Importance Of Anypoint Dedicated Load Balancer in MuleSoft Ecosystem
Dedicated Load Balancer is an optional component in Anypoint Platform which allows the route of external HTTP/HTTPs traffic.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIntroduction
Dedicated Load Balancer is an optional component in Anypoint Platform which allows the route of external HTTP/HTTPs traffic to multiple applications deployed to Cloudhub within VPC.
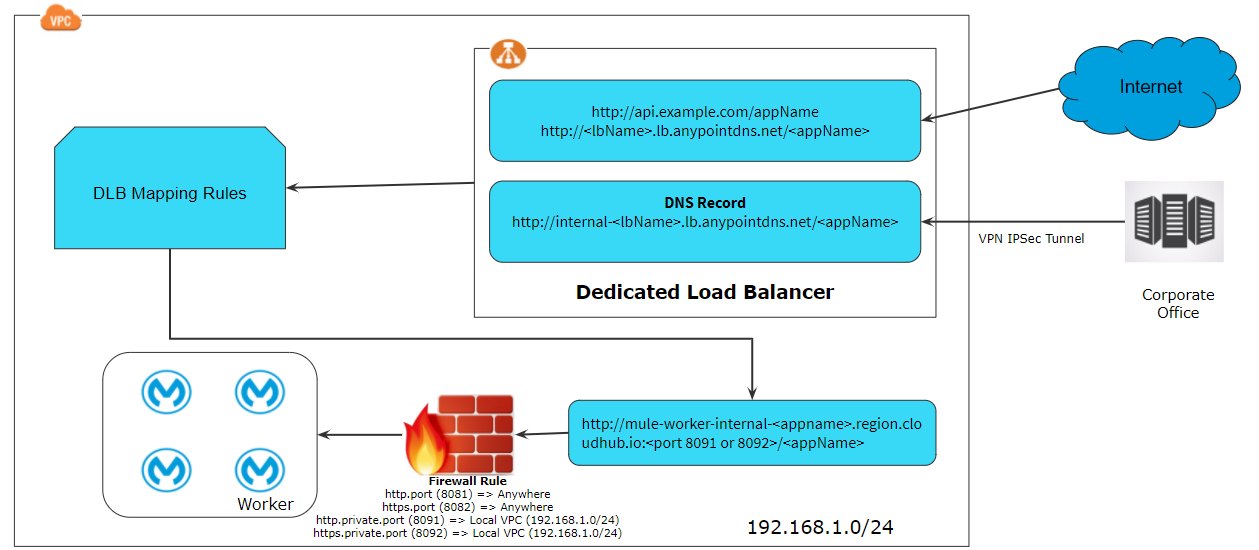
Each Dedicated Load Balancer has a DNS A record lb-name.lb.anypointdns.net that resolves to the two public IP addresses of the two instances.
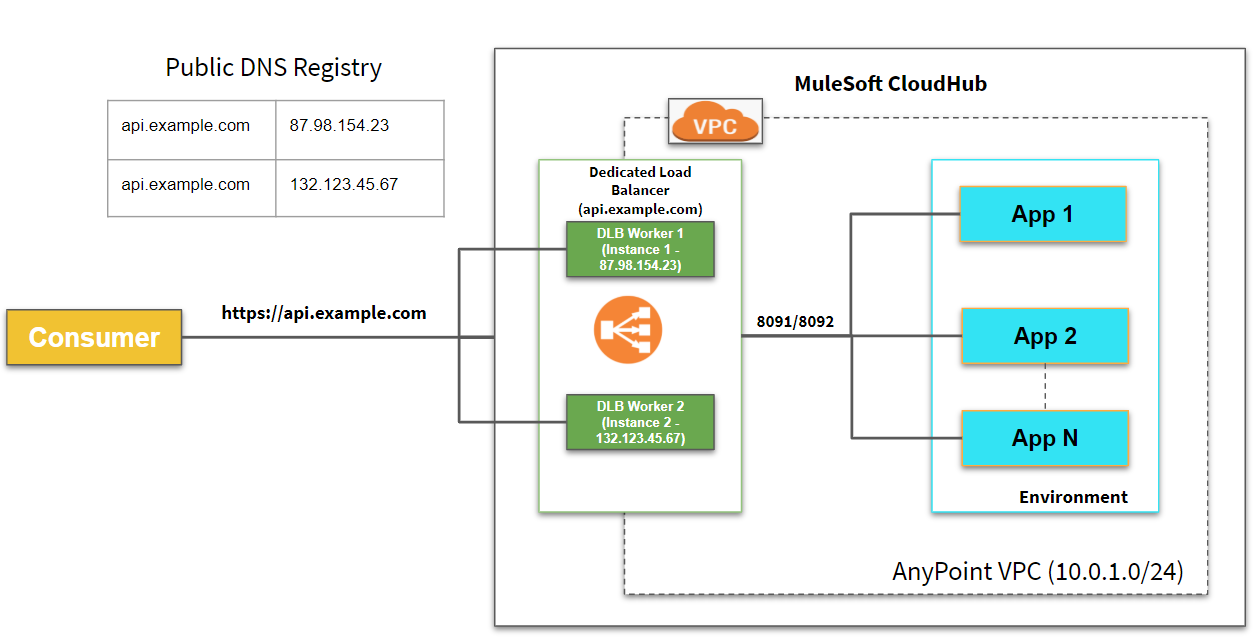
To create a dedicated load balancer, you must first create the Anypoint VPC which can be mapped to the multiple environments and the same dedicated load balancer can be used for different environments. You can use multiple DNS for the same dedicated load balancer (i.e. api-dev.example.com and api-test.example.com)
Why Dedicated Load Balancer in MuleSoft Ecosystem?
- One of the limitations of SLB is the lower rate limit. To avoid that issue, you can use a dedicated load balancer.
- All applications can be hosted under a single domain.
- Custom SSL certificates can be configured on DLB.
- Handle load balancing among the different Cloudhub workers that run your application.
- To access apis publicly or whitelisted client deployed within VPC.
- To support Mutual Authentication (Two Way SSL).
Prerequisites
- At least one VPC configured to create DLB.
- SSL Certificates in .pem format.
Whitelisted CIDRs
To allow dedicated load balancers must be used by a set of IP addresses or single IP addresses, you need to add those IP addresses in the form of CIDR notations (e.g. 192.168.1.0/24).
By default, all the public traffic allowed on DLB as default CIDR allowed is 0.0.0.0/0. In case if you want to allow public traffic from few clients, you can delete default CIDR and allow only CIDR from which DLB has to accept the traffic.
HTTP Inbound Mode
- Off: Causes the load balancer to silently drop the request.
- On: Accepts the inbound request on the default SSL endpoint using the HTTP protocol.
- Redirect: Redirects the request to the same URL using the HTTPS protocol.
Other Configurations
- Disable Static IPs specifies to use dynamic IPs, which do not persist when the DLB restarts.
- Keep URL encoding specifies the DLB passes only the %20 and %23 characters as is.
If you deselect this option, the DLB decodes the encoded part of the request URI before passing it to the CloudHub worker.
Support TLS 1.0 specifies to support TLS 1.0 between the client and the DLB. - Upstream TLS 1.2 specifies to force TLS 1.2 between the DLB and the upstream Cloudhub worker.
Dedicated Load Balancer Certificates
Configure SSL certificate to enable HTTPS (Public Key and Private Key). For two way authentication, you can configure Client Certificate and that is optional. The dedicated load balancer must be associated with at least a pair of one certificate.
Generally, we configure the certificates on Dedicated Load Balancer from CA authority. For testing purposes, you can use self-signed certificates.
Note: - Always use CA signed certificates instead of self signed certificates. It is not recommended to use self signed certificates as it is not secure and even not recognized by browsers and few or more clients.
Generating Self Signed Certificates
openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout test-private.pem -x509 -days 3000 -out test-public-crt.pem
The above command will generate Private Key and Public Key that can be configured on a dedicated load balancer.
Generating Self Signed Certificates Using .cfg File
You can generate certificates by adding below content in .cfg file and pass to OpenSSL command.
xxxxxxxxxx
[ req ]
default_bits = 2048
distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name
req_extensions = req_ext
prompt = no
[ req_distinguished_name ]
countryName = US
stateOrProvinceName = Arizona
localityName = Phoenix
organizationName = Test
commonName = example.com
[ req_ext ]
subjectAltName =
[alt_names]
DNS.1 = api-dev.example.com
DNS.2 = api-qa.example.com
xxxxxxxxxx
openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout test-private.pem -x509 -days 3000 -out test-public-crt.pem -config test-com.cfg
Generating Self Signed Wildcards Certificates
xxxxxxxxxx
[ req ]
default_bits = 2048
distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name
prompt = no
[ req_distinguished_name ]
countryName = US
stateOrProvinceName = Arizona
localityName = Phoenix
organizationName = Test
commonName = *.example.com
Dedicated Load Balancer Mapping Rules
Mapping rules are used on dedicated load balancers to translate input URI to call applications deployed on Cloudhub. A pattern is a string that defines a template for matching an input text. Whatever value is placed within curly brackets ({ }) is treated as a variable. Variable names can contain only lowercase letters (a-z) and no other characters, including slashes.
Input Path |
Target App |
Output Path |
Protocol |
/{app}/ |
{app} |
/ |
http |
/{app}/ |
org-{app}-{subdomain} |
/ |
http |
One Dedicated Load Balancer Mapped With One Environment

One Dedicated Load Balancer Mapped With Multiple Environment
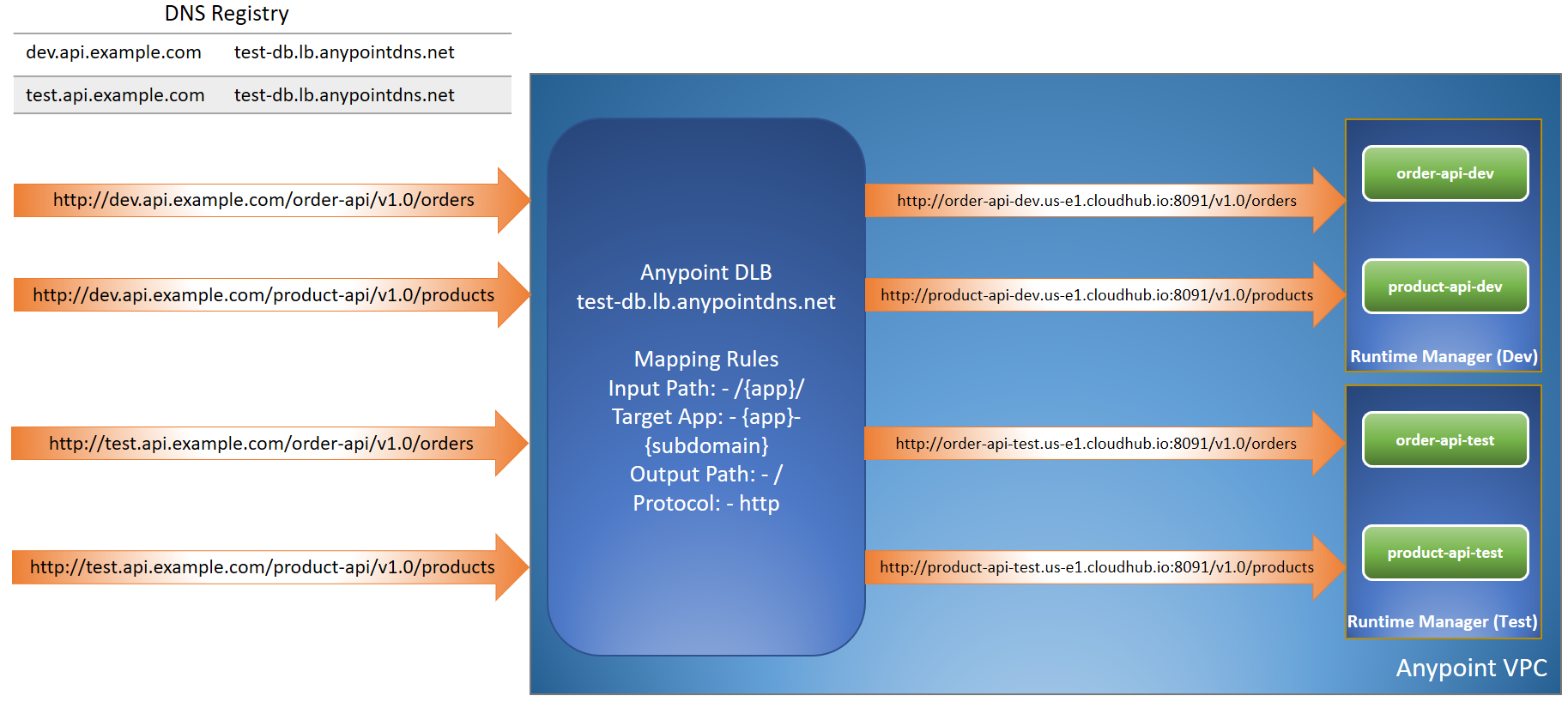
Let's consider that we have 2 DNS (i.e. api-dev.example.com and api-test.example.com) setup on a dedicated load balancer.
api-dev.example.com is for the Dev environment whereas api-test.example.com is for the Test environment.
Use Case 1
We are receiving requests on the DLB https://api-dev.example.com/ecommerce/v1.0/invoices and need to redirect them to http://org-ecommerce-api.cloudhub.io/v1.0/invoices (the Cloudhub application name will be org-ecommerce-api)
We can use this mapping rule to achieve this.
Input Path |
Target App |
Output Path |
Protocol |
/{app} |
org-{app}-api |
/v1.0 |
http |
This above rule will be applied when requests come on DLB and route to the Cloudhub application in the VPC.
- https://api-dev.example.com/ecommerce/v1.0/invoices ==> http://org-ecommerce-api.us-e1.cloudhub.io:8091/v1.0/invoices
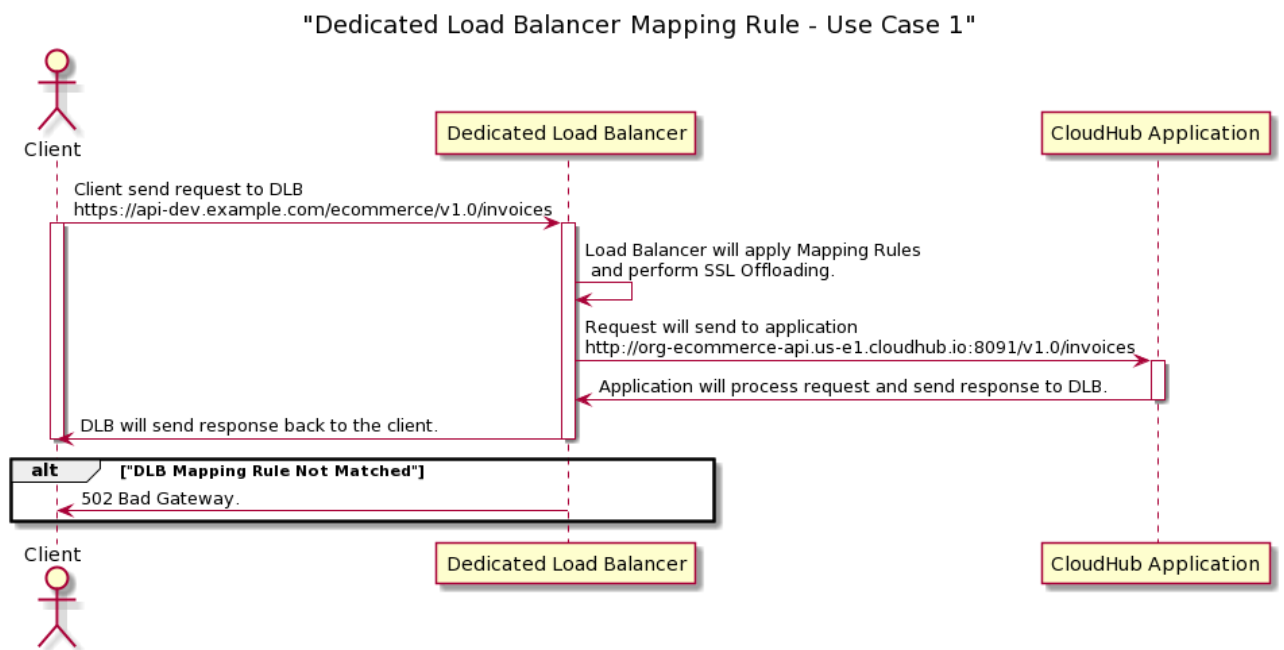 But here we have some problems that on our DLB, we have set up 2 DNSs, one for Dev and another for Test. Now, how will the DLB know this is a request that needs to route to either the Dev or Test application because the same rule will be applied for both?
But here we have some problems that on our DLB, we have set up 2 DNSs, one for Dev and another for Test. Now, how will the DLB know this is a request that needs to route to either the Dev or Test application because the same rule will be applied for both?
To avoid this, we will be using a subdomain in the next use case.
Use Case 2
In this case, we will be using a subdomain for routing the request to the correct environment from DLB.
Our application name format must be org-app-subdomain (e.g. org-ecommerce-api-dev for dev environment and org-ecommerce-api-test for test environment) when deploying to CloudHub workers in VPC .
So, our mapping rule will look like this.
Input Path |
Target App |
Output Path |
Protocol |
/{app} |
org-{app}-{subdomain} |
/v1.0 |
http |
subdomain is variable to map any subdomain.
- https://api-dev.example.com/ecommerce/v1.0/invoices (DLB) ==> http://org-ecommerce-api-dev.us-e1.cloudhub.io:8091/v1.0/invoices (CloudHub Dev Environment)
- https://api-test.example.com/ecommerce/v1.0/invoices (DLB) ==> http://org-ecommerce-api-test.us-e1.cloudhub.io:8091/v1.0/invoices (CloudHub Test Environment)
In this use case, we solve the issue of routing the request from DLB to the correct environment.

Let's consider another scenario where you want to route the request to CloudHub on the basis of the application version. We will see this in the next use case.
Use Case 3
In this case, when we will deploy an application to CloudHub, and it will be in format org-app-subdomain-version (e.g. org-ecommerce-api-dev-v1-0 for Dev environment and org-ecommerce-api-test-v1-0 for Test environment).
Whenever we will get request on DLB, then the version in the URL will be v1.0 and v2.0 but when you deploy application on CloudHub it doesn't allow to use "." in the application name. That is the reason we are using "-" in the version of the application deploying to CloudHub.
So, our mapping rule will look like this.
Input Path |
Target App |
Output Path |
Protocol |
/{app}/v{versiona}.{versionb} |
org-{app}-{subdomain}-v{versiona}-{versionb} |
/v1.0 |
http |
- https://api-dev.example.com/ecommerce/v1.0/invoices (DLB) ==> http://org-ecommerce-api-dev-v1-0.us-e1.cloudhub.io:8091/v1.0/invoices (CloudHub Dev Environment)
- https://api-test.example.com/ecommerce/v1.0/invoices (DLB) ==> http://org-ecommerce-api-test-v1-0.us-e1.cloudhub.io:8091/v1.0/invoices (CloudHub Test Environment)
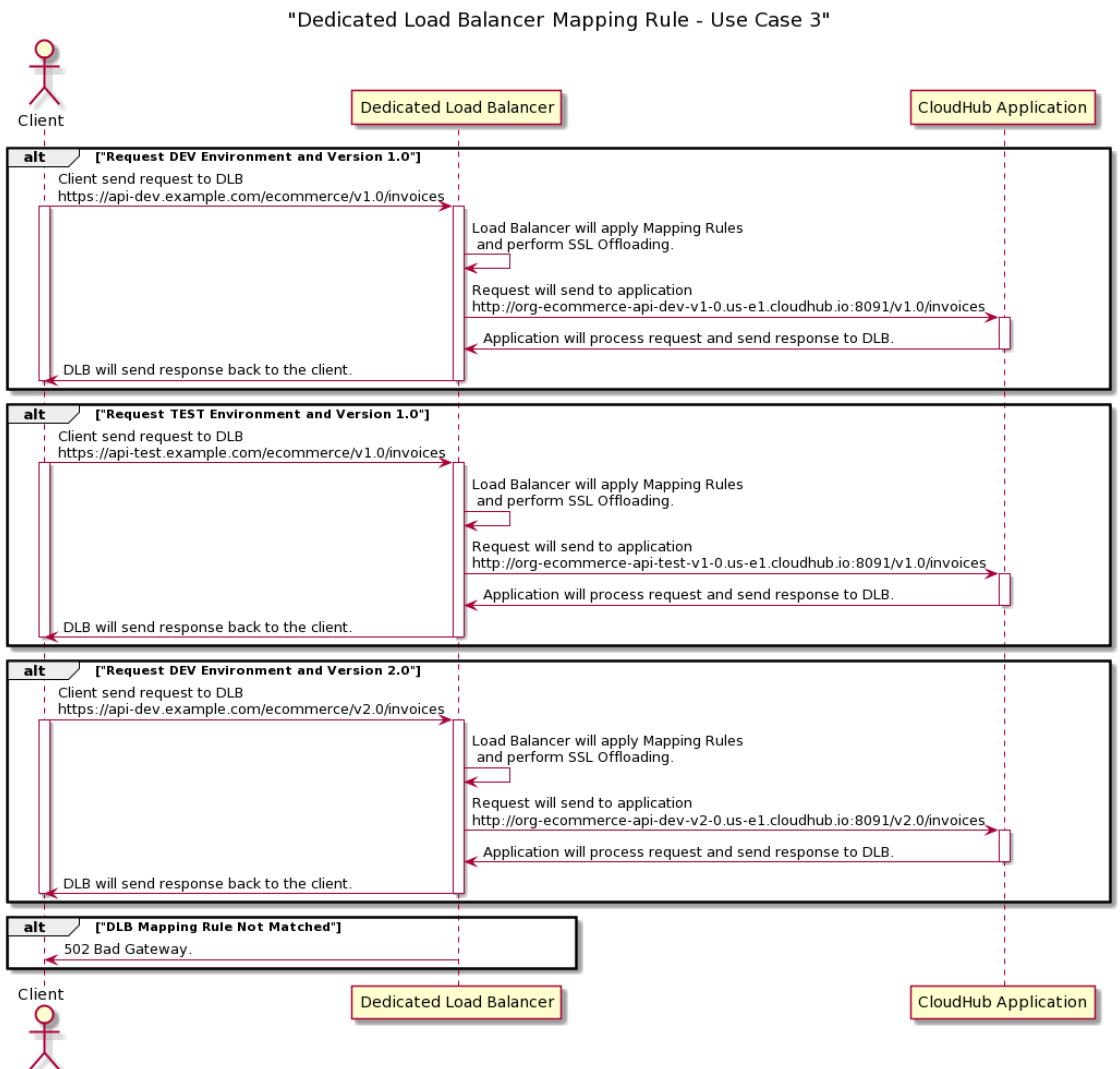
DLB Mapping Rules Priority
DLB will apply the first matching rule regardless of more exact matching rules available. A rule defined first, at index 0 has higher priority against other rules defined after it. The higher the index assigned, the less priority the mapping rule has.
Introduction To Anypoint VPC DLB and VPN
Dedicated Load Balancer Architecture and Concepts
Dedicated Load Balancer - Demonstration
Dedicated Load Balancer With Anypoint CLI
Accessing Dedicated Load Balancer Publicly and Internally
References
https://docs.mulesoft.com/runtime-manager/dedicated-load-balancer-tutorial
https://dzone.com/articles/deep-dive-into-mulesoft-anypoint-vpc-vpn-and-dedic
https://dzone.com/articles/implementing-mapping-rules-with-mulesoft-dedicated
https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL5GwZHHgKcuDQ6vWarTLgVbrPEQipzbOM
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments