How Are CRUD Operations Used for File Handling in Java?
This article will give you a hands-on approach to implementing the CRUD Operations: Create, Read, Update and Delete through various example codes.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeJava is a high-level language. Java programs generally execute on a terminal that is not stored; some programs need some source to store information fetched from the program that is in the form of a file. CRUD operations stand for Create, Read, Update and Delete.
As said, some Java programs need some files to store information fetched from the program. A file stores different types of information, including text, images, videos, and more.
We can perform many operations on File:
- Creation
- Opening
- Reading
- Writing
- Moving
- Closing
Let us discuss CRUD operations in a better way by using example codes.
CRUD Operations
CRUD stands for Create, Read/ Retrieve, Update and Delete; these are used in file handling in Java. Creation of a file is done using POST, Reading of the file is done using GET, Updating the file using PUT, and for deleting a file, we use DELETE.
Now let us discuss each of the operations with an example using Java.
Firstly, Let us discuss the Creation of the file:
- For creating a file in Java, we use the createNewFile() method.
- It returns a boolean value that is TRUE if the file is created successfully; else returns FALSE.
Code:
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
class cfile {
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
File file = new File("C:JavaPrograms/sample.txt");
if (file.createNewFile()) {
System.out.println("File " + file.getName() + " is created successfully.");
} else {
System.out.println("File is already exists");
}
} catch (IOException exception) {
System.out.println("Exception Occurred");
}
}
} Output:
File sample.txt is created successfully.
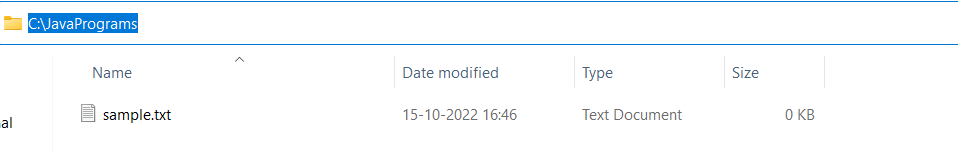
Let us create another file for better understanding.
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
class cfile1 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
File file = new File("C:JavaPrograms/sample1.txt");
if (file.createNewFile()) {
System.out.println("File " + file.getName() + " is created successfully.");
} else {
System.out.println("File is already exists");
}
} catch (IOException exception) {
System.out.println("Exception Occurred");
}
}
} Output:
File sample1.txt is created successfully.
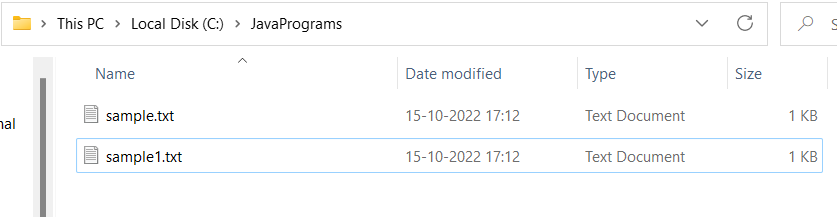
Now, let us discuss Reading or Retrieving the file.
For reading or retrieving a file in Java, we use the Scanner class and which helps to read the contents of the file.
Code:
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.util.Scanner;
class rfile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
File file = new File("C:JavaPrograms/sample.txt");
Scanner dataReader = new Scanner(file);
while (dataReader.hasNextLine()) {
String fileData = dataReader.nextLine();
System.out.println(fileData);
}
dataReader.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException exception) {
System.out.println("Exception Occurred");
}
}
}
Output:
#Reads file from the mentioned location.
This is a Java file used as a sample!
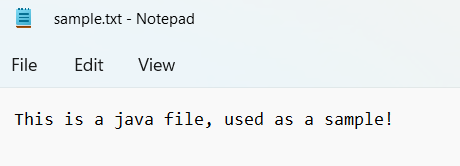
One more example for reading sample1.text file.
Code:
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.util.Scanner;
class rfile1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
File file = new File("C:JavaPrograms/sample1.txt");
Scanner dataReader = new Scanner(file);
while (dataReader.hasNextLine()) {
String fileData = dataReader.nextLine();
System.out.println(fileData);
}
dataReader.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException exception) {
System.out.println("Exception Occurred");
}
}
} Output:
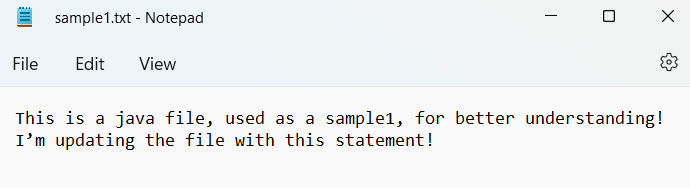
#Reads file from the mentioned location.
This is a Java file, used as a sample1, for better understanding!
Now, let us discuss writing or Updating the file,
For writing or updating a file in Java, we use the FileWriter class with the write() method and use it to write or update some content to the file.
Code:
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
class ufile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileWriter fwrite = new FileWriter("C:JavaPrograms/sample.txt");
fwrite.write("I’m updating the file with this statement!");
fwrite.close();
System.out.println("Content is successfully wrote to the file.");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Exception Occurred");
}
}
} Output:
#Updates file from the mentioned location.
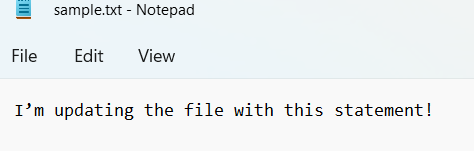
I’m updating the file with this statement!
Now Updating the sample1.txt file,
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
class ufile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileWriter fwrite = new FileWriter("C:JavaPrograms/sample.txt");
fwrite.write("I’m updating the file with this statement!");
fwrite.close();
System.out.println("Content is successfully wrote to the file.");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Exception Occurred");
}
}
} Output:
#Updates file from the mentioned location.
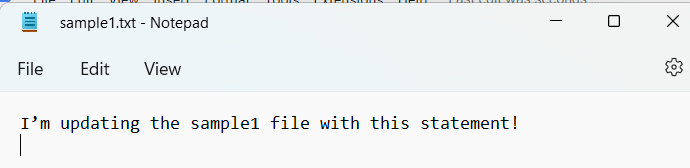
I’m updating the sample1 file with this statement!
Now, let us discuss deleting the file.
For deleting a file in Java, we use the delete() method, which is used to delete files.
Code:
import java.io.File;
class DeleteFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file= new File("C:JavaPrograms/sample.txt");
if (file.delete()) {
System.out.println(file.getName()+ " file is deleted successfully.");
} else {
System.out.println("Error Occurred");
}
}
} Output:
#Deletes file from the mentioned location.
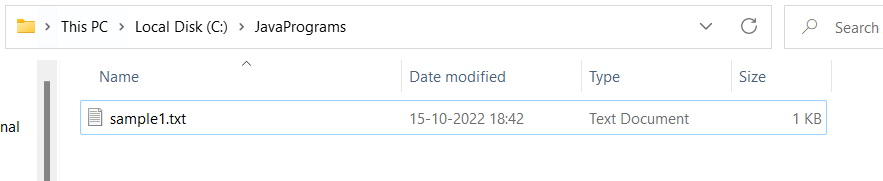
sample.txt file is deleted successfully.
Now let us delete the sample1.txt file from the JavaPrograms folder in the C drive.
Code:
import java.io.File;
class DeleteFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file= new File("C:JavaPrograms/sample1.txt");
if (file.delete()) {
System.out.println(file.getName()+ " file is deleted successfully.");
} else {
System.out.println("Error Occurred");
}
}
} Output:
#Deletes file from the mentioned location.
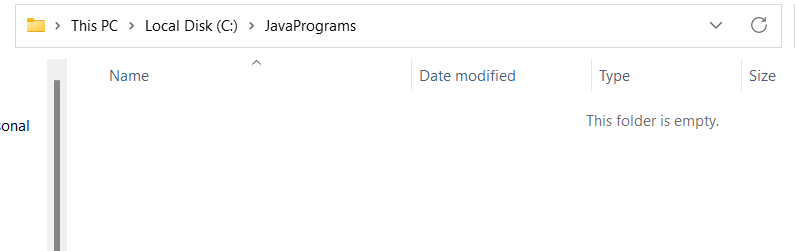
sample1 .txt file is deleted successfully.
File Handling in Java
We have some streams in Java used for performing input-output operations on files. Stream is nothing but the sequence of data.
Here we have two types of streams in Java:
- Input Stream
- Output Stream
In Java, we also have some file class methods like createNewFile(), canRead(), canWrite(), delete(), and more.
Conclusion
- We discussed how CRUD operations are used in Java.
- Also discussed why CRUD operations are used in Java.
- CRUD operations are Create, Read, Update and Delete.
- Basically, CRUD operations are used to handle files in Java.
- C for Creating a file is used for creating a file using Java.
- R for Reading or Retrieving a file for reading a file using Java.
- U for Updating the file using Java.
- D for Deleting the file using Java.
- We can perform many other operations on files using Java.
- We discussed the different examples using Java Programs for a better understanding of concepts.
I hope this blog was informative.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments