Build an Android Mobile Application Using Azure DevOps
Explore this tutorial as an introduction to learn how to use Azure DevOps to construct, build, and deploy a mobile app using Gradle.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn the dynamic realm of Android app development, efficiency is key. Enter Azure DevOps, Microsoft's integrated solution that transforms the development lifecycle. This tutorial will show you how to leverage Azure DevOps for seamless Android app development.
What Is Azure DevOps?
Azure DevOps is not just a version control system; it's a comprehensive set of development and deployment tools that seamlessly integrate with popular platforms and technologies. From version control (Azure Repos) to continuous integration and delivery (Azure Pipelines), and even application monitoring (Azure Application Insights), Azure DevOps offers a unified environment to manage your entire development cycle. This unified approach significantly enhances collaboration, accelerates time-to-market, and ensures a more reliable and scalable deployment of your Android applications.
Azure DevOps is a game-changer in the development of feature-rich Android mobile applications, offering a unified platform for version control, continuous integration, and automated testing. With Azure Pipelines, you can seamlessly orchestrate the entire build and release process, ensuring that changes from each team member integrate smoothly. The integrated nature of Azure DevOps promotes collaboration, accelerates the development cycle, and provides robust tools for monitoring and troubleshooting. This unified approach not only helps meet tight deadlines but also ensures a reliable and scalable deployment of the Android application, enhancing the overall efficiency and success of the project.
Use the azure-pipelines.yml file at the root of the repository. Get this file to build the Android application using a CI (Continuous Integration) build.
Follow the instructions in the previously linked article, "Introduction to Azure DevOps," to create a build pipeline for an Android application.
After creating a new build pipeline, you will be prompted to choose a repository. Select the GitHub/Azure Repository. You then need to authorize the Azure DevOps service to connect to the GitHub account. Click Authorize, and this will integrate with your build pipeline.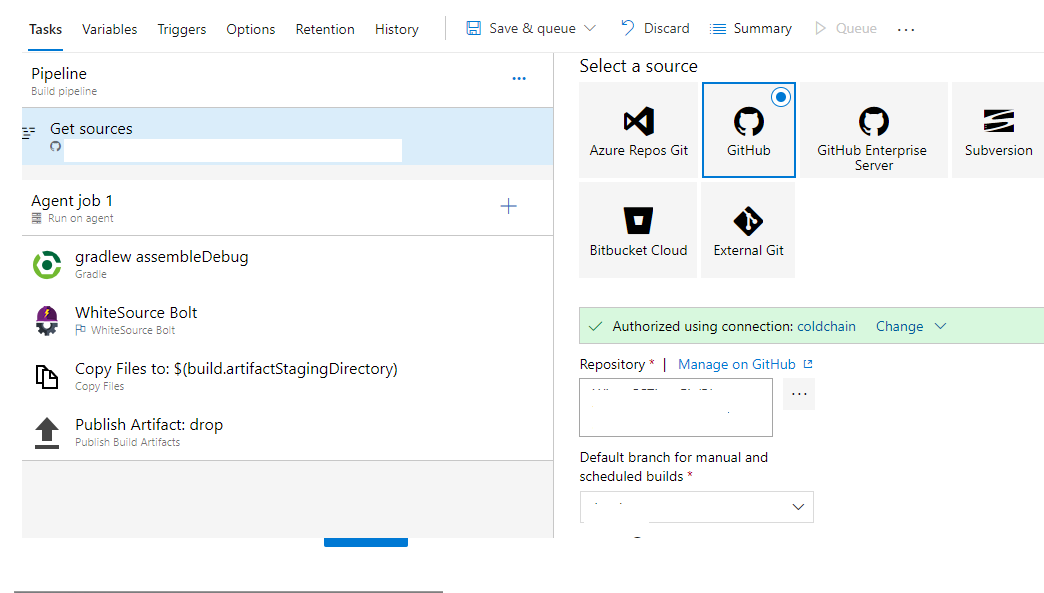
After the connection to GitHub has been authorized, select the right repo, which is used to build the application.
How To Build an Android Application With Azure
Step 1: Get a Fresh Virtual Machine
Azure Pipelines have the option to build and deploy using a Microsoft-hosted agent. When running a build or release pipeline, get a fresh virtual machine (VM). If Microsoft-hosted agents will not work, use a self-hosted agent, as it will act as a build host.
pool:
name: Hosted VS2017
demands: java
Step 2: Build a Mobile Application
Build a mobile application using a Gradle wrapper script. Check out the branch and repository of the gradlew wrapper script. The gradlew wrapper script is used for the build. If the agent is running on Windows, it must use the gradlew.bat; if the agent runs on Linux or macOS, it can use the gradlew shell script.
Step 3: Set Directories
Set the current working directory and Gradle WrapperFile script directory.
steps:
- task: Gradle@2
displayName: 'gradlew assembleDebug'
inputs:
gradleWrapperFile: 'MobileApp/SourceCode -Android/gradlew'
workingDirectory: 'MobileApp/SourceCode -Android'
tasks: assembleDebug
publishJUnitResults: false
checkStyleRunAnalysis: true
findBugsRunAnalysis: true
pmdRunAnalysis: true
This task detects all open source components in your build, security vulnerabilities, scan libraries, and outdated libraries (including dependencies from the source code). You can view it from the build level, project level, and account level.
task: whitesource.ws-bolt.bolt.wss.WhiteSource Bolt@18
displayName: 'WhiteSource Bolt'
inputs:
cwd: 'MobileApp/SourceCode -Android'Step 4: Copy Files
Copy the .apk file from the source to the artifact directory.
- task: CopyFiles@2
displayName: 'Copy Files to: $(build.artifactStagingDirectory)'
inputs:
SourceFolder: 'MobileApp/SourceCode -Android'
Contents: '**/*.apk'
TargetFolder: '$(build.artifactStagingDirectory)'
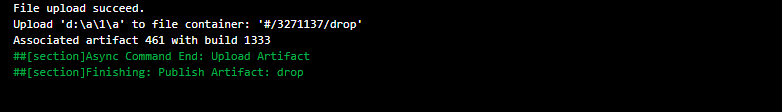
Use this task in the build pipeline to publish the build artifacts to Azure pipelines and file share.it will store it in the Azure DevOps server.
- task: PublishBuildArtifacts@1
displayName: 'Publish Artifact: drop'
The new pipeline wizard should recognize that you already have an azure-pipelines.yml in the root repository.
The azure-pipeline.yml file contains all the settings that the build service should use to build and test the application, as well as generate the output artifacts that will be used to deploy the app's later release pipeline(CD).
Step 5: Save and Queue the Build
After everything is perfect, save and queue the build so you can see the corresponding task of logs to the respective job.
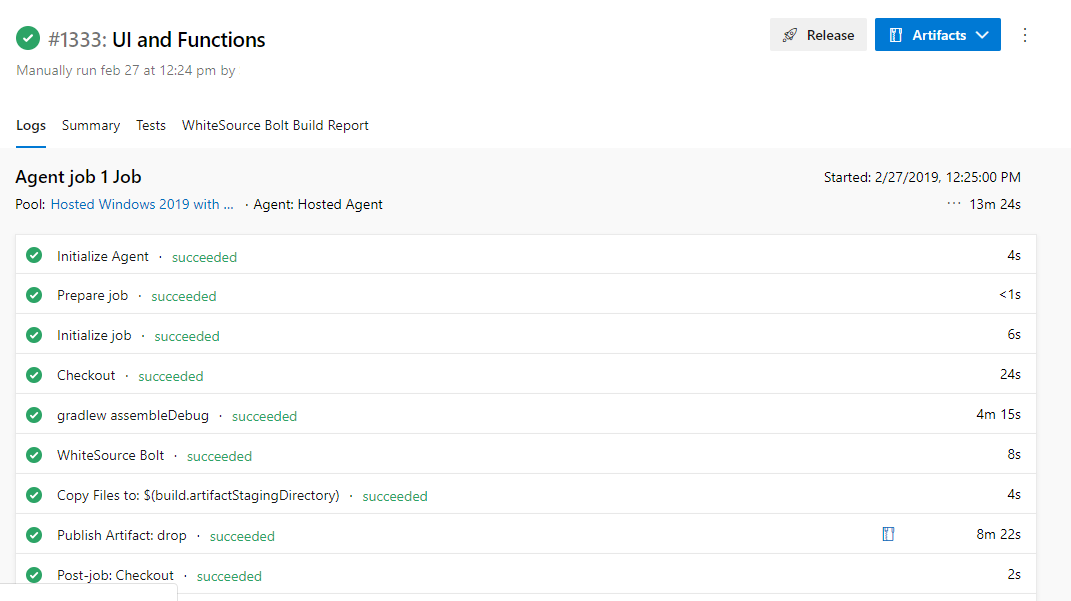
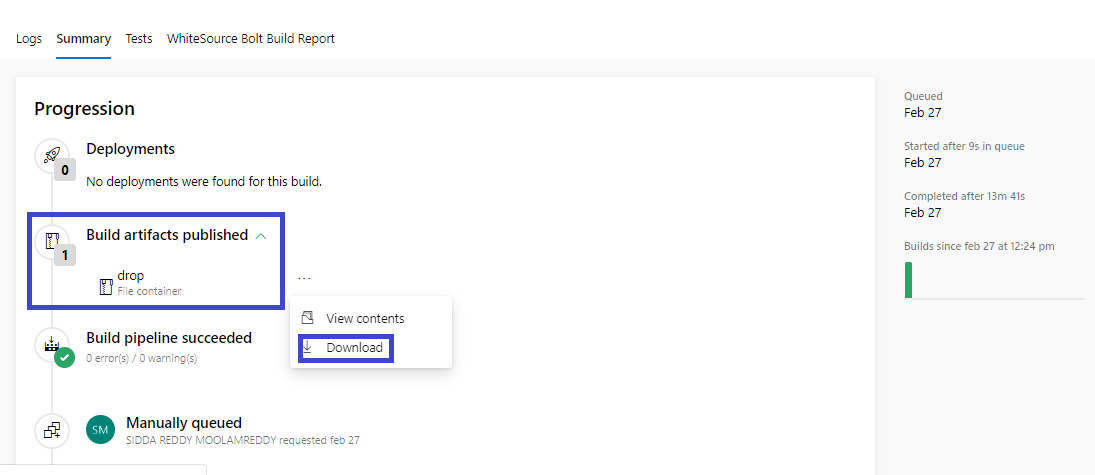
Step 6: Extract the Artifact Zip Folder
After everything is done, extract the artifact zip folder, copy the .apk file into the mobile device, and install the .apk file.
Conclusion
Azure DevOps is a game-changer for Android app development, streamlining processes and boosting collaboration. Encompassing version control, continuous integration, and automated testing, this unified solution accelerates development cycles and ensures the reliability and scalability of Android applications.
The tutorial has guided you through the process of building and deploying an Android mobile application using Azure DevOps. By following these steps, you've gained the skills to efficiently deploy Android applications, meet tight deadlines, and ensure reliability. Whether you're optimizing your workflow or entering Android development, integrating Azure DevOps will significantly enhance your efficiency and project success.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments