JWT Token: Lightweight, Token-Based Authentication
Securing your website is the goal of every developer.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeSecuring your website is the goal of every developer. As of now, there are many possible ways to deal with website security. With the HTTP protocol, it is a bit challenging since it is stateless.
What Is Stateless?
When a sender sends a request to the server, the server processes it and sends back a response to the sender. Then, the cycle is over and the state is closed. The next request, even from the same sender, is considered a new request, or a new state. In short, every request is new to the server.
In this situation, if a sender requests a secured resource, then the sender has to be authenticated and verified of its genuineness, and they should have true permission to access the resource. This is done through the authentication by credentials.
Now, as every request is stateless, is it like we need to send the username/password every time. Yes, it is quite possible but not at all feasible. To deal with this problem, there are many mechanisms that can be used, and one of them is token-based authentication.
What Is Token-Based Authentication?
In this mechanism, when the server first receives a request with the username and password, it validates it with the values stored in its database (collected through registration) and allows the request to access the secured resource, but additionally, in the response, the server sends an authentication token and this token is stored in the database as well. When the subsequent request is sent by the same user, instead of the sending the username and password, this authentication token is being sent in the request packet. This token is validated against the token stored in the database for its validity and authenticity, and based on that, the user is allowed access.
There are many tokens based authentication available, a JSON web token (JWT) is one of them. OAuth is also another well-known mechanism. JWT follows a different technique for making it more secure because it is signed. This helps in detecting any modifications.
What Is a JWT Token?
A JSON web token (JWT) is an open standard (RFC 7519) that is a compact and self-contained way for securely transmitting information between systems as a JSON object. This information can be verified and trusted because it is digitally signed. JWTs can be signed using a secret (with the HMAC algorithm) or a public/private key pair using RSA or ECDSA.
Why Should We Use the JWT Token?
Secure
JWT digitally signs the content, and since only the server knows the secret to decrypt the information, it is vastly more secure. If anything is changed between the transmission, then the system can detect it and will provide an invalid signature error.
Compact
The JWT is simply a JSON object that is transmitted between systems with all its information, which is encoded with an algorithm. Because of this size, it can be sent through URL, POST Parameter, or inside HTTP Headers.
Faster
As this is compact, and being just an object, the transmission speed is very low. Also, it contains much-required information that eliminates the DB calls to fetch information, thus reducing overhead time.
Self-Contained
Because the JSON token contains sufficient information about the user, it does not need to query the database more than once.
Easy
As JSON is less verbose than XML, it is compact and smaller in size. We have great debugging tools for seeing the information of JWT. (Note: While this is a great feature, we must keep secret information from being leaked or made public — so, restrain from putting secure data in a token.)
When Should We Use JWT Token?
Authentication and Authorization
Once the user is logged in and authenticated by the server, then the JWT token is generated and passed in response, and in each subsequent request, the token is passed to the server. This JWT token contains the information for the user's access and permission, which is part of the authorization.
Information Exchange
This can also be used for transmitting information between two systems, as JWT tokens can be signed with public-private key pairs.
That is enough information, for now, about JWTs, now let's understand the structure of the JWT.
JWT Structure
Basically, JWT Token is a pure JSON object. So, it has its own structure where we put the information.

Header
This contains information about the algorithm used for signing and the type of the token.
This is kind of metadata of the token is generated by the server. This contains an algorithm used in signing the token and the type of token used. Once this object is created, it is encoded with Base64Url to form the first part of the JWT token.

Payload
This usually contains the information about a dataset, which the server wants to send to the client so it can use it when the token is passed back to the server. This data can typically count as user data. Also, this should not contain any sensitive information about the user, e.g. password, email, etc.
The second part of the token is the payload, which contains the claims. There are three types of claims: registered, public, and private claims.

Registered claims: These are a set of predefined claims, which are not mandatory but recommended, to provide a set of useful, interoperable claims. Some of them are:
iss(issuer),exp(expiration time),sub(subject),aud(audience),and more.
Notice that the claim names are only three characters long, as JWT is meant to be compact.
Public claims: These can be defined at will by those using JWTs.
Private claims: These are the custom claims created to share information between systems.
Once this object is created, it is encoded with Base64Url to form the second part of the JWT token.
Signature
It is created by encoding the HEADER and the PAYLOAD with a secret in the algorithm specified in the header and sign the same with the secret. The secret is only known to the server.

The signature is formed by concatenating the encoded headers and the encoded payload, and then, we sign it using the secret that is only known to the server with the algorithm specified in the header. If there is any alteration in the content of the JWT token, then it is marked as "Invalid." If the secret is also not correct, then also it is marked as "Invalid" and cannot be trusted.
Here is a complete example of the generated token...

How Does the JWT Token Work?
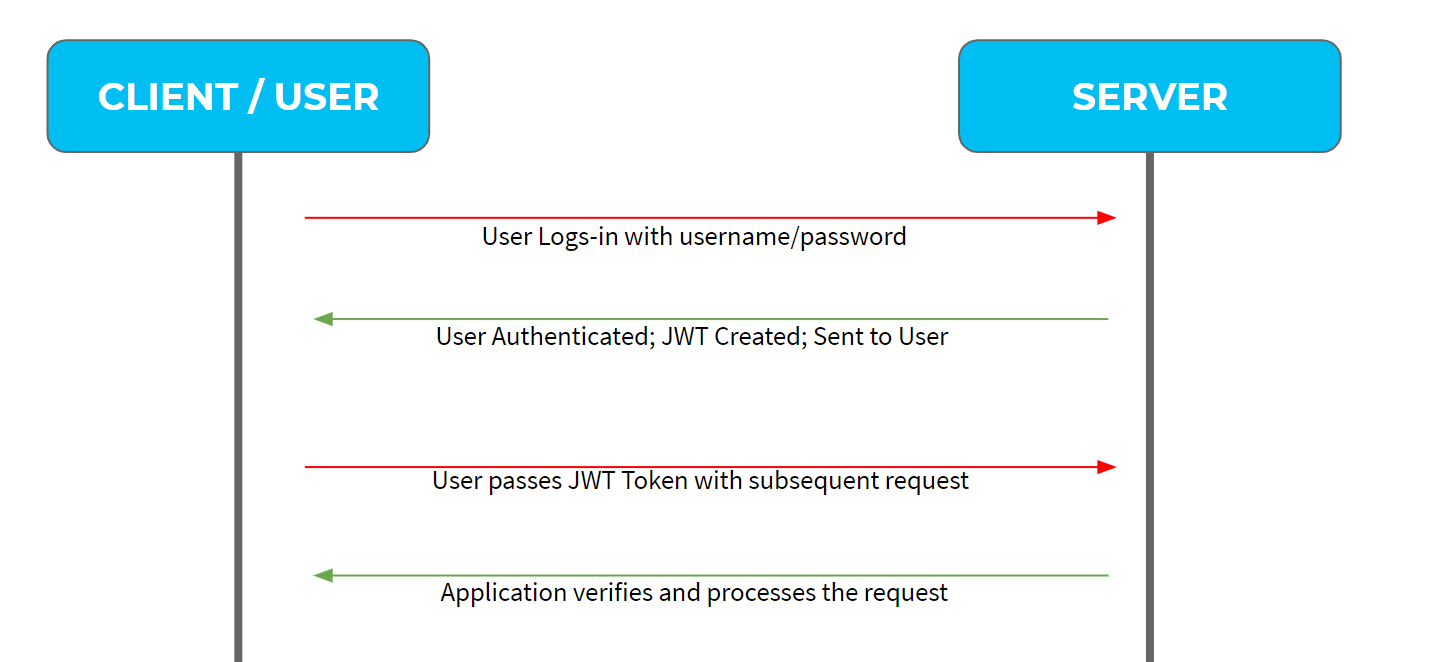
1. The user logs in by providing the username and password for the first time.
2. The server authenticates the information based on the username and password provided by the user and retrieves the user information from the database.
3. Invokes the JWT libraries to create a JSON web token (JWT) with this information, along with access permission and authority levels. Keep in mind that sensitive information should not be sent in the token as the token can be decoded. Before sending the token, the token is stored in the database associated with the user.
4. With the subsequent calls to the server, the user sends the JWT as a header to the server.
5. The server then encodes the information and validates the information before granting access to the user for secure data in the server.
6. Once the user logged out, the JWT token is cleared out.
Conclusion
Now, most of the web application is replacing the old token-based authentication technique with JWT token-based authentication. This is a very compact and lightweight mechanism to secure the resources. In comparison to other token-based methods, it is very suitable and easy to implement and maintain.
Thanks for reading this article, and I hope this gave you an idea about JWT token-based web authentication. This is a widely adopted approach, and there are lots of libraries available to helps implement JWT with any technology stack.
Thank you!
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments