Open Dashboard and Visualization Workshop: Introduction and Installing Perses
In this article, explore an updated introduction to the background of Perses, as well as an open dashboard and visualization workshop.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeBack in December of 2022, I started a series taking you on a tour of the Perses project. These articles covered this fairly new open dashboard and visualization project targeting cloud-native environments. I used a getting started workshop (linked below) to guide you through this series and to provide a hands-on experience for those new to visualizing observability data.
Being a developer from my early days in IT, it's been very interesting to explore the complexities of cloud-native observability (o11y). Monitoring applications goes way beyond just writing and deploying code, especially in the cloud-native world. One thing remains the same: maintaining your organization's architecture always requires both a vigilant outlook and an understanding of available open standards.
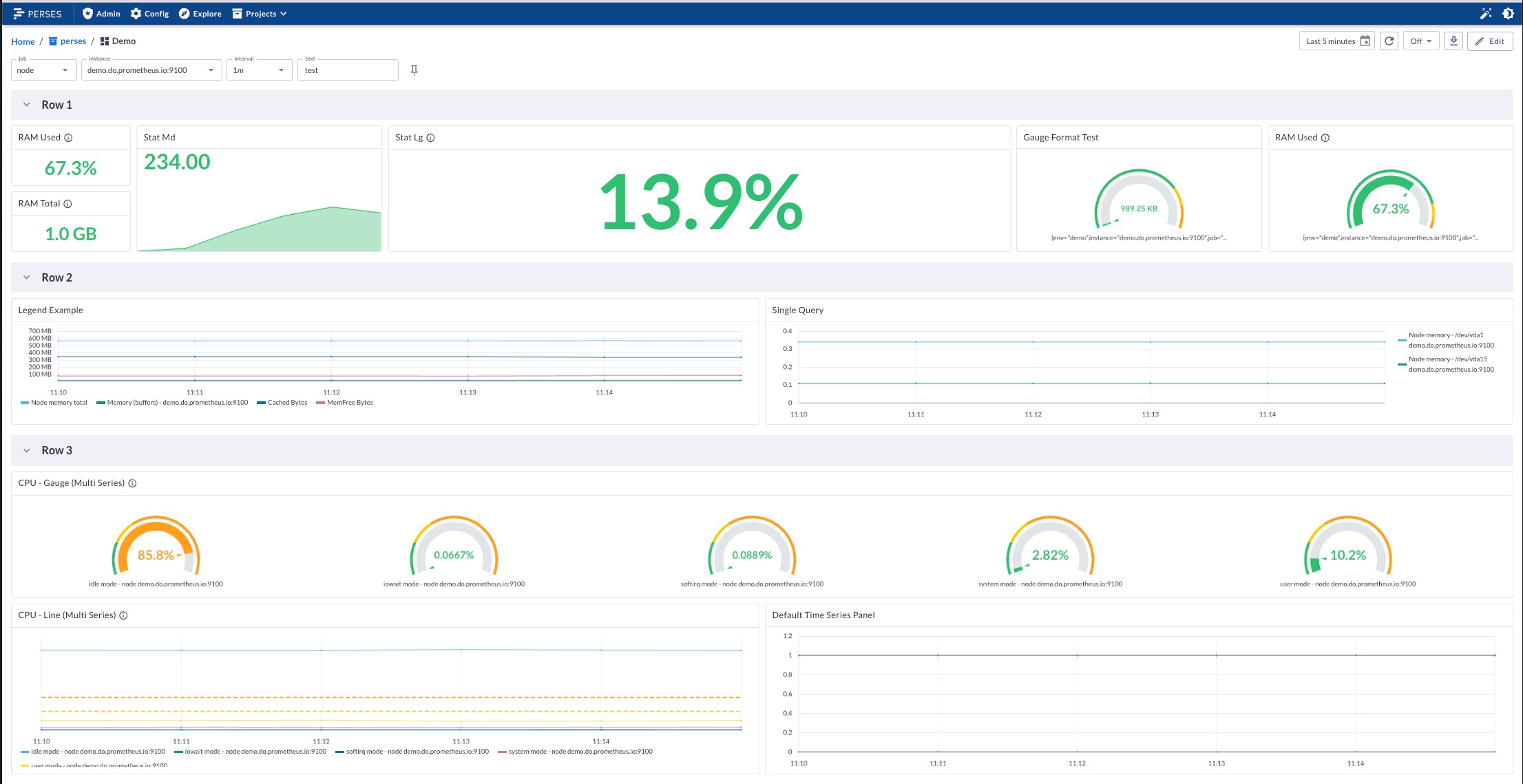
Now that it's almost a year since my last dive into Perses, let's revisit this workshop and explore the latest release. If you tried the first iteration of this workshop found in this repository tag, you'll remember that it was a lot of diving into JSON. This time around, the UI has been flushed out so that many of the tasks you need to design projects, dashboards, data sources, and more are a smoothly guided experience.
Let's see what's new, shall we?
As promised, in this article, I'll kick off an updated introduction to the background of Perses as covered in my workshop lab before diving into the actual hands-on with the project.
You can find the free workshop here online:
The Origins of Perses
Perses is the first project under the CoreDash community umbrella, which is part of the Linux Foundation. It's a centralized effort to define a standard for visualization and dashboards. Perses is licensed under the Apache License 2.0, which is a big difference from the recent changes to what used to be the default dashboard project before they opted to change to Affero General Public License (AGPL) v3. This change means users who apply any modification have to share them back into the project: a bit more restrictive than most users want.
Its main goal is becoming an exploration into finding an open-source standard for visualization and dashboards for metrics monitoring. Its first code commit was made on Jan 26, 2022, and since then has been quite active. There are clear project goals:
- Become an open standard dashboard visualization tool
- Provide embeddable charts and dashboards in any user interface
- Target Kubernetes (k8s) native mode
- Provide complete static validation for CI/CD pipelines
- Architecture supporting future plugins
There are plans to submit this project soon to the CNCF as a sandbox project, so stay tuned.
Check out a more in-depth introduction in this free online workshop lab 1:
Next, we can look at installation options for this project.
Installing Perses
There are two options for installing Perses on your local machine. One, you can build the source code project and run it locally, but there are a few software dependencies that you need to meet first to do that. Second, if the bar is too high to build the project from its source, you can install and run Perses from a container image.
I've put together a simple supporting project that you can use called the "Perses Easy Install" project. This project contains a simple installation script that allows you to choose either a container install using Podman, or to build the project from its source code. Both methods include sanity checks for the dependencies on your machine before allowing you to install the project.
Install in a Container (Podman)
In the workshop, I walk you through the simple steps to launch Perses from the project-provided image. You can do this using either Docker or Podman, but Podman is featured in the remainder of the workshop.
This step is followed by an installation using the project mentioned above, ensuring the same steps you were just shown are captured in a single automated script. Also included is the installation of a pre-configured workshop demo project to get started with for the following labs. You will run this Perses container on a virtual machine provided by Podman.
Prerequisites: Podman 4.x+ with your Podman machine started
- Download and unzip this demo
- Run
init.shwith the correct argument:
$ ./init.sh podman
The Perses container image is now running and pre-loaded with demo examples, connect in your browser (http://localhost:8080). For an installation from the source, the following process is needed.
Install on Your Local Machine
This is an installation from the source code of the Perses project. You will test, build, and deploy the Perses server locally on your machine.
Prerequisites: Go version 1.18+, NodeJS version 16+, npm version 8+
- Download and unzip this demo
- Run
init.shwith the correct argument:
$ ./init.sh source
Perses is now running, connect to the Perses dashboards in your browser (http://localhost:8080).
For step-by-step instructions on how to install Perses using a container image or from the source code in the project itself, see this free online workshop lab 2:
More to Come
Next up, I'll continue working with you through the Perses project with more workshop materials to share. Stay tuned for more insights into a real practical experience as my cloud native o11y journey continues.
Published at DZone with permission of Eric D. Schabell, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.




Comments