Kafka Topic Architecture - Replication, Failover, and Parallel Processing
Digging deeper into Kafka architecture, this article covers the details of replication, failover, and parallel processing in this data pipeline software.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Freethis article covers some lower level details of kafka topic architecture. it is a continuation of the kafka architecture article.
this article covers kafka topic’s architecture with a discussion of how partitions are used for fail-over and parallel processing.
kafka topics, logs, and partitions
recall that a kafka topic is a named stream of records. kafka stores topics in logs. a topic log is broken up into partitions. kafka spreads log’s partitions across multiple servers or disks. think of a topic as a category, stream name or feed.
topics are inherently published and subscribe style messaging. a topic can have zero or many subscribers called consumer groups. topics are broken up into partitions for speed, scalability, and size.
kafka topic partitions
kafka breaks topic logs up into partitions. a record is stored on a partition usually by record key if the key is present and round-robin if the key is missing (default behavior). the record key, by default, determines which partition a producer sends the record.
kafka uses partitions to scale a topic across many servers for producer writes. also, kafka also uses partitions to facilitate parallel consumers. consumers consume records in parallel up to the number of partitions.
the order guaranteed per partition. if partitioning by key then all records for the key will be on the same partition which is useful if you ever have to replay the log. kafka can replicate partitions to multiple brokers for failover.
kafka topic log partition’s ordering and cardinality
kafka maintains record order only in a single partition. a partition is an ordered, immutable record sequence. kafka continually appended to partitions using the partition as a structured commit log. records in partitions are assigned sequential id number called the offset. the offset identifies each record location within the partition. topic partitions allow kafka log to scale beyond a size that will fit on a single server. topic partitions must fit on servers that host it, but topics can span many partitions hosted on many servers. also, topic partitions are a unit of parallelism - a partition can only be worked on by one consumer in a consumer group at a time. consumers can run in their own process or their own thread. if a consumer stops, kafka spreads partitions across the remaining consumer in the same consumer group.
kafka architecture: topic partition layout and offsets
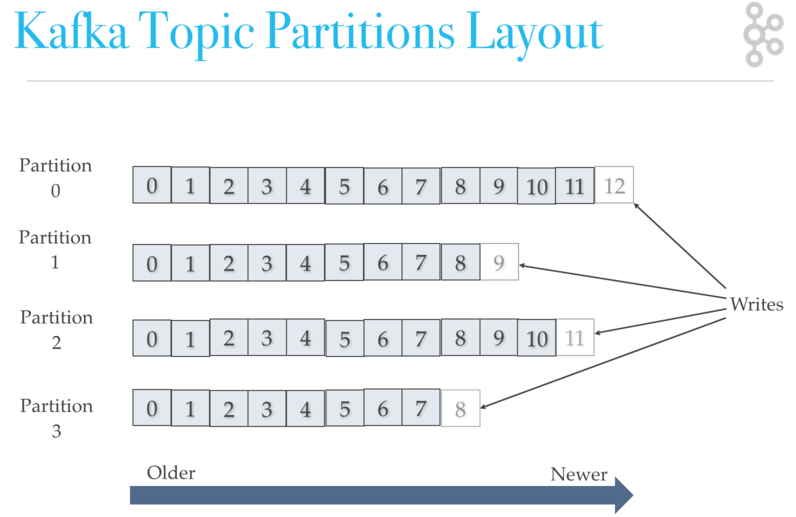
kafka topic partition replication
kafka can replicate partitions across a configurable number of kafka servers which is used for fault tolerance. each partition has a leader server and zero or more follower servers. leaders handle all read and write requests for a partition.
followers replicate leaders and take over if the leader dies. kafka uses also uses partitions for parallel consumer handling within a group. kafka distributes topic log partitions over servers in the kafka cluster. each server handles its share of data and requests by sharing partition leadership.
replication: kafka partition leaders, followers, and isrs
kafka chooses one broker’s partition’s replicas as leader using zookeeper.
the broker that has the partition leader handles all reads and writes of records for the partition. kafka replicates writes to the leader partition to followers (node/partition pair). a follower that is in-sync is called an isr (in-sync replica). if a partition leader fails, kafka chooses a new isr as the new leader.
replicating to partition 0
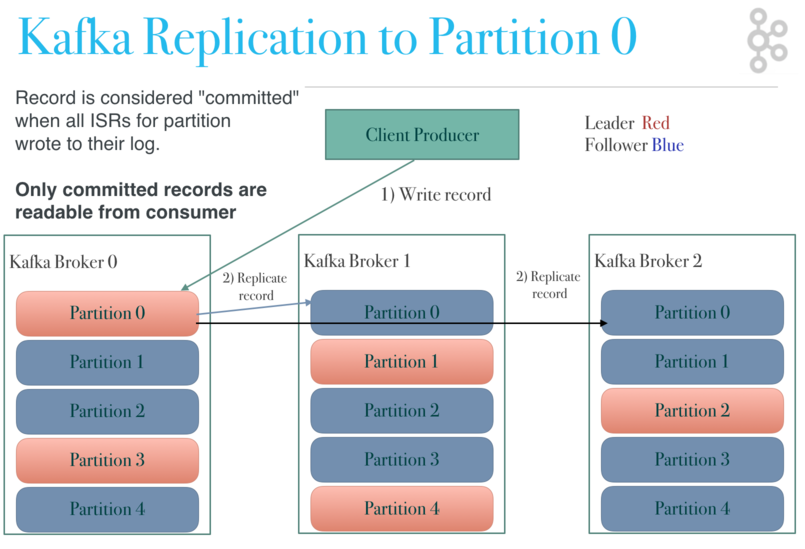
the record is considered “committed” when all isrs for partition wrote to their log. only committed records are readable from consumer. another partition can be owned by another leader on another kafka broker.
replicating to partition 1
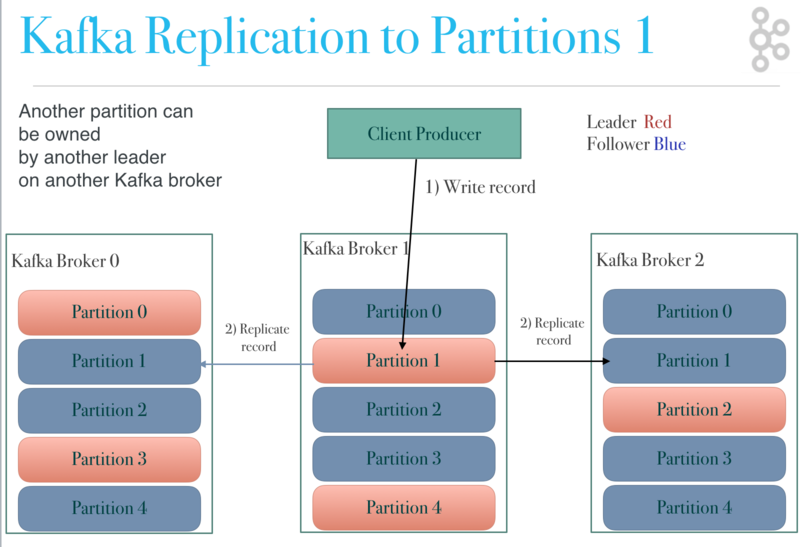
kafka topic architecture in review
what is an isr?
an isr is an in-sync replica. if a leader fails, an isr is picked to be a new leader.
how does kafka scale consumers?
kafka scales consumers by partition such that each consumer gets its share of partitions. a consumer can have more than one partition, but a partition can only be used by one consumer in a consumer group at a time. if you only have one partition, then you can only have one consumer.
what are leaders? followers?
leaders perform all reads and writes to a particular topic partition. followers replicate leaders.
how does kafka perform failover for consumers?
if a consumer in a consumer group dies, the partitions assigned to that consumer is divided up amongst the remaining consumers in that group.
how does kafka perform failover for brokers?
if a broker dies, then kafka divides up leadership of its topic partitions to the remaining brokers in the cluster.
please continue reading about kafka architecture. the next article covers kafka producer architecture with a discussion of how partitions are picked for records.
Published at DZone with permission of Jean-Paul Azar. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments