Send Email Using Spring Boot (SMTP Integration)
This article explores Spring Boot integration with SMTP and how to send emails from your very own Spring Boot application.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis article explores how to send emails from your very own Spring Boot application.
Yes, you can have a dedicated REST API, which accepts the email sender's and receiver's email addresses, the subject, and the body — the classic attributes that make up a business email. This API can then be invoked at will from your front-end team by passing in the necessary parameters, and Voila! Your email is sent in a breeze.
Spring Boot provides a built-in dependency, which has all the required methods. This can be used to send the email to a valid email address. It's completely free of cost and very easy to integrate with in a classic Spring Boot application.
In this article, we'll look at how to send emails from a simple Spring Boot application.
Spring uses SimpleMailMessage and does it by integrating with spring-boot-starter-mail.
So, let's get started.
Step 1
Head over to start.spring.io and create a new Spring Boot project with just the below dependencies
- Spring web
- Java Mail sender
Click "generate project." This will create a zip file, extract it and open it in IntelliJ.
At this point, you have a base Spring Boot project. Just start the application by hitting the play button to ensure everything is up and running.

We are good to go for integration with JMS!
Step 2: Configuring Our Email Server
Next, we need to provide the configuration for Spring Mail. Simply add the below properties for your email configuration to the application.properties file:
# email configs
spring.mail.host=smtp.gmail.com
spring.mail.username=<your email id>
spring.mail.password=<your password>
spring.mail.properties.mail.smtp.auth=true
spring.mail.properties.mail.smtp.starttls.enable=trueStep 3
With all the required config in place, we are ready to expose our rest endpoint/mail, which will be accepting incoming requests to send emails to a particular email address.
Let's add the below code for the controller layer to be able to hit our API, which will trigger the email.
@RestController
public class EmailController {
@Autowired
private EmailService emailService;
@PostMapping("/mail")
public void sendEMail(@RequestBody EmailRequest emailRequest) {
System.out.println("Going to Send email: " + emailRequest.toString());
emailService.sendEmail(emailRequest);
}
}
As we can see, the controller is expecting the request object named EmailRequest.
So, make a request body for the email request, which consists of the below attributes to identify the email:
public class EmailRequest {
// Class data members
private String recipient;
private String msgBody;
private String subject;
private String attachment;
//generate getters
}Service Layer
Let's talk about the implementation class. It will contain an object of the JavaMailSender which has a method called send() which has the below signature:
void send(SimpleMailMessage simpleMessage) throws MailException;
The SimpleMailMessage class is from the package "org.springframework.mail".
It has attributes like from, to, text, and subject. We set all these vital attributes from our incoming request. as below and will ultimately use the 'javaMailSender' to fire the send method.
@Service
public class EmailServiceImpl implements EmailService {
@Autowired
private JavaMailSender javaMailSender;
@Override
public void sendEmail(EmailRequest emailRequest) {
SimpleMailMessage mailMessage = new SimpleMailMessage();
mailMessage.setFrom("abc@xyz");
mailMessage.setTo(emailRequest.getRecipient());
mailMessage.setText(emailRequest.getMsgBody());
mailMessage.setSubject(emailRequest.getSubject());
javaMailSender.send(mailMessage);
}
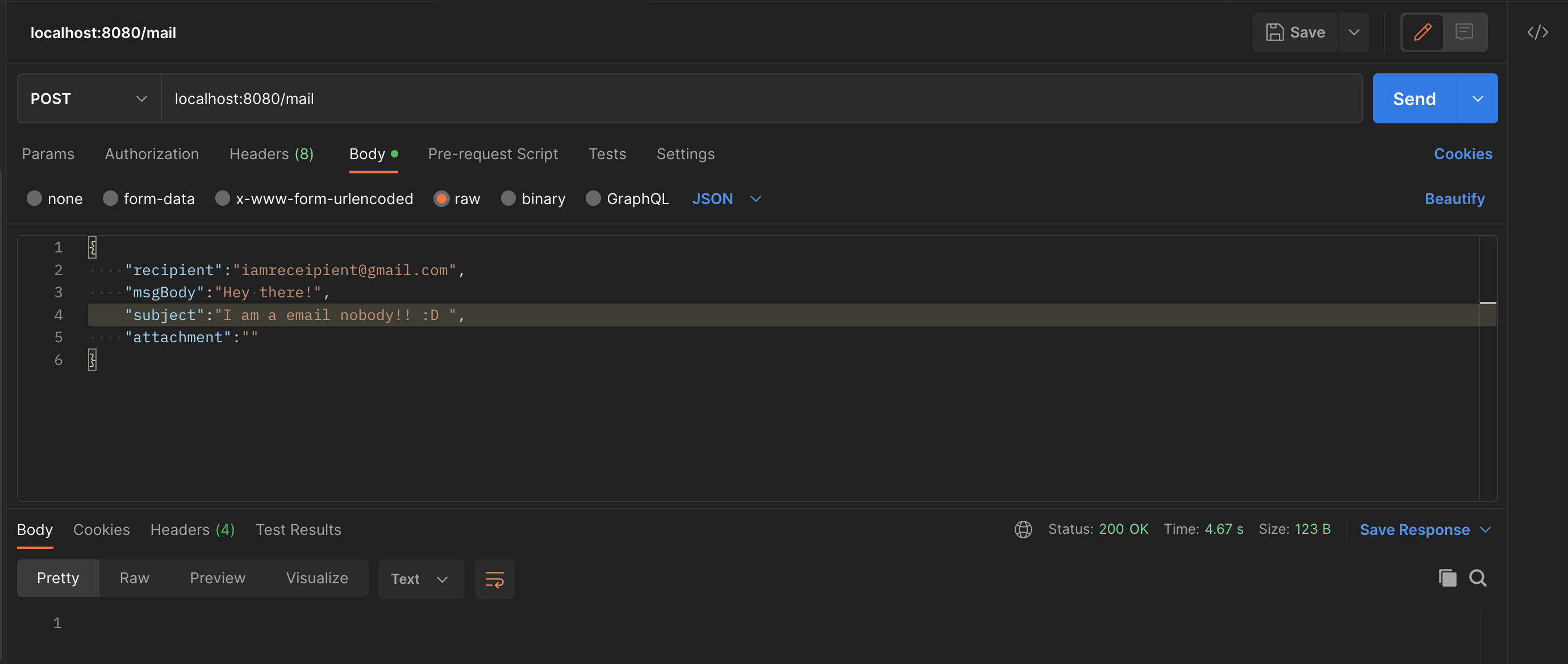
}With this, we are done! Start the application and head over to Postman. We are using the default port for spring (which is 8080) hence call the API at localhost:8080/mail
Call the API from Postman as below:
Conclusion
In this article, we learned a simple way to send emails from our spring boot application. It uses JMS JavaMailSender for sending emails using a simple REST API.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments