Entity Creation With Asynchronous Pipelines in Distributed Systems
This article explores the benefits and challenges of async pipelines and provides practical solutions for creating resilient and scalable systems.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeCreating entities asynchronously in distributed systems presents challenges and benefits, especially for large enterprises seeking scalability, fault tolerance, and efficient user experiences. Asynchronous (async) pipelines for entity creation decouple services, handle failures gracefully, and minimize latency. These qualities enable enterprises to maintain flexible, high-performing systems as they scale. Let's explore the benefits, challenges, and solutions to build an effective pipeline in depth.
Benefits of Asynchronous Pipelines in Entity Creation
Graceful Failure Handling
In complex distributed systems, certain tasks in the entity creation process are non-critical. Async pipelines allow failure isolation, meaning failures in non-critical tasks won’t disrupt the entire process. These tasks can either be retried or ignored, allowing the pipeline to continue smoothly.
Latency Reduction and Parallelism
By decoupling high-latency tasks, async pipelines ensure that other tasks can proceed without waiting. This parallelism reduces the overall time for entity creation, especially when tasks that do not depend on each other can be executed concurrently, improving throughput and responsiveness.
Independence and Scalability
Async pipelines enable different services to work independently, scaling as needed. For example, a service handling notifications may have different scaling needs than the core entity creation service. As services are loosely coupled, they can be replaced, updated, or scaled without disrupting the pipeline, enhancing system resilience.
Improved Fault Tolerance and Eventual Consistency
Async pipelines allow for automatic retries in case of service downtime or delays. While some tasks might take longer, the system ensures eventual consistency, guaranteeing that data across services will eventually synchronize, even if temporarily out of sync.
Non-Blocking Operations
With async systems, services can proceed without waiting for responses from other services, improving resource utilization and system responsiveness. This non-blocking nature allows multiple tasks to run in parallel, increasing overall system throughput.
Loose Coupling and Flexibility
Async communication between services promotes a loosely coupled architecture, where different services interact via event streams or message queues. This separation enables independent updates or replacements, allowing large enterprises to manage complex architectures and adopt continuous deployment strategies.
Responsive Front-End Experiences
Asynchronous pipelines allow front-end applications to provide immediate feedback to users, even if back-end processes take time to complete. This can be done by notifying the user that the entity creation is in progress, while the back-end performs the heavy lifting. Real-time user notifications ensure a smooth and responsive user experience.
Event-Driven Architectures
Async pipelines excel in event-driven architectures, where certain tasks (like notifications or updates) are triggered by specific events. These architectures efficiently handle high event volumes while maintaining system responsiveness.
Support for Microservices and Service Specialization
In a microservices-based architecture, where each service is independently managed, async pipelines allow services to specialize in tasks like authentication or logging without being dependent on others. This specialization enhances performance and simplifies maintenance at scale.
Challenges of Async Pipelines in Entity Creation
While async pipelines offer significant benefits, they come with a set of challenges:
Eventual Consistency
Distributed systems rely on eventual consistency, which can cause temporary inconsistencies between services. Some services may recognize an entity as created while others do not. Maintaining synchronized data across systems, especially during the entity creation process, becomes a challenge.
Error Handling and Retries
Failures can occur at any step of the pipeline. Error handling requires mechanisms like retries and idempotency to avoid duplicate or corrupted data. Identifying failure points and ensuring graceful recovery from partial successes is critical for system reliability.
Race Conditions
When multiple services work asynchronously, race conditions may arise. For example, a service may act on incomplete data if it assumes an entity has been fully created. Effective coordination and orchestration between services are essential to avoid such issues.
Latency and Performance
Async pipelines can introduce latency due to communication across distributed services. If any step in the entity creation process is delayed, the entire operation may be slowed down. This is especially problematic when users are waiting for real-time responses.
Monitoring and Observability
Tracking the status of async operations is harder than in synchronous systems. Proper logging, monitoring, and observability are essential for detecting issues and troubleshooting failures, but these capabilities are often more difficult to implement in async pipelines.
Coordination of Dependent Entities
When one entity depends on the successful creation of another, asynchronous coordination becomes complex. Failures in this coordination can lead to broken dependencies or deadlocks.
Schema Mismatch and Evolution
Changes in the schema can break async pipelines, especially when backward compatibility is not maintained. Rolling back schema changes can result in inconsistent data across services.
A Practical Solution for Entity Creation With Async Pipelines
To address the challenges of async pipelines, we can implement a resilient architecture with the following steps:
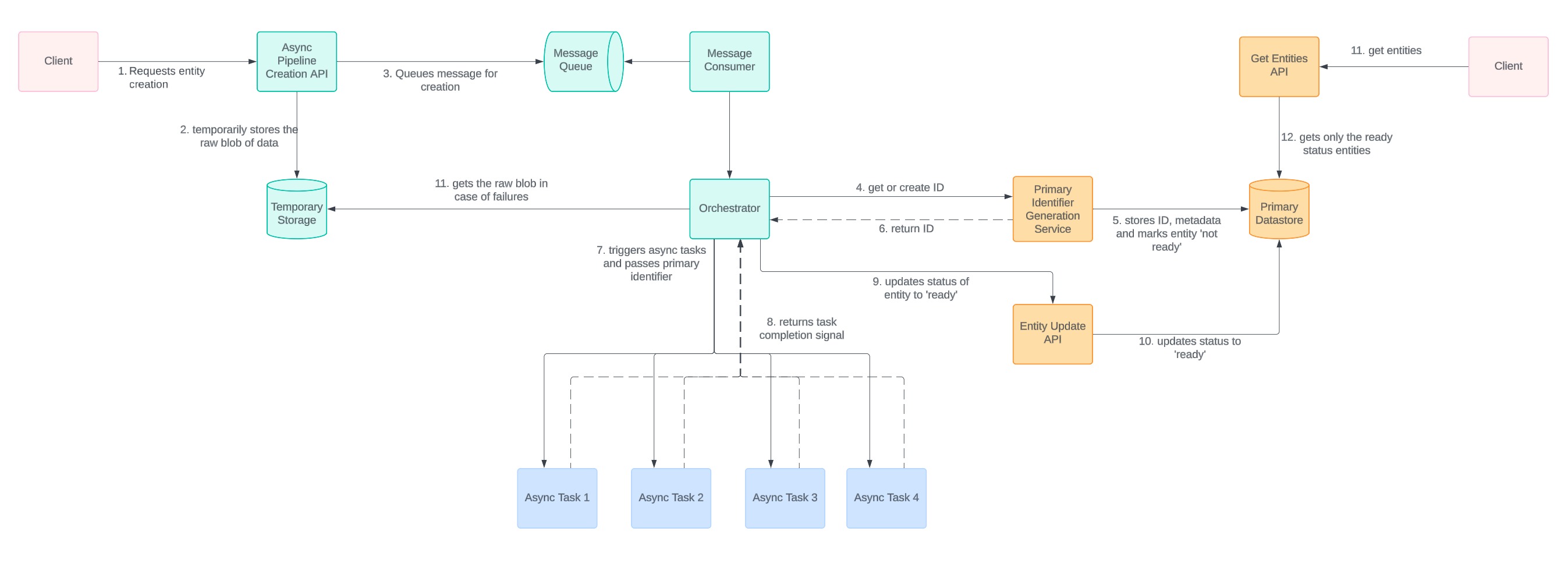
Synchronous Primary Identifier Creation
The entity creation process begins with the synchronous creation of a primary identifier, which anchors the rest of the operation. The entity is marked as "not ready for consumption" in the database until the entire process is completed. This ensures no incomplete data is exposed to users.
Async Pipeline for Entity Completion
After the primary identifier is created, other tasks, such as populating different data stores, are handled asynchronously. Each task references the primary identifier, ensuring consistency throughout the pipeline.
Orchestration Layer
Using an orchestration platform like Temporal, the system can manage task execution, retries, and state tracking. The orchestration layer listens for the successful completion of all tasks before marking the entity as "ready for consumption."
Entity Status Management
Implement multiple statuses such as Pending Creation, Error, and Ready for Consumption. This improves tracking and provides users with timely feedback through notifications or email updates.
Logging and Observability
Comprehensive logging is critical for diagnosing issues and tracking the health of the pipeline. Tools for observability should be used to monitor the status of async operations and provide insights into system bottlenecks.
Temporary Data Storage
A temporary storage layer can store raw data blobs at the start of the pipeline. This enables data recovery and task retries without corrupting or losing information during service failures.
User Interaction and Feedback
Providing real-time feedback to users through a responsive interface is crucial for user experience. Implement mechanisms like notifications or UI elements that allow users to refresh and check the status of their entity creation request.
Conclusion
Async pipelines for entity creation offer powerful benefits for large enterprises, improving scalability, resilience, and user experience. However, they come with challenges related to data consistency, error handling, and latency. By adopting a structured approach with a synchronous identifier creation step, orchestration layers, and careful monitoring, organizations can overcome these challenges and build systems that are both scalable and reliable.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments