How Does the Milvus Vector Database Ensure Data Security?
This article aims to analyze how Milvus, the vector database ensures data security with user authentication and TLS connection.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis article aims to analyze how Milvus, the vector database ensures data security with user authentication and TLS connection and explain how you can utilize these two features as a user who wants to ensure data security when using the vector database.
What Is Database Security and Why Is It Important?
Database security refers to the measures taken to ensure that all data in the database are safe and kept confidential. Recent data breach and data leak cases at Twitter, Marriott, and Texas Department of Insurance, etc, makes us all the more vigilant to the issue of data security. All these cases constantly remind us that companies and businesses can suffer from severe loss if the data are not well protected and the databases they use are secure.How Does the Milvus Vector Database Ensure Data Security?
In the current release of 2.1, the Milvus vector database attempts to ensure database security via authentication and encryption. More specifically, on the access level, Milvus supports basic user authentication to control who can access the database. Meanwhile, on the database level, Milvus adopts the transport layer security (TLS) encryption protocol to protect data communication.User Authentication
The Authentication Workflow in the Milvus Vector Database
All gRPC requests are handled by the Milvus proxy; hence authentication is completed by the proxy. The workflow of logging in with the credentials to connect to the Milvus instance is as follows.- Create credentials for each Milvus instance, and the encrypted passwords are stored in etcd. Milvus uses bcrypt for encryption as it implements Provos and Mazières's adaptive hashing algorithm.
- On the client side, SDK sends ciphertext when connecting to the Milvus service. The base64 ciphertext (<username>:<password>) is attached to the metadata with the key
authorization. - The Milvus proxy intercepts the request and verifies the credentials.
- Credentials are cached locally in the proxy.
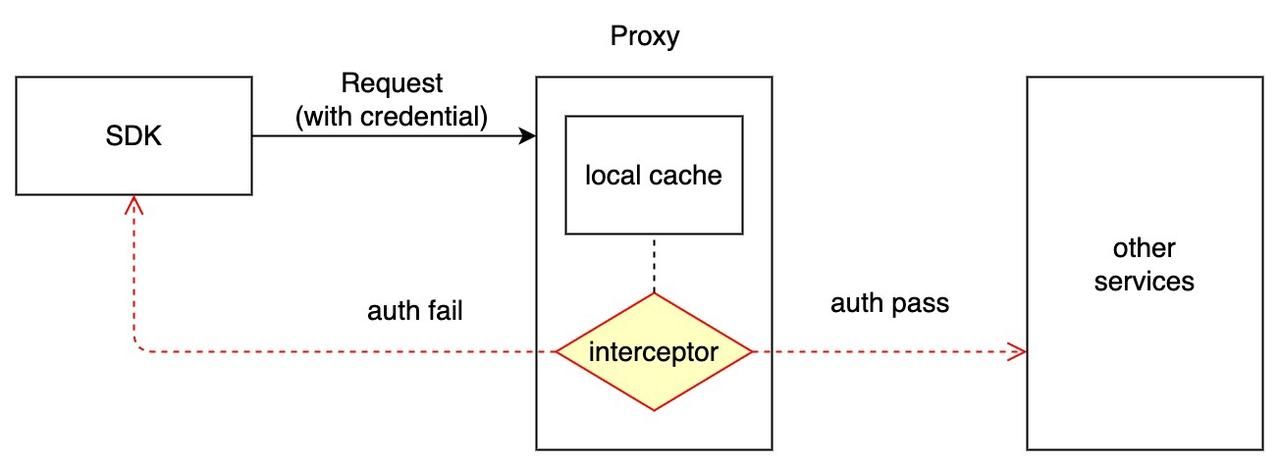
- ..Root coord is in charge of the credentials when insert, query, and delete APIs are called.
- When you update the credentials because you forget the password, for instance, the new password is persisted in, etcd. Then all the old credentials in the proxy's local cache are invalidated.
- The authentication interceptor looks for the records from local cache first. If the credentials in the cache is not correct, the RPC call to fetch the most updated record from root coord will be triggered. And the credentials in the local cache are updated accordingly.

How to Manage User Authentication in the Milvus Vector Database
To enable authentication, you need to first setcommon.security.authorizationEnabled to true when configuring Milvus in the milvus.yaml file.
Once enabled, a root user will be created for the Milvus instance. This root user can use the initial password of
Milvus to connect to the Milvus vector database.
from pymilvus import connections
connections.connect(
alias='default',
host='localhost',
port='19530',
user='root_user',
password='Milvus',
)Then root user can further create more new users for authenticated access by running the following command to create new users.
from pymilvus import utility
utility.create_credential('user', 'password', using='default')- As for the new username, it can not exceed 32 characters in length and must start with a letter. Only underscores, letters, or numbers are allowed in the username. For example, a username of "2abc!" is not accepted.
- As for the password, its length should be 6-256 characters.
from pymilvus import connections
connections.connect(
alias='default',
host='localhost',
port='19530',
user='user',
password='password',
)from pymilvus import utility
utility.reset_password('user', 'new_password', using='default')TLS Connection
Transport layer security (TLS) is a type of authentication protocol to provide communications security in a computer network. TLS uses certificates to provide authentication services between two or more communicating parties.How to Enable TLS in the Milvus Vector Database
To enable TLS in the Milvus vector database, you need to first run the following command to prepare two files for generating the certificate: a default OpenSSL configuration file namedopenssl.cnf and a file named gen.shused to generate relevant certificates.
mkdir cert && cd cert
touch openssl.cnf gen.shWhen the two files are ready, you can run the
gen.shfile to create nine certificate files. Likewise, you can also modify the configurations in the nine certificate files to suit your need.
chmod +x gen.sh
./gen.shtlsEnabled to true and configure the file paths of server.pem, server.key, and ca.pem for the server in config/milvus.yaml. The code below is an example.
tls:
serverPemPath: configs/cert/server.pem
serverKeyPath: configs/cert/server.key
caPemPath: configs/cert/ca.pem
common:
security:
tlsEnabled: trueclient.pem, client.key, and ca.pemfor the client when using the Milvus connection SDK. The code below is also an example.
from pymilvus import connections
_HOST = '127.0.0.1'
_PORT = '19530'
print(f"\nCreate connection...")
connections.connect(host=_HOST, port=_PORT, secure=True, client_pem_path="cert/client.pem",
client_key_path="cert/client.key",
ca_pem_path="cert/ca.pem", server_name="localhost")
print(f"\nList connections:")
print(connections.list_connections())Published at DZone with permission of Charles Xie. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments