Integrating Node.js Build Tools With Maven
In this detailed tutorial, learn how to integrate Node.JS build automation tools in an Angular app using a Maven plugin.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeSingle Page Applications (SPAs) have been the biggest web development trend for a while now. Developers from all around the world have started creating new applications based on this technique, and started migrating existing ones too. For many years, Java developers relied on technologies specific to the Java world, such as JavaServer Faces. But, as JavaScript frameworks started to gain more power, become more popular and well supported, Java developers started migrating their front-end code to these frameworks. Today we will see how we integrate Node.js build tools, used to process JavaScript source code, into Maven's lifecycle.
Node.js Build Tools
Being one of the most vibrant communities of all time, it is no surprise that many build tools were developed to automate tasks like concatenation of source files, minification of JavaScript code, and so on. Luckily, all the popular tools were developed around a single technology, Node.js, which made it easier to integrate with other technologies, such as Maven.
In this article, we will use a Maven plugin, called Frontend Maven Plugin, to integrate Gulp tasks into Maven's generate-resources phase. If instead of Gulp you are using some other tool, like Webpack or Grunt, fear not, the approach shown throughout the article is the same for those.
Cloning a Maven Application
To give us some leverage, let's clone a simple RESTful application based on Spring Boot. This application has a trivial API that handles HTTP requests to add new tasks, delete existing ones, and retrieve all tasks. Upon this API we will build a very small AngularJS application. If you are not familiar with AngularJS or Spring Boot but would like to learn how to integrate Node.js tools with Maven, don't worry. As both the backend API and the front-end application that we will build are deadly simple, you will still be able to keep up with this article.
To start, let's issue the following commands.
git clone https://github.com/auth0-blog/nodejs-maven.git
cd nodejs-maven
mvn clean package
java -jar target/nodejs-maven-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
These commands will download the RESTful application in our computer, build it with Maven, and then run the app. If everything goes well, we will be able to issue HTTP requests to it, like so:
# saves a new task called 'First task'
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST -d \
'{ "title":"First task",
"description":"This is my first task."
}' http://localhost:8080/api/task
# retrieves all tasks
curl http://localhost:8080/api/tasks
# delete task with id = 1
curl -X DELETE http://localhost:8080/api/task/1
Creating the AngularJS Application
Now that we have our application cloned and working, we can create an interface for it. As mentioned before, we will create an AngularJS application that will allow users to interact with the existing API. To start, let's add an index.html file that will be shown for our web users. Let's create this file in the src/main/resources/static/ directory with the following code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Integrating Node.js build tools with Maven</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css"/>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container" ng-app="app">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-xs-12" ng-controller="mainController as mainCtrl">
<h1>Integrating Node.js build tools with Maven</h1>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-xs-4">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="title">Title</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control"
ng-model="mainCtrl.task.title"
id="title" placeholder="Task title">
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-xs-4">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="description">Description</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control"
ng-model="mainCtrl.task.description"
id="description" placeholder="Task description">
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-xs-4">
<div class="form-group">
<button class="btn btn-default" ng-click="mainCtrl.addTask()" style="margin-top: 25px;">
Add task
</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<table class="table" style="margin-top: 10px;">
<tr>
<th>Title</th>
<th>Description</th>
<th>Options</th>
</tr>
<tr ng-repeat="task in mainCtrl.tasks">
<td>{{task.title}}</td>
<td>{{task.description}}</td>
<td>
<button class="btn btn-danger" ng-click="mainCtrl.removeTask(task)">
<span class="glyphicon glyphicon-remove-circle"></span>
</button>
</td>
</tr>
<tr ng-if="mainCtrl.tasks.length == 0">
<td colspan="4">No tasks available.</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/angular.js/1.6.1/angular.js"></script>
<script src="/js/app.js"></script>
</body>
</html>As you can see above, the application uses Bootstrap to give us a nice interface and has only two JavaScript dependencies: angular.js and /js/app.js . The first one is AngularJS source code, which enables us to use the framework in our app, and the second one is the application that we will build.
Our AngularJS application will contain two files. The first one, which will be responsible for defining a new AngularJS module, will be called app-definition.js and will be created in a new directory called web under the src/main/ directory. This file will have the following code:
(function(angular) {
var app = angular.module('app', []);
}(angular));
Usually, this file would be used to define dependencies and to configure these dependencies behaviors, but as our application won't have any dependency, this file will be used only to define the new AngularJS module called app .
The second file that our front-end application will have is the mainController controller used in the index.html file above. Let's call this new file as app-controller.js , add it to the src/main/web/ directory, and insert the following code in it:
(function(angular) {
var app = angular.module('app');
var mainController = function ($http) {
var ctrl = this;
ctrl.tasks = [];
ctrl.task = {};
loadTasks();
ctrl.addTask = function() {
$http.post('/api/task', ctrl.task).then(function() {
alert('Task added');
ctrl.task = {};
loadTasks();
}, function(error) {
alert(error);
});
};
ctrl.removeTask = function(task) {
$http.delete('/api/task/' + task.id).then(function() {
alert('Task removed');
loadTasks();
}, function(error) {
alert(error);
});
};
function loadTasks() {
$http.get('/api/tasks').then(function(response) {
ctrl.tasks = response.data;
}, function(error) {
alert(error);
});
}
};
mainController.$inject = ['$http'];
app.controller('mainController', mainController);
}(angular));
As you can see, this controller has three functions. One to add new tasks, one to remove a task passed as parameter, and one to load all tasks from the RESTful application. These files are everything that our AngularJS SPA needs to interact with our RESTful API. Now we just need to assemble these files in a single one, called app.js , and add it to src/main/resources/static/js/ to make it available to our index.html web page.
Assembling AngularJS With Gulp
To process the AngularJS source files created above we will use Gulp.js and a few plugins available on it. But first, let's define our application as a Node.js app. To do that, let's issue the following command in the root directory of our application:
npm init -y
This will add a file called package.json which will hold details, such as dependencies, about our app. After that, we can install Gulp and its plugins:
npm install --save-dev gulp gulp-concat gulp-if gulp-sourcemaps gulp-uglify gulp-util
And then define a new file called gulpfile.js in the root directory, with the following code:
var gulp = require('gulp');
var gulpif = require('gulp-if');
var concat = require('gulp-concat');
var sourcemaps = require('gulp-sourcemaps');
var uglify = require('gulp-uglify');
var util = require('gulp-util');
gulp.task('clean', function () {
return gulp.src([
'./src/main/resources/static/js/**/*.js'
], {read: false})
.pipe(clean());
});
gulp.task('default', function () {
var uglifyFlag = util.env.envName === 'production';
return gulp.src([
'./src/main/web/app-definition.js',
'./src/main/web/**/!(app-definition)*.js'
])
.pipe(sourcemaps.init())
.pipe(concat('app.js'))
.pipe(gulpif(uglifyFlag, uglify({mangle: true})))
.pipe(gulpif(uglifyFlag, sourcemaps.write()))
.pipe(gulp.dest('./src/main/resources/static/js/'));
});
This file contains two tasks. The first one is responsible for cleaning our project, by removing all js files from the src/main/resources/static/js/ directory. The second one is responsible for processing the AngularJS source files created before, assembling it as a single one called app.js and adding it to the src/main/resources/static/js/ directory. This task also checks if it is running on production to decide if it should uglify the JavaScript source code or not.
Uglifying JavaScript code is a good technique, but can make debugging harder. Therefore, we use this plugin only when releasing our code to production. We will see in a bit where the envName paramaters, that triggers or blocks the uglify process, comes from.
With this file in place, we are now able to generate the app.js that our web page depends on, and we can access our web application to see if it is really working. Let's issue the following commands to accomplish that:
# executes the default task in the gulpfile.js file
gulp
# packages the whole app together
mvn clean package
# runs the app
java -jar target/nodejs-maven-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
If we open a web browser now and access [http://localhost:8080], we will see a screen like this:
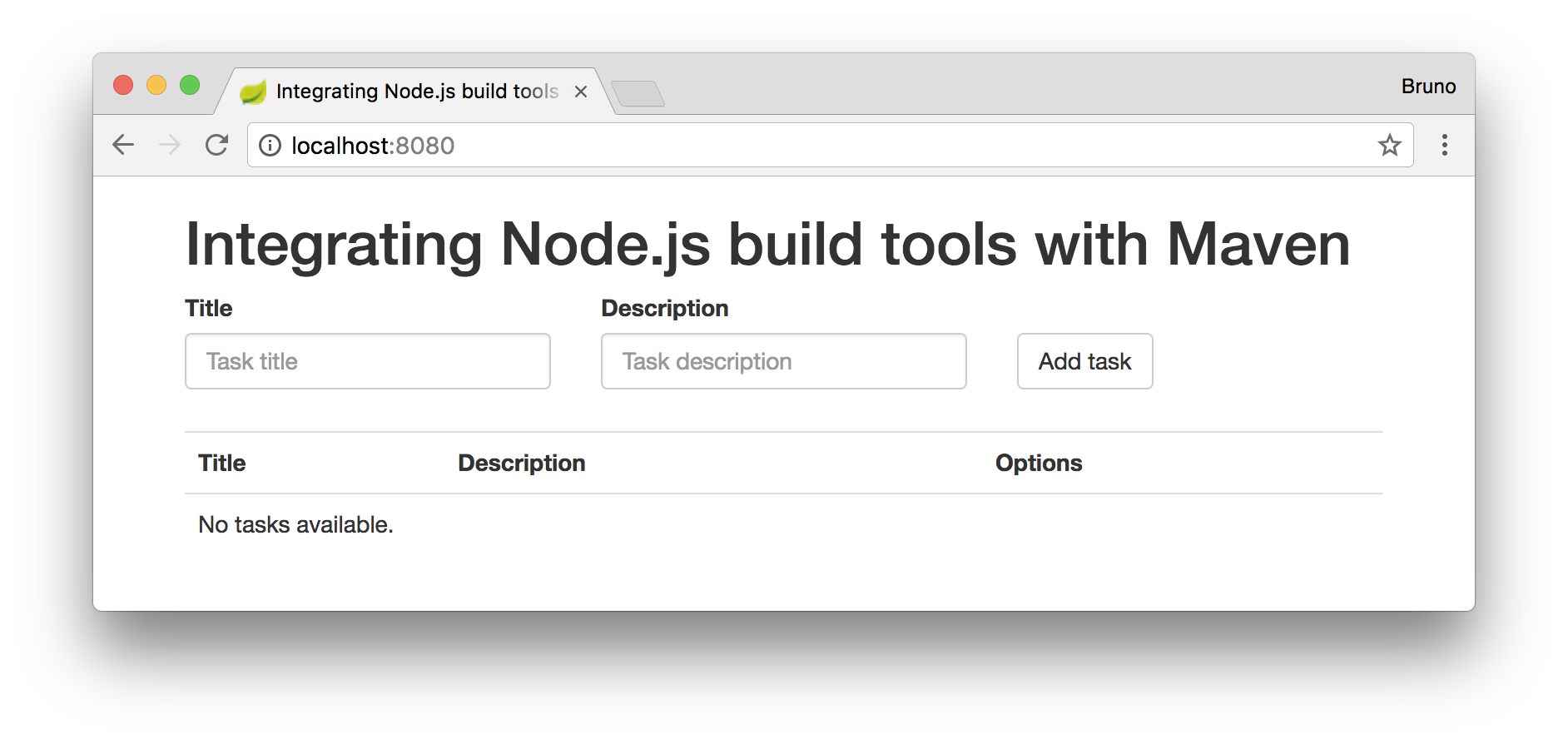
Cool- our AngularJS application is up, running, and working as expected. But wait! This is not the process that we want. We don't want to remember yet another command to generate the static resources that compose our front-end application. We want to integrate this in our current release process. That is, we want to integrate this process with Maven.
Integrating Gulp With Maven
To integrate Gulp and its tasks into Maven's lifecycle, we just need to add the Maven plugin previously mentioned, Frontend Maven Plugin, and configure a few steps on it. To do that, let's open the pom.xml file and add the following element in the build/plugins element:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project>
<!-- ... everything else -->
<build>
<plugins>
<!-- ... other plugins -->
<plugin>
<groupId>com.github.eirslett</groupId>
<artifactId>frontend-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>install node and npm</id>
<goals>
<goal>install-node-and-npm</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<nodeVersion>v7.10.0</nodeVersion>
</configuration>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>npm install</id>
<goals>
<goal>npm</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<arguments>install</arguments>
</configuration>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>gulp</id>
<goals>
<goal>gulp</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<arguments>default --envName ${environment.name}</arguments>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
In this plugin, we have defined three execution goals. The first one, called install node and npm , is responsible for installing Node.js and NPM in the current directory to use them in the next steps. The second one, called npm install , will install all our Node.js dependencies (Gulp and its plugins). The last one will execute the gulp command as we did manually before. The difference in this case is that it will explicitly define default as the task to be executed and it will add the envName environment variable with a value that we still need to define. This is how Gulp will decide if it should uglify the AngularJS source code or not.
The environment.name , passed as an argument to Gulp, will be tied to Maven profiles that we will add to our application. These profiles will be defined by adding the following elements to the pom.xml file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project>
<!-- ... everything else -->
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>development</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>
<properties>
<environment.name>development</environment.name>
</properties>
</profile>
<profile>
<id>production</id>
<properties>
<environment.name>production</environment.name>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
</project>
With these elements, we can choose what kind of release we are going to do. If we want to package our app to production, which will uglify our AngularJS source code, we will need to execute the following command:
mvn clean package -P production
And then if we run:
java -jar target/nodejs-maven-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
We will be able to see that our AngularJS code is indeed uglified by opening http://localhost:8080/js/app.js in a web browser.
If we run Maven without the profile definition, -P production , Maven will use the development profile (which is marked with activeByDefault ) and build our application without uglifying our AngularJS code.
Aside: Securing Spring Boot Applications With Auth0
One of the most complex features to implement in an application is user authentication and identity management. Security for authentication and identity is an entire glossary unto itself.
If you need to implement a robust, highly customizable identity and access management system quickly and easily for your Spring Boot application, Auth0 can help. Take a look at Securing Spring Boot with JWTs to properly secure your application.
Developing SPAs is indeed a good practice, as it gives a smooth interface for our users with seamless navigation and great user experience. Besides that, the frameworks available have big communities and a lot of resources available that make web developers very productive. Therefore, integrating JavaScript with Java applications is a good idea and, as we saw today, easy as well. If we are using Maven on our project, we just need to register a single plugin to the build process and configure a few steps to automate the whole process.
Published at DZone with permission of Bruno Krebs, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments