Messaging in AWS Using SNS and SQS
Learn how to use asynchronous messaging in AWS using SNS and SQS.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThere are two main communication paradigms in event-driven architectures used in microservices design.
- Queueing provides a messaging system to integrate two different services.
- Publish/subscribe messaging is a form of asynchronous service-to-service communication used in microservices architectures. In contrast to queueing, publish/subscribe messaging allows multiple consumers to receive each message in a topic.
They allow us to de-couple producers and consumers of messages. By combining publish/subscribe messaging systems with queueing systems, we can build fault-tolerant, scalable, resilient, and reactive application architectures. Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a number of services which provide these two communication paradigms. In this article, we will learn how to program AWS services – Simple Notification Service (SNS) for publish/subscribe messaging and Simple Queue Service (SQS) for queueing using AWS SDK in Java.
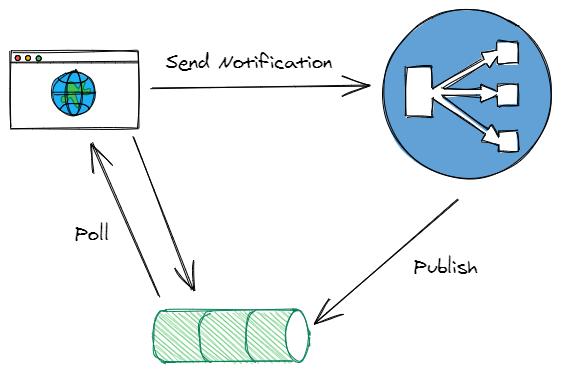
System Architecture
We have an application which needs to publish notifications if there is a change. This change is published to a topic in SNS. There are different subscription mechanisms available for an SNS topic – SQS being one of them. We will use an SQS queue to receive change notifications. An application may poll SQS queues for any message.
Implementation
To develop and deploy the system, we'll need following infrastructure components:
- SNS topic.
- SQS queue.
- Subscription to the topic.
- Permission for SNS to publish to the SQS queue.
We will use Terraform to provision the infrastructure on AWS. Terraform is an open-source infrastructure as code software tool created by HashiCorp.
SNS Topic
Let's create the SNS topic. To create an SNS topic we only need to provide a name.
resource "aws_sns_topic" "config_updates" {
name = "config-updates-topic"
}
We need permission to publish to this SNS topic. In our architecture, an application will publish change notifications to the topic. The application will use a user account with permissions to publish to the topic.
SQS Queue
We have to provide a name for the queue and a policy which allows SNS to send messages to the queue.
xxxxxxxxxx
resource "aws_sqs_queue" "config_updates" {
name = "config-updates-listener"
}
Next, create a subscription of the SNS topic for the SQS queue.
xxxxxxxxxx
resource "aws_sns_topic_subscription" "sqs" {
topic_arn = aws_sns_topic.config_updates.arn
protocol = "sqs"
endpoint = aws_sqs_queue.config_updates.arn
}
Next, allow SNS to publish messages to the queue.
xxxxxxxxxx
resource "aws_sqs_queue_policy" "test" {
queue_url = aws_sqs_queue.config_updates.id
policy = <<POLICY
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Id": "sqspolicy",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "First",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": "*",
"Action": "sqs:SendMessage",
"Resource": "${aws_sqs_queue.config_updates.arn}",
"Condition": {
"ArnEquals": {
"aws:SourceArn": "${aws_sns_topic.config_updates.arn}"
}
}
}
]
}
POLICY
}
Creating the Infrastructure
Let us run our Terraform scripts to create the infrastructure.
xxxxxxxxxx
terraform init
terraform plan
terraform apply
The output of terraform apply provides us the SQS Queue URL and the SNS topic ARN that we will use in our application.
Develop the Application
Next, we develop our application that will publish a notification to an SNS topic and also poll an SQS queue to receive messages. We will use Java and the AWS SDK to develop our application.
Send Notifications to an SNS Topic
xxxxxxxxxx
import com.randhirks.sns.model.ChangeNotification;
import com.randhirks.sns.model.NotificationRequest;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import software.amazon.awssdk.regions.Region;
import software.amazon.awssdk.services.sns.SnsClient;
import software.amazon.awssdk.services.sns.model.PublishRequest;
import software.amazon.awssdk.services.sns.model.PublishResponse;
import software.amazon.awssdk.services.sns.model.SnsException;
public class NotificationService {
("${sns.topic.arn}")
private String topicArn;
("${aws.region}")
private String awsRegion;
private SnsClient snsClient;
private void init() {
snsClient = SnsClient.builder()
.region(Region.of(awsRegion))
.build();
}
public ChangeNotification sendNotification(NotificationRequest notificationRequest) {
ChangeNotification changeNotification = ChangeNotification.builder()
.sentMessage(notificationRequest.getMessage()).build();
try {
init();
PublishRequest request = PublishRequest.builder()
.message(notificationRequest.getMessage())
.topicArn(topicArn)
.build();
PublishResponse result = snsClient.publish(request);
System.out.println(result.messageId() + " Message sent. Status was " + result.sdkHttpResponse().statusCode());
changeNotification.setId(result.messageId());
} catch (SnsException e) {
System.err.println(e.awsErrorDetails().errorMessage());
}
return changeNotification;
}
}
Receive Messages From an SQS Queue
xxxxxxxxxx
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.randhirks.sns.model.ChangeNotification;
import com.randhirks.sns.model.SNSMessage;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import software.amazon.awssdk.regions.Region;
import software.amazon.awssdk.services.sqs.SqsClient;
import software.amazon.awssdk.services.sqs.model.Message;
import software.amazon.awssdk.services.sqs.model.ReceiveMessageRequest;
import software.amazon.awssdk.services.sqs.model.SqsException;
public class NotificationListener {
("${aws.region}")
private String awsRegion;
("${sqs.id}")
private String queueUrl;
private SqsClient sqsClient;
private void init() {
sqsClient = SqsClient.builder()
.region(Region.of(awsRegion))
.build();
}
public ChangeNotification receiveMessage(ChangeNotification changeNotification) {
try {
init();
ReceiveMessageRequest receiveMessageRequest = ReceiveMessageRequest.builder()
.queueUrl(queueUrl)
.maxNumberOfMessages(1)
.build();
Message message = sqsClient.receiveMessage(receiveMessageRequest).messages().get(0);
Gson gson = new Gson();
SNSMessage snsMessage = gson.fromJson(message.body(), SNSMessage.class);
changeNotification.setReceivedMessage(snsMessage.getMessage());
} catch (SqsException e) {
System.err.println(e.awsErrorDetails().errorMessage());
}
return changeNotification;
}
}
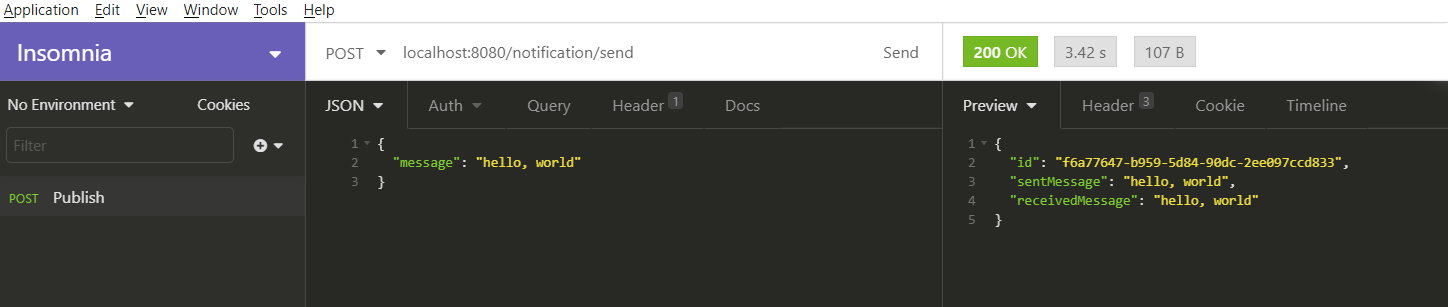
The complete code is available in my GitHub repo. Run the application as a Spring Boot application and hit the application URL to send a message. The output shows the received message from the SQS Queue.
Conclusion
In this article, we reviewed two important communication mechanisms in event-driven programming. We implemented an architecture on AWS leveraging the services – SNS and SQS – that implement these communication mechanisms. We provided a sample Java application using the AWS SDK to send and receive messages from our system.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments