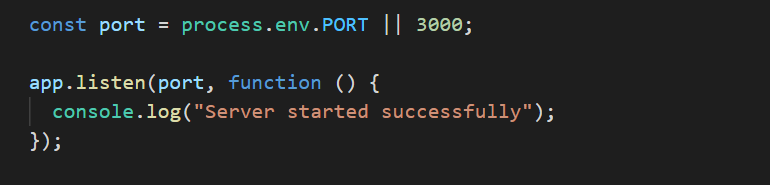
This ensures that when connected to Heroku the app runs on process.env.PORT and if tested locally it can also run on port 3000.
Step 2: Change package.json
While initializing npm it creates package.json.
Here you will find a property of scripts that comes by default.
Just add the following line inside scripts property:-
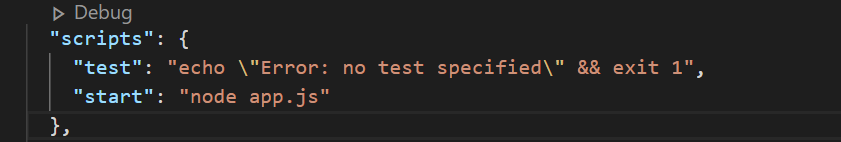
Step 3: Install Heroku CLI.
You can download it from this link.
After that, verify it by running the following command (if you are on windows)
heroku -v
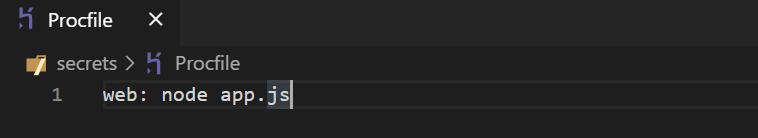
Step 4: Create Your Procfile
Inside the root of your folder, create a Procfile(make sure that there is no extension in the file and “P” is capital). It is the Heroku file in which you will define the dynos setting like after uploading the app, how Heroku will start the node js web server.
Your Procfile should look like this (specify your project entry file) like app.js, index.js, or anything you named it.
Like mine here is app.js
Step 5: Heroku Logging from Terminal
Open your terminal inside the root of the project. Type the following command to log in to your Heroku command.
heroku login
If you are not already login it will open a separate web-window asking for your login credentials.
Step 6: Initialize git.
You must initialize your project to a git repo using the following command.
git init
Then type the following command.
heroku create <app-name>
This will create your app in the Heroku server using the specified name.
(If the name is not specified it uses its own generated name which is sometimes not pleasing)
Its now time to push your files to the Heroku platform. (Using the git commands)
git add .
git commit -m “< Any message you want to give>”
Push the changes to the server.
git push heroku master
After that, you can see that we have successfully deployed our node js application.
Step 7: If Your App Has a Separate .env file
.env files are very useful for storing environment variables to keep API keys and other credentials in private mode.
But these pose a problem while deploying to Heroku. So you have to configure Heroku so that its server can also use those hidden keys.
Run the following commands on your terminal
heroku config:set <key=value>
Note: You must do this for all the key and value pairs in your created .env files.
Step 8: View Your Heroku App on The Browser.
In your terminal, type the following command to open the application in life.
heroku open
This will open your app up in the browser
Congrats!! Your app has been successfully deployed and ready to be shared with your friends.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments