How to Upload, Cache, Save and Share Images in an Android App
Encouraging app users to share images increases user engagement. Learn to upload, cache, save, and share images in an Android app.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Freewhat if i ask you to guess the icon image for whatsapp or instagram? even before your mind processes my question, decides on an image and responds, your mouth would have already answered me. images play that important role in making an app, or to specify, an android app. here, for example, i will upload an image from an android sd card using the app42 upload service . thereafter, i will perform caching, sharing, and saving operations on the image.
- upload an image on the server from android sd card.
- make a more swift app for image caching.
- increase user engagement by pushing users to share these images.
- save these images to an sd card.
image uploading
first, upload an image from an android sd card to the server so as to get a web url to perform operations on the image, like sharing. here, we are using app42′s service to upload an image to the server.
image caching
when you build a mobile or a web application, you have to make sure it runs as fast as possible. for this, the most important function is caching. if you are using a certain resource in your application, you should know that it isn’t easy to retrieve. i used the lrucache algorithm to implement this mechanism.
lrucache
lru
stands for least recently used. the term itself clarifies the way cache works. lrucaches have a fixed cache size and work like a queue. if a new object is added to the cache, it is placed at the beginning of the queue. later, when the app asks to get an object from the cache, it is placed at the start of a queue. this way the lru objects are left at the initial point of the queue
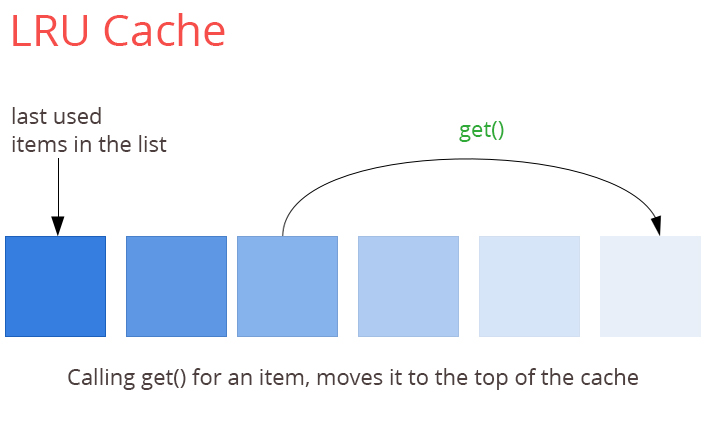
image sampling
while loading an image from the web, its resolution can be larger than the device. sampling can provide a better way of loading and optimizing memory.
image sharing
using images in the app from the gallery and sharing it within your contacts will increase user engagement in android.
image saving
after loading an image from the web, if you need to save it, you can do so on an sd card for further usage.
sample application
- register with the app42 platform .
- create an app once you are on the quick-start page after the registration
- if you are already registered, login to apphq console and create an app from app manager -> app create link
- download the project from here and import it into eclipse.
-
open mainactivity.java file and pass the required information in
oncreatemethod as shown below (application keys for apphq console).
app42api.initialize(this,"app42 api key","app42 secret key");change the application name with your application name in res/strings (useful to save image in sd card), then build and run the application
design details
get an image for your app from an android sd card with the code written in the mainactivity.java file.
/*
* call when user clicks on browse photo
*/
private void browsephoto(string imagename) {
if (this.imagename != null && !this.imagename.equals(""))
this.imagename = imagename;
intent i = new intent(intent.action_pick,
android.provider.mediastore.images.media.extern
al_content_uri);
startactivityforresult(i, result_load_image);
}
/*
* callback when user select image from gallery for upload
* get a callback
* @see android.app.activity#onactivityresult(int, int,
* android.content.intent)
*/
@override
protected void onactivityresult(int requestcode, int resultcode, intent data) {
super.onactivityresult(requestcode, resultcode, data);
if (requestcode == result_load_image && resultcode == result_ok
&& null != data) {
uri selectedimage = data.getdata();
string[] filepathcolumn = { mediastore.images.media.data };
cursor cursor = getcontentresolver().query(selectedimage,
filepathcolumn, null, null, null);
cursor.movetofirst();
int columnindex = cursor.getcolumnindex(filepathcolumn[0]);
string picturepath = cursor.getstring(columnindex);
cursor.close();
progressdialog.setmessage("uploading image");
progressdialog.show();
uploadimage(picturepath);
}
}if you want to upload an image on the server from android sd card gallery, you can follow the code written in the mainactivity.java file.
private void uploadimage(string imagepath) {
app42api.builduploadservice().uploadfile(imagename, imagepath,
uploadfiletype.image, description, new app42callback() {
public void onsuccess(object uploadobj) {
// todo auto-generated method stub
onuploadresult(uploadobj);
}
public void onexception(exception ex) {
// todo auto-generated method stub
system.out.println(ex);
onuploaderror(ex);
}
});
}if you want to share an image with your friends using several apps installed on your device, you can follow the code written in the mainactivity.java file.
intent intent = new intent(intent.action_send);
intent.settype("text/plain");
intent.putextra(intent.extra_text, "hey friends checkout this image"+"\n\n"+imageurl);
intent.putextra(android.content.intent.extra_subject,
"check my image ");
startactivity(intent.createchooser(intent, "share"));imagecacher.java file contains all types of code which is required to share an image from the web or cache accordingly.
if you want to load an image without sampling that you should use in our android activity class file, here is the code:
imageview imglogo = (imageview) findviewbyid(r.id.my_image);
imagecacher imagecacher=new imagecacher(this, -1);
imagecacher.loadimage(imageurl, imglogo);if you want to load an image with sampling that can be used in your android activity class, please follow the code below:
imageview imglogo = (imageview) findviewbyid(r.id.my_image);
imagecacher imagecacher=new imagecacher(this, samplingimagesize);
imagecacher.loadimage(imageurl, imglogo);if you want to load an image from the web or cache, you should follow the code below:
public bitmap getbitmap(string url) {
string filename = string.valueof(url.hashcode());
file f = new file(cachedir, filename);
// from sd cache
bitmap b;
if (issamplingreq) {
b = decodewithoutsampling(f);
} else {
b = decodewithsampleing(f);
}
if (b != null)
return b;
// from web
try {
bitmap bitmap = null;
inputstream is = new url(url).openstream();
outputstream os = new fileoutputstream(f);
utility.copystream(is, os);
os.close();
if (issamplingreq) {
bitmap = decodewithoutsampling(f);
} else {
bitmap = decodewithsampleing(f);
}
return bitmap;
} catch (throwable ex) {
ex.printstacktrace();
if (ex instanceof outofmemoryerror)
clearcache();
return null;
}
}code for image sampling:
private bitmap decodewithsampleing(file f) {
try {
// decode image size
bitmapfactory.options o = new bitmapfactory.options();
o.injustdecodebounds = true;
bitmapfactory.decodestream(new fileinputstream(f), null, o);
int width_tmp = o.outwidth, height_tmp = o.outheight;
int scale = 1;
while (true) {
if (width_tmp / 2 < requiredsize
|| height_tmp / 2 < requiredsize)
break;
width_tmp /= 2;
height_tmp /= 2;
scale *= 2;
}
bitmapfactory.options o2 = new bitmapfactory.options();
o2.insamplesize = scale;
return bitmapfactory.decodestream(new fileinputstream(f), null, o2);
} catch (filenotfoundexception e) {
}
return null;
}code without sampling:
private bitmap decodewithoutsampling(file f) {
try {
return bitmapfactory.decodestream(new fileinputstream(f));
} catch (exception e) {
}
return null;
}
save image in sd card gallery:
if you want to save an image in android sd card gallery,
you can follow the code written in mainactivity.java file.
void savemyimage() {
bitmap bmimg = imagecacher.getbitmap(imageurl);
file filename;
try {
string path1 = android.os.environment.getexternalstoragedirectory()
.tostring();
log.i("in save()", "after mkdir");
file file = new file(path1 + "/" + appname);
if (!file.exists())
file.mkdirs();
filename = new file(file.getabsolutepath() + "/" + imagename
+ ".jpg");
log.i("in save()", "after file");
fileoutputstream out = new fileoutputstream(filename);
log.i("in save()", "after outputstream");
bmimg.compress(bitmap.compressformat.jpeg, 90, out);
out.flush();
out.close();
log.i("in save()", "after outputstream closed");
//file parent = filename.getparentfile();
contentvalues image = getimagecontent(filename);
uri result = getcontentresolver().insert(
mediastore.images.media.external_content_uri, image);
toast.maketext(getapplicationcontext(),
"file is saved in " + filename, toast.length_short).show();
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
public contentvalues getimagecontent(file parent) {
contentvalues image = new contentvalues();
image.put(images.media.title, appname);
image.put(images.media.display_name, imagename);
image.put(images.media.description, "app image");
image.put(images.media.date_added, system.currenttimemillis());
image.put(images.media.mime_type, "image/jpg");
image.put(images.media.orientation, 0);
image.put(images.imagecolumns.bucket_id, parent.tostring()
.tolowercase().hashcode());
image.put(images.imagecolumns.bucket_display_name, parent.getname()
.tolowercase());
image.put(images.media.size, parent.length());
image.put(images.media.data, parent.getabsolutepath());
return image;
}in this blog, i have explained uploading, caching, saving, and sharing of images in an android application.
Published at DZone with permission of Vishnu Garg. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments