Microservices vs. SOA
If you have worked with SOA before, you might wonder what is the difference between SOA and Microservices. Here I have explained both architectures and compared them in details.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThese days, there are a lot of discussions about Microservices at the workplace or in tech talks. And if you have worked with SOA before, you might wonder what is the difference between SOA and Microservices. Here is a comparison of both architectures in details.
1. SOA
A Service Oriented Architecture is a software architecture pattern, which application components provide services to other components via a communications protocol over a network. The communication can involve either simple data passing or it could involve two or more services coordinating connecting services to each other. Services (such as RESTful Web services) carry out some small functions, such as validating an order, activating account, or providing shopping cart services.
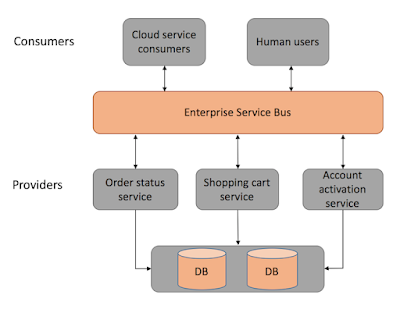
There are 2 main roles in SOA, a service provider and a service consumer. A software agent may play both roles. The Consumer Layer is the point where consumers (human users, other services or third parties) interact with the SOA and Provider Layer consists of all the services defined within the SOA. The following figure shows a quick view of an SOA architecture.
Figure 1: SOA architecture
Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) is a style of the integration architecture that allows communication via a common communication bus that consists of a variety of point-to-point connections between providers and consumers . In addition to above, the data storage is shared within all services in SOA.
Now, let's take a look at Microservices architecture, then compare both together.
2. Microservices Architecture
Microservices is a software architecture pattern in which complex applications are composed of small, independent processes communicating with each other using language-agnostic APIs.
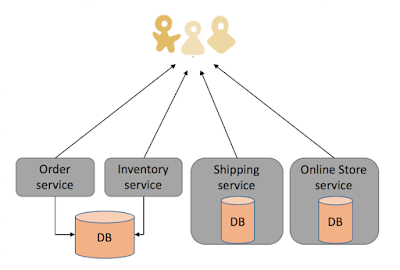
Microservices must be a real need in the system architecture as it could be designed wrongly. It means a service should be independently deployable, or be able to shut-down a service when is not required in the system and that should not have any impact on other services. The following figure shows a quick view of a Microservices architecture.
Figure 2: Microservices architecture
As shown above, each service has its own database or a database is shared between a few of microservices.
3. Microservices Architecture vs. SOA
As discussed above, both architectures have similar pros and cons and some differences. In both architectures, each service - unlike a monolithic architecture - has a certain responsibility. Thus, services can be developed in various technology stacks which bring technology diversity into the development team. The development of services can be organized within multiple teams, however, each team needs to know about the common communication mechanism in SOA.
In microservices, services can operate and be deployed independently of other services, unlike SOA. So, it is easier to deploy new versions of services frequently or scale a service independently.
In SOA, ESB could become a single point of failure which impacts the entire application. Since every service is communicating through ESB, if one of the services slow down, could cause the ESB to be clogged up with requests for that service. On the other hand, microservices are much better in fault tolerance. For example, if there is a memory leak in one microservice then only that microservice will be affected. The other microservices will continue to handle requests.
In both architectures, developers must deal with the complexity of architecture and a distributed system. Developers must implement the inter-service communication mechanism between microservices (if the message queue is used in Microservice architectures) or within ESB and services.
Unit Testing is more difficult as developers must mock the communication mechanism in tests. Due to many different service types, deployment and operational complexity are a concern in both architectures.
In SOA, services share the data storage (as shown in Figure 1) while each service can have an independent data storage in microservices. Sharing data storage has its pros and cons. for example, the data can be re-used by between all services while it brings dependency and tightly coupling within services.
Last but not least, the main difference between SOA and microservices lies in the size and scope. Microservice has to be significantly smaller than what SOA tends to be and mainly is a small(er) independently deployable service. On the other hand, an SOA can be either a monolith or it can be comprised of multiple microservices.
Figure 3: SOA and Microservices
It is also important that SOA has been designed and implemented in various styles which could be different with what it is described here, usually due to a focus on ESBs which is used to integrate monolithic applications.
Published at DZone with permission of Ima Miri, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.


Comments