How Dependency Injection (DI) Works In Spring Java Application Development
This article explains the concept of Dependency Injection (DI) and how it works in Spring Java application development.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis article explains the concept of Dependency Injection (DI) and how it works in Spring Java application development. You will learn about the advantages, disadvantages, and basics of DI with examples. Look further for more information.
Advantages of Dependency Injection
DI allows a client the flexibility of being configurable. Only client's behavior is fixed.
Testing can be performed using mock objects.
Loosely couple architecture.
DI advantages of high cohesion are:
Reduced module complexity
Increased system maintainability, because logic changes in the domain affect fewer modules.
Increased module reusability.
DI does not require any changes in code behavior it can be applied to legacy code as refactoring.
DI allows a client to remove all knowledge of a concrete implementation that needs to use. It is more reusable, more testable, more readable code.
DI makes it possible to eliminate, or at least reduce unnecessary dependencies.
DI allows concurrent or independent development.
DI decreases coupling between a class and its dependency.
Disadvantages of Dependency Injection
DI creates clients that demand configure details supplied by construction code.
DI can make code difficult to trace because it separates behavior from construction; this means developers refer to more files to follow how a system performs.
DI can cause an explosion of types, especially in languages that have explicit interface types like C# and Java.
DI can encourage dependence on DI framework.
Tight coupling :
A change in only one module usually forces a ripple effect of changes in other modules.
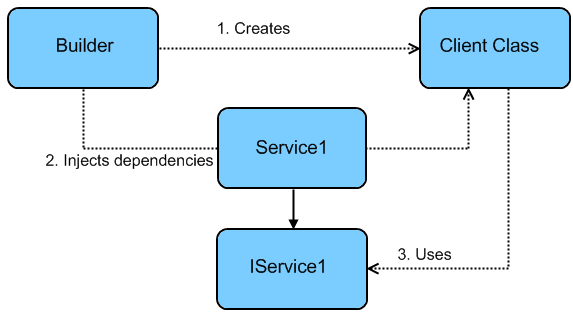
Dependency Injection (DI)
Dependency Injection (DI) is a software design pattern that implements inversion of control for resolving dependencies.
An injection is the passing of a dependency to a dependent object that would use it.
DI is a process whereby objects define their dependencies. The other objects they work with—only through constructor arguments or arguments to a factory method or property—are set on the object instance after it is constructed or returned from a factory method.
The container then injects those dependencies, and it creates the bean. This process is named Inversion of Control (IoC) (the bean itself controls the instantiation or location of its dependencies by using direct construction classes or a Service Locator).
DI refers to the process of supplying an external dependency to a software component.
Dependency Injection Performed Two Ways
1. Constructor-Based Dependency Injection
Constructor-based DI is when the container invokes a constructor with a number of arguments, each of which represents a dependency or other class.
Calling a static factory method with particular arguments to construct the bean is approximately equivalent, treating arguments to a constructor and to a static factory method. The following example shows a class that can only be dependency-injected with constructor injection. It is a POJO that has no dependencies on container specific interfaces, base classes, or annotations.
public class SimpleStudentList {
// the SimpleStudentList has a dependency on StudentFind
private StudentFind studentFind;
// a constructor that Spring container can 'inject' a StudentFind
public SimpleStudentList(StudentFind studentFind ) {
this.studentFind = studentFind ;
}
// business logic code
}Example of Constructor-Based DI
Book.java
package com.spring.example;
public class Book {
private int id;
private String bookName;
public Book() {System.out.println("Java");}
public Book(int id) {this.id = id;}
public Book(String bookName) { this.bookName = bookName;}
public Book(int id, String bookName) {
this.id = id;
this.bookName = bookName;
}
void display(){
System.out.println(id+" "+bookName);
}
} applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<bean id="book" class="com.spring.example.Book">
<constructor-arg value="1" type="int"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans> Main.java
package com.spring.example;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.core.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Resource r=new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml");
BeanFactory factory=new XmlBeanFactory(r);
Book b=(Book)factory.getBean("book");
b.display();
}
} Output:
1 null
2. Setter-Based Dependency Injection
Setter-based DI is the when the container calls setter methods on your beans after it has invoked a no-argument constructor or no-argument static factory method to instantiate that bean.
The following example shows a class that can only have pure setter injection.
public class SimpleStudentList {
// the SimpleStudentList has a dependency on StudentFind
private StudentFind studentFind;
// a setter method that Spring container can 'inject' a StudentFind
public void setStudentFind(StudentFind studentFind ) {
this.studentFind = studentFind ;
}
// business logic
}Example of Setter Based DI
Book.java
package com.spring.example;
public class Book {
private int id;
private String bookName;
private String author;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getBookName() {
return bookName;
}
public void setBookName(String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
void display(){
System.out.println(id+" "+bookName+" "+author);
}
}applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<bean id="book" class="com.spring.example.Book">
<property name="id">
<value>1</value>
</property>
<property name="bookName">
<value>The Complete Reference J2EE</value>
</property>
<property name="author">
<value>Herbert Schildt</value>
</property>
</bean>
</beans> Main.java
package com.spring.example;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.core.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Resource r=new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml");
BeanFactory factory=new XmlBeanFactory(r);
Book b=(Book)factory.getBean("book");
b.display();
}
} Output :
The Complete Reference J2EE Herbert Schildt
Our Java application development team has just explained the concept of Dependency Injection, its advantages, disadvantages, and uses in Spring with examples. If you still have any confusion, tell us and get the answer from professionals.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments