Development Environments for Microservices
How do you set up the most productive environment for coding and testing, especially when the service in question depends upon other resources and services?
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeHow do you set up a productive development environment for microservices? While the tooling and infrastructure for building traditional web applications have been highly optimized over time, the same cannot be said for microservices.
In particular, setting up a productive development environment for microservices can be considerably more complex than a traditional web application:
- Your service likely relies on resources like a database or a queue.In production, these will often be provided by your cloud provider, e.g., AWS RDS for databases or Google Pub/Sub for publish/subscribe messaging.
- Your service might rely on other services that either you or your coworkers maintain. For example, your service might rely on an authentication service.
These external dependencies add complexity to creating and maintaining a development environment. How do you set up your service so you can code and test it productively when your service depends on other resources and services?
This article discusses the various approaches to setting up a development environment, and the tradeoffs.
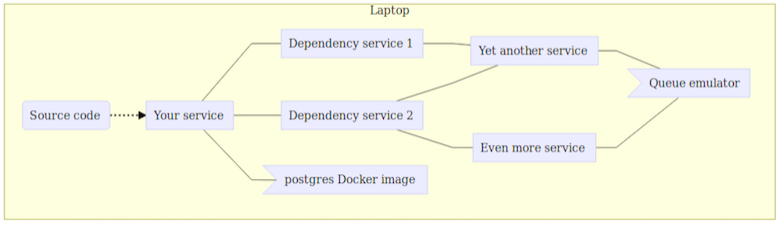
Option #1: Spin Up the Full System Locally
Using tools like Minikube or Docker Compose, you can spin up multiple services locally.
For resources like databases you use Docker images that match them:
- For a database like PostgreSQL, you can use the
postgresDocker image as a replacement for AWS RDS.It won’t quite match, but much of the time it will be close enough. - For other cloud resources you can often spin up emulators; Google provides an emulator for Google Pub/Sub that you can run locally.
If you’re unable to use containers, Daniel Bryant outlines a number of other approaches for developing microservices locally with various tradeoffs.
Pros:
- Fast, local development.
Cons:
- Some resources can be hard to emulate locally (e.g., Amazon Kinesis).
- You need a way to set up and run all your services locally and keep this setup in sync with how you run services in production.
- Not completely realistic. Depending on the option chosen, there can be major or minor differences from production, e.g., the
postgresDocker image doesn’t quite match the AWS RDS PostgreSQL configuration, mocks/stubs are not a substitute for running a full-blown service. - You potentially need to spin up the whole system locally, which will become difficult once you have a large enough number of services and resources.
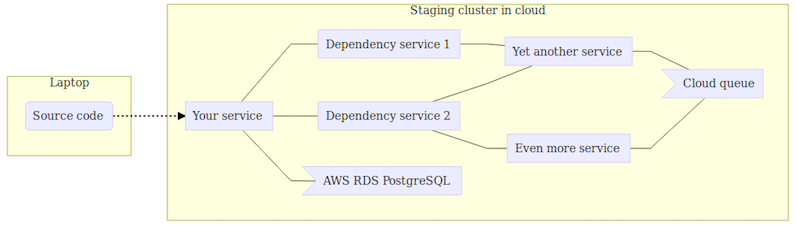
Option #2: Spin Up the Full System in the Cloud
You spin up a realistic cluster in the cloud, a staging/testing environment. It might not have as many nodes as the production system since load will be much lower, but it is quite close. Your code also runs in this cluster.
Pros:
- Very realistic.
Cons:
- Development is slower since you need to push code to cloud after every change in order to try it out.
- Using tools like debuggers is more difficult since the code all runs remotely.
- Getting log data for development is considerably more complex.
- Need to pay for additional cloud resources, and spinning up new clusters and resources is slow (even if you use an automated tool).
- As a result, you may end up using a shared staging environment rather than one per-developer, which reduces isolation.
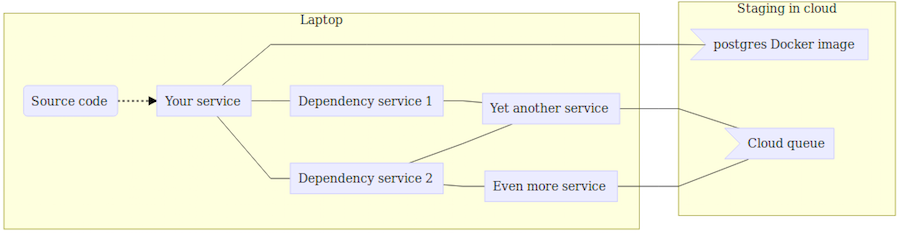
Option #3: Spin Up All Business Logic Locally, Route Cloud Services to Laptop
As with option #1, all services run locally. However, cloud resources (AWS RDS, etc.) are made available locally on your development machine via some sort of tunneling or proxying, e.g., a VPN.
Pros:
- Fast, local development.
- Very realistic.
Cons:
- You need a way to set up and run all your services locally and keep this setup in sync with how you run services in production.
- Need to pay for additional cloud resources, and spinning up new cloud resources is slow.
- As a result, you may end up using a shared staging environment rather than one per-developer, which reduces developer isolation.
- You potentially need to spin up the whole system locally, which will become difficult once you have a large enough number of services.
Option #4: Make Local Code for Single Service Available in Remote Cluster
You spin up a realistic cluster in the cloud, a staging/testing environment, but your service runs locally and is proxied/VPNed into the remote cluster.
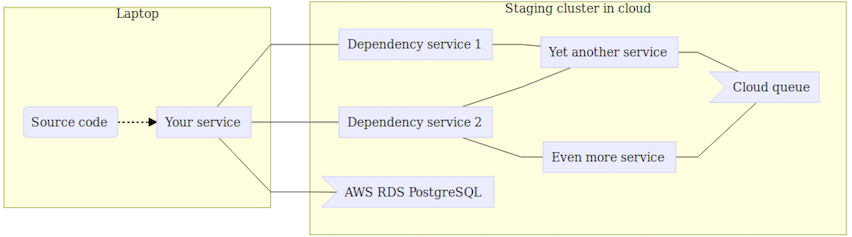
Pros:
- Fast, local development.
- Very realistic.
- Simple local setup.
Cons:
- Need to pay for additional cloud resources, and spinning up new cloud resources is slow.
- As a result, you may end up using a shared staging environment rather than one per-developer, which reduces developer isolation. This is mitigated by the fact that your changes (and that of others) are local to your environment.
- Configuring a proxy or VPN that works with your cluster can be complex (although automated tools like Telepresence make this easier).
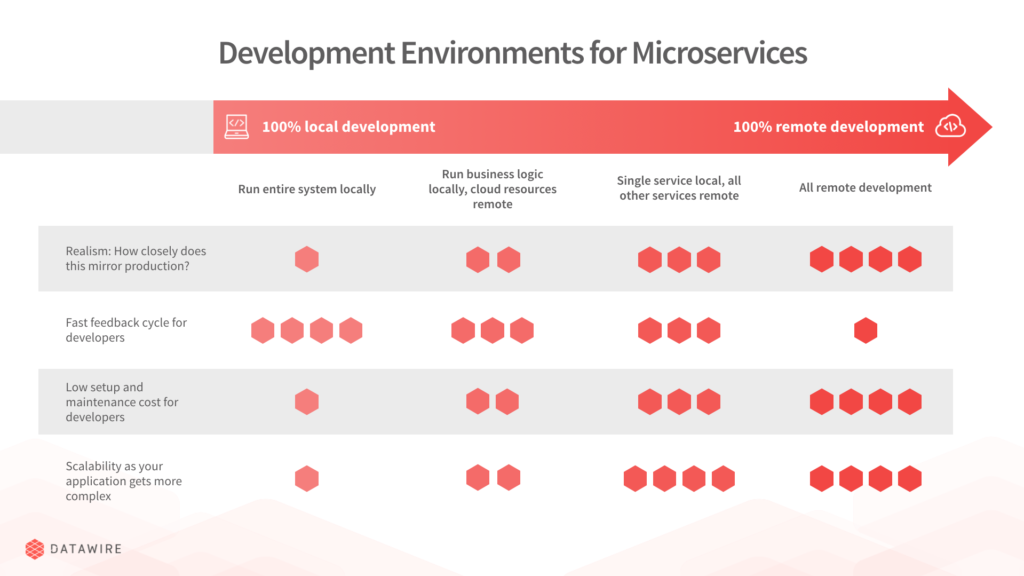
When deciding on the most effective method for setting up a productive development environment for microservices at your organization, you can consider these four options in terms of four main tradeoffs:
How closely does the environment mirror production?
How fast is the feedback cycle for developers?
What are the setup and maintenance costs for developers?
How scalable is the environment as your application gets more complex?
Published at DZone with permission of Itamar Turner-Trauring. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments