How to Move System Databases to Different Locations in SQL Server on Linux
In this article, we will explain how to move the system databases to different locations in Ubuntu Linux.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeLinux is a complex operating system, undoubtedly very secure but complex, especially for users who never had experience working on the Linux platform. As you know, the SQL Server on Linux is becoming mature and easy to use. Still, it does not support MMC consoles in Linux which makes the administration of the SQL Server a little bit complicated.
In this article, I will explain how we can move the system databases to different locations in Ubuntu Linux. SQL Server on Linux does not have SQL Server Configuration Manager, so we will use the mssql-config commands to perform administrative tasks. Please note that the operations which we are performing require elevated permissions. I am using root user. So let us begin.
Demo Setup and Default Location of System Databases
To explain the process properly, I have installed Ubuntu Linux on the virtual machine and installed SQL Server 2022 on it. I have installed it with default parameters. First, let us see the current Location of SQL Server system databases. To do that, we can execute queries on SQL Server management studio. You can also use dbForge Studio for SQL Server, a good GUI tool used to perform various administration tasks. You can view the file location by querying sys.master_files or sys.database_files.
Query:
USE master
GO
SELECT
DB_NAME(Database_id) [Database Name],
name AS [Logical Name],
mf.physical_name Location of file],
state_desc [File status],
size [File Size]
FROM sys.master_files mf WHERE database_id <4Output:

As you can see, the system database's default location is /var/opt/mssql/data/. We want to move the files to /SQLServer/SystemDatabase/ directory. First, we will create the directory and assign permissions to the user. Execute the commands in sequence.
Command to Create Directories
root@SQLLinux:/# mkdir /SQLServer/
root@SQLLinux:/# mkdir /SQLServer/SystemDatabaseCommand to Assign Permissions
root@SQLLinux:/# chmod ugo+rwx /SQLServer/SystemDatabase/Command to View the Permissions
root@SQLLinux:/# ls -l /SQLServer/Screenshot:
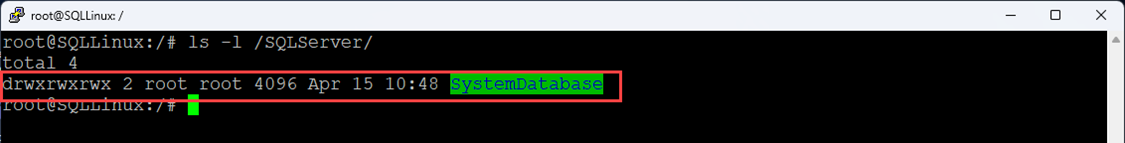
Note: I have assigned all read, write, and execute permission to all users and groups. Make sure that you apply only the required permissions to the user and group.
Now, the directory and permissions are configured. Let us move the master database.
Steps to Move the Master Database
We must follow the steps below to move master databases from '/var/opt/mssql/data/' location to '/SQLServer/SystemDatabase/' location. To change the Location, we will use the mssql-conf tool. The mssql-conf is used to configure the various parameters of the SQL Server instance. You can read this article to learn more about it.
Step 1: Change the datafile and logfile location using mssql-config.
Run the below commands to change the master databases' file locations.
root@SQLLinux:/# sudo /opt/mssql/bin/mssql-conf set filelocation.masterdatafile /SQLServer/SystemDatabase/master.mdf
root@SQLLinux:/# sudo /opt/mssql/bin/mssql-conf set filelocation.masterlogfile /SQLServer/SystemDatabase/mastlog.ldf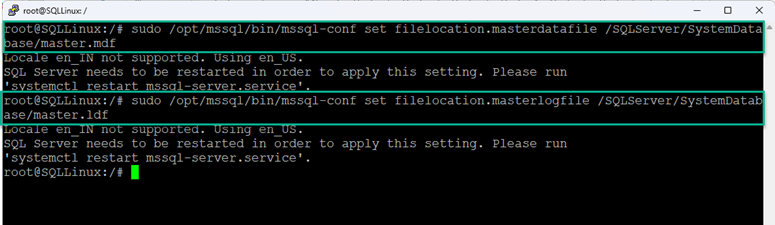
Step 2: Stop the SQL Service and move the database files.
Now, we will move the database files. To do that, first, we must stop SQL Services. To do that, run the following command.
root@SQLLinux:/# service mssql-server stopOnce services are stopped gracefully, run the move (mv) command to move the files.
root@SQLLinux:/# mv /var/opt/mssql/data/master.mdf /SQLServer/SystemDatabase/
root@SQLLinux:/# mv /var/opt/mssql/data/mastlog.ldf /SQLServer/SystemDatabase/Step 3: Start SQL Services and verify the Location.
Once files are moved, start the services.
root@SQLLinux:/# service mssql-server startMake sure SQL Services are running without errors.
root@SQLLinux:/# service mssql-server status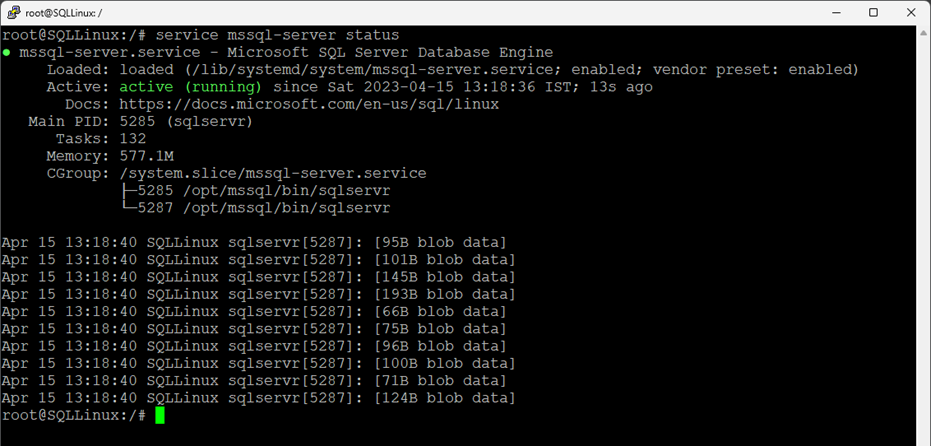
As you can see, the services are working fine. Connect to the database server using SSMS and execute the query below to verify the new Location of the master database.
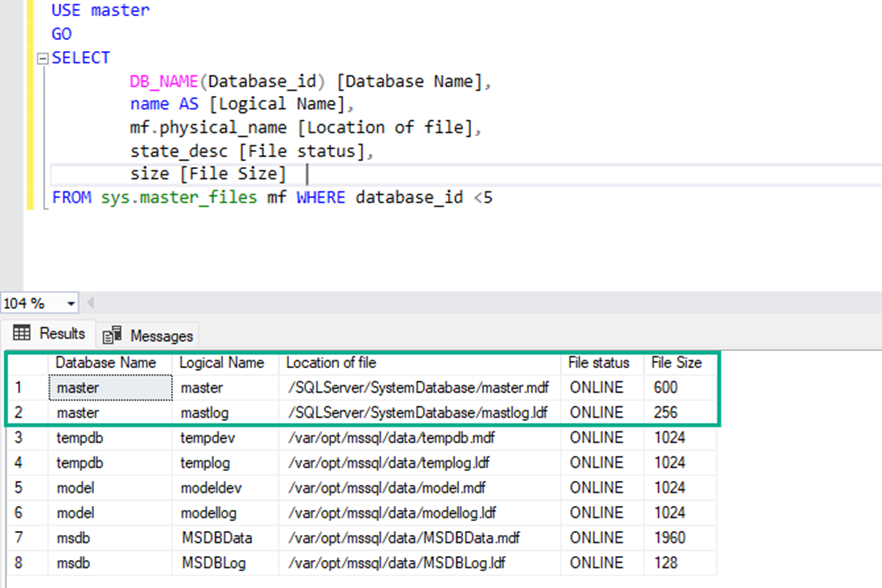
As you can see, the master database has been moved to '/SQLServer/SystemDatabase/ location. Now, let us see how we can move the other system databases.
Steps to Move Msdb, Model, and TempDB Database
The process of moving other system databases is relatively simple. In this example, we want to move the database files to /SQLServer/SystemDatabase/ location. The steps are below:
Step 1: Change the Location in the meta-data of the SQL Server instance.
First, we will make changes in meta-data so that when SQL Services starts, it points to the new Location. We can use ALTER DATABASE MODIFY FILE command.
ALTER DATABASE model MODIFY FILE (NAME=modeldev, FILENAME='/SQLServer/SystemDatabase/model.mdf')
ALTER DATABASE model MODIFY FILE (NAME=modellog, FILENAME='/SQLServer/SystemDatabase/modellog.ldf')
ALTER DATABASE msdb MODIFY FILE (NAME=MSDBData, FILENAME='/SQLServer/SystemDatabase/MSDBData.mdf')
ALTER DATABASE msdb MODIFY FILE (NAME=MSDBLog, FILENAME='/SQLServer/SystemDatabase/MSDBLog.ldf')
ALTER DATABASE tempdb MODIFY FILE (NAME=tempdev, FILENAME='/SQLServer/SystemDatabase/tempdb.mdf')
ALTER DATABASE tempdb MODIFY FILE (NAME=templog, FILENAME='/SQLServer/SystemDatabase/templog.ldf')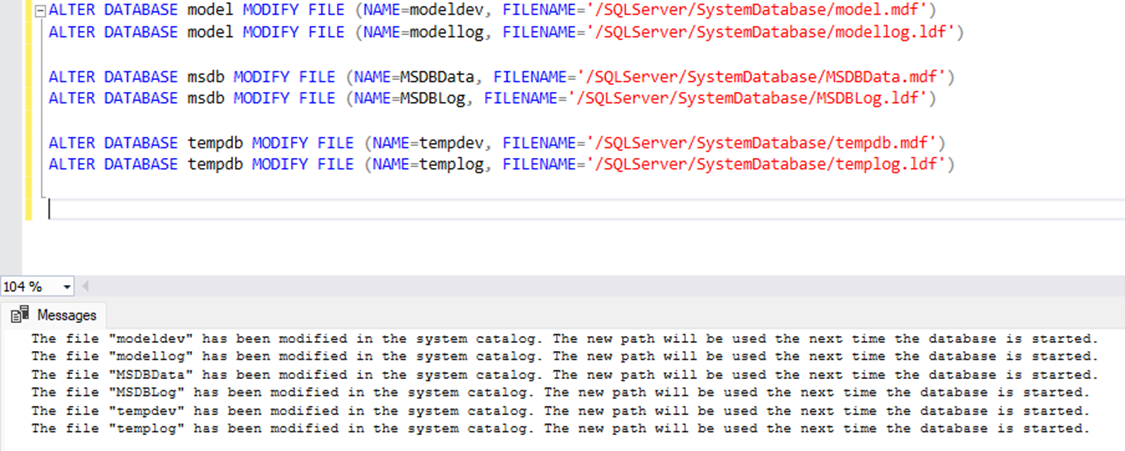
Once meta-data is updated, move forward to step 2.
Step 2: Stop the SQL Services and physically move the files.
Stop the SQL Server services.
root@SQLLinux:/# service mssql-server stopMove the database files.
root@SQLLinux:/# mv /var/opt/mssql/data/model.mdf /SQLServer/SystemDatabase/
root@SQLLinux:/# mv /var/opt/mssql/data/modellog.ldf /SQLServer/SystemDatabase/
root@SQLLinux:/# mv /var/opt/mssql/data/msdbdata.mdf /SQLServer/SystemDatabase/
root@SQLLinux:/# mv /var/opt/mssql/data/msdblog.ldf /SQLServer/SystemDatabase/
root@SQLLinux:/# mv /var/opt/mssql/data/tempdb.mdf /SQLServer/SystemDatabase/
root@SQLLinux:/# mv /var/opt/mssql/data/templog.ldf /SQLServer/SystemDatabase/Once the files are moved to a new location, proceed to step 3.
Step 3: Start the services and verify the changes.
root@SQLLinux:/# service mssql-server startMake sure SQL Services are running without errors.
root@SQLLinux:/# service mssql-server status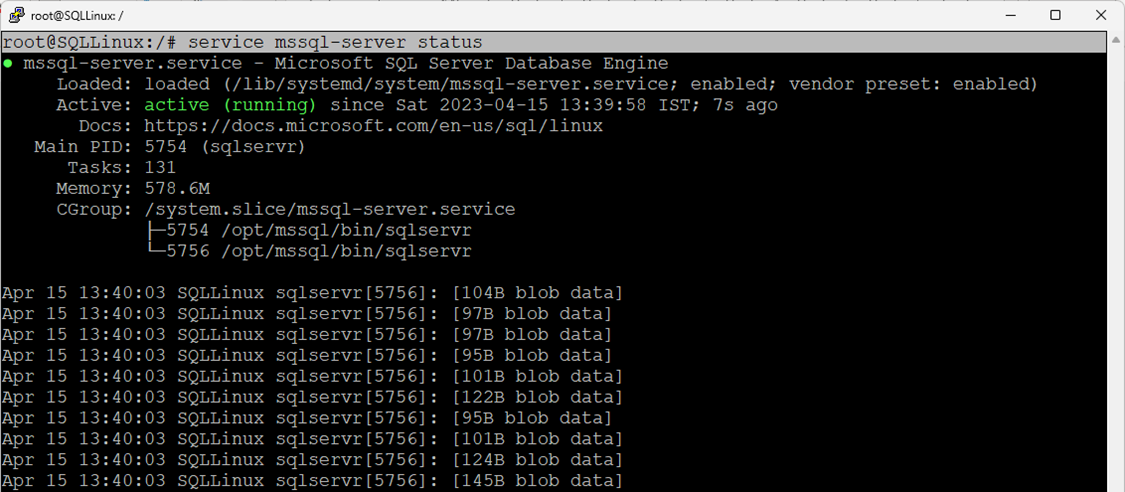
As you can see, the SQL Server is running without error. Execute the below T-SQL query to verify the Location of system database files.
USE master
GO
SELECT
DB_NAME(Database_id) [Database Name],
name AS [Logical Name],
mf.physical_name Location of file],
state_desc [File status],
size [File Size]
FROM sys.master_files mf WHERE database_id <5
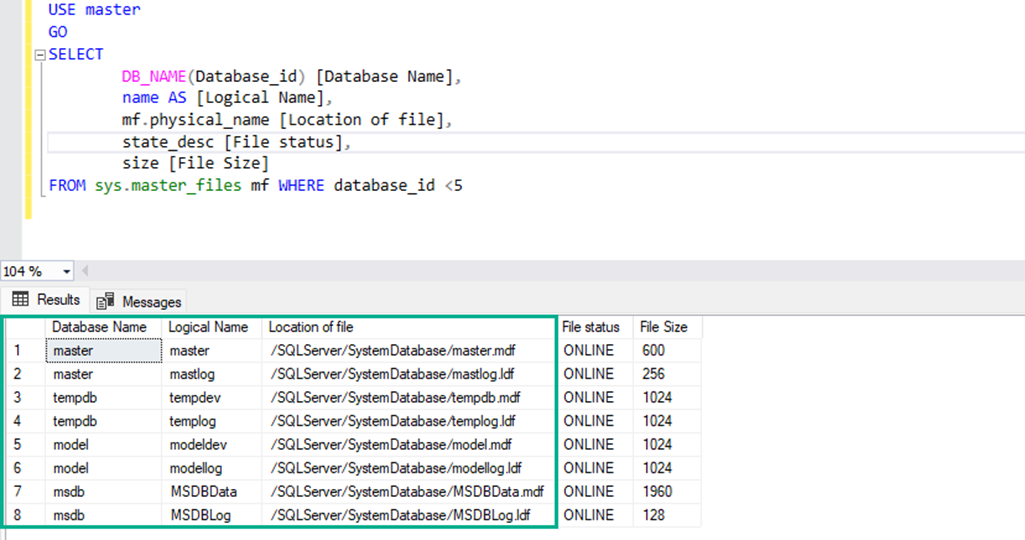
As you can see, the database files have been moved successfully.
Summary
This article taught us to move the database files of SQL Server master databases to a different directory. I have separately explained the process of moving the master database. If you are working on a Live environment, you should perform all steps in one go so you do not have to restart the SQL Services multiple times.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments