Cloud Build Unleashed: Expert Techniques for CI/CD Optimization
Discover strategies to enhance speed and efficiency and ensure that your deployments are secure, compliant, and resilient.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeCI/CD and Its Importance
We all know what CI/CD is and how it fosters a sense of collaboration among teams and enables them to deliver high-quality software efficiently and reliably. By automating the integration, testing, and deployment processes, CI/CD helps maintain code quality, reduce manual effort, and provide continuous feedback, ultimately leading to faster and more reliable software delivery.
CI/CD is important for the following reasons:
Enhanced Code Quality
CI/CD allows for frequent testing and integration, catching issues early in the development cycle. This helps maintain higher code quality and reduces the likelihood of bugs reaching production.
Faster Time to Market
CI/CD streamlines testing and deployment, ensuring swift and reliable feature delivery.
Reduced Manual Effort
Using automation in CI/CD reduces the need for manual intervention and human error. This enables developers to concentrate on more important tasks.
Improved Collaboration
With CI/CD, team members can work on different features simultaneously and merge their code changes frequently. This encourages better collaboration and communication within the team.
Consistent Environments
CI/CD pipelines can include automated processes to create consistent and reproducible development, testing, and production environments. This ensures that the code runs as expected across different stages.
Continuous Feedback
CI/CD provides continuous feedback to developers through automated testing and monitoring, helping them to understand the impact of their changes quickly and make necessary adjustments.
Increased Reliability and Stability
CI/CD reduces the risk associated with each deployment by deploying smaller, incremental updates rather than large, monolithic releases.
In order to take full advantage of all the above-mentioned advantages of CI/CD, it is very important that the CI/CD pipeline is optimized. We will discuss the important aspects of optimizing a CI/CD pipeline using Cloud Build.
Time To Get into Cloud Build
We would not discuss CI/CD when using Google Cloud without mentioning Cloud Build. Cloud Build supports various environments and integrates with various source code repositories, allowing for seamless CI/CD pipelines.
Key Concepts
Let's talk about key concepts within Cloud Build that make it very effective.
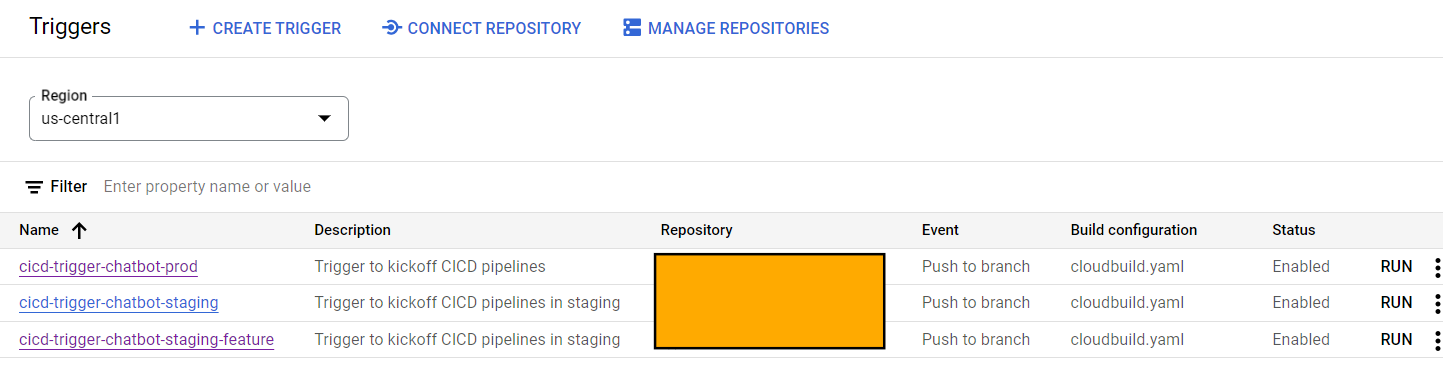
Triggers
Triggers automate the execution of builds based on specified conditions. They help streamline the CI/CD process by automatically initiating builds when certain events occur or at specified times.
The builds can be triggered manually via the Cloud Build UI, CLI, or API without relying on external events, through a webhook to initiate a build in response to events from external systems, such as changes in a source code repository or notifications from other services, or through a scheduled initiation of the build at a specified time similar to cron jobs.
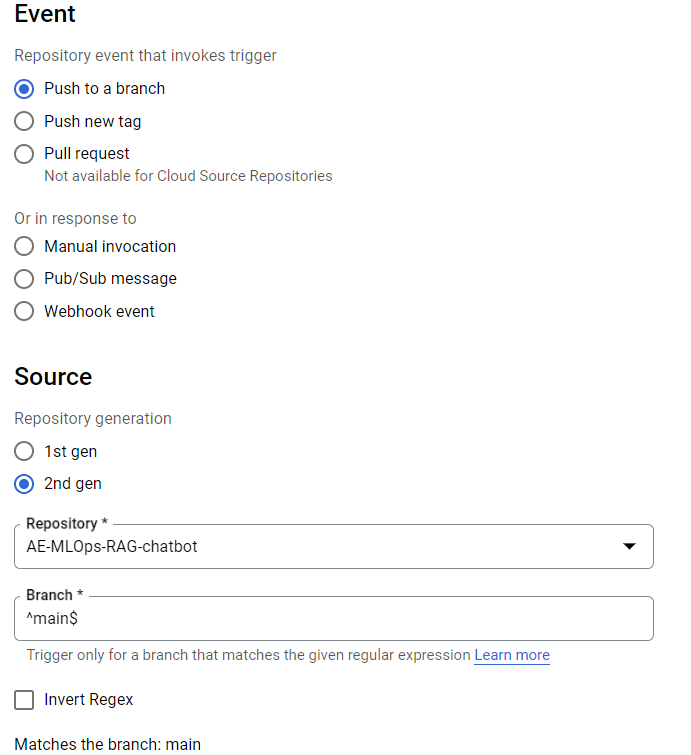
Cloud Build triggers allow you to select the event for kicking off the pipeline, a.k.a Build. Some of the most commonly used trigger event types are:
- GitHub integrated:
- On a push to a branch
- On a pull request
- On a new tag/release creation
- Manual invocations/other events:
- Manual runs
- On a Pub/Sub message (based on a trigger event from other systems)
- Webhook event (Trigger via API calls)
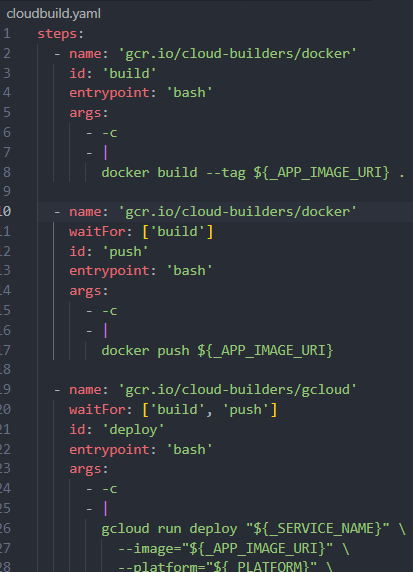
Build Steps
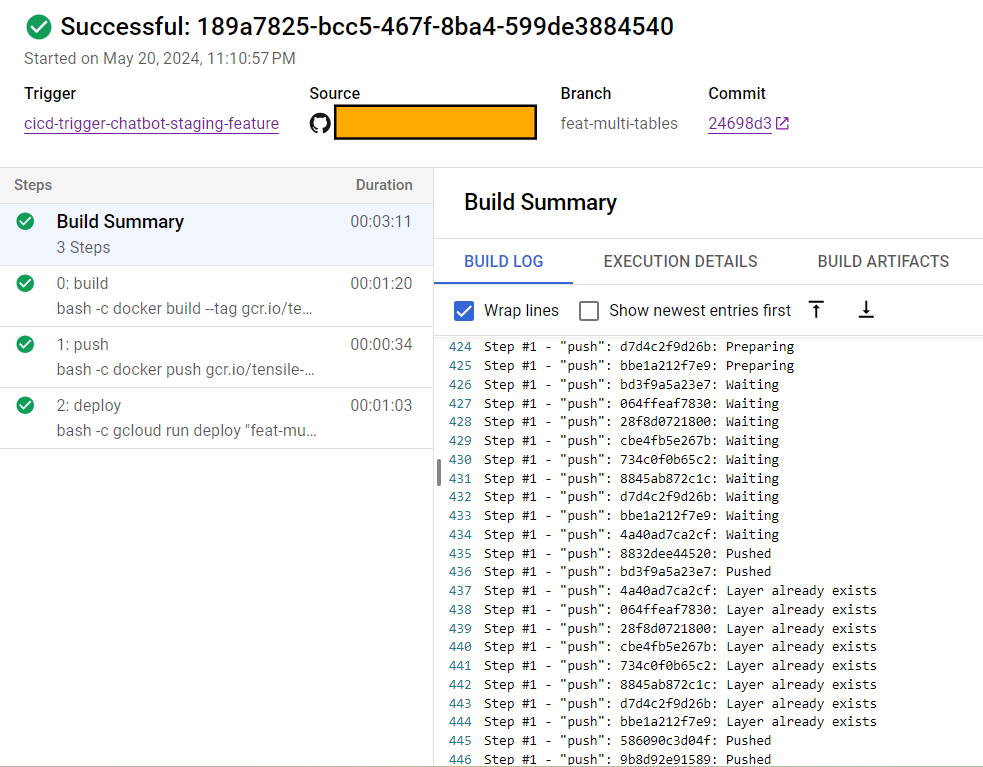
Build steps are individual actions executed sequentially as part of the build process, such as compiling code, running tests, and deploying applications. The image below shows an example of build steps.
Repository Objects
Repository objects encompass the source code and configuration files stored in a version control system (e.g., GitHub, GitLab, Cloud Source Repositories) utilized in the build process (see Cloud Build Repositories for more info).
Connections
Connections in Cloud Build refer to the integrations between Cloud Build and external version control systems or other services. These connections allow Cloud Build to access the source code and trigger builds based on repository events.
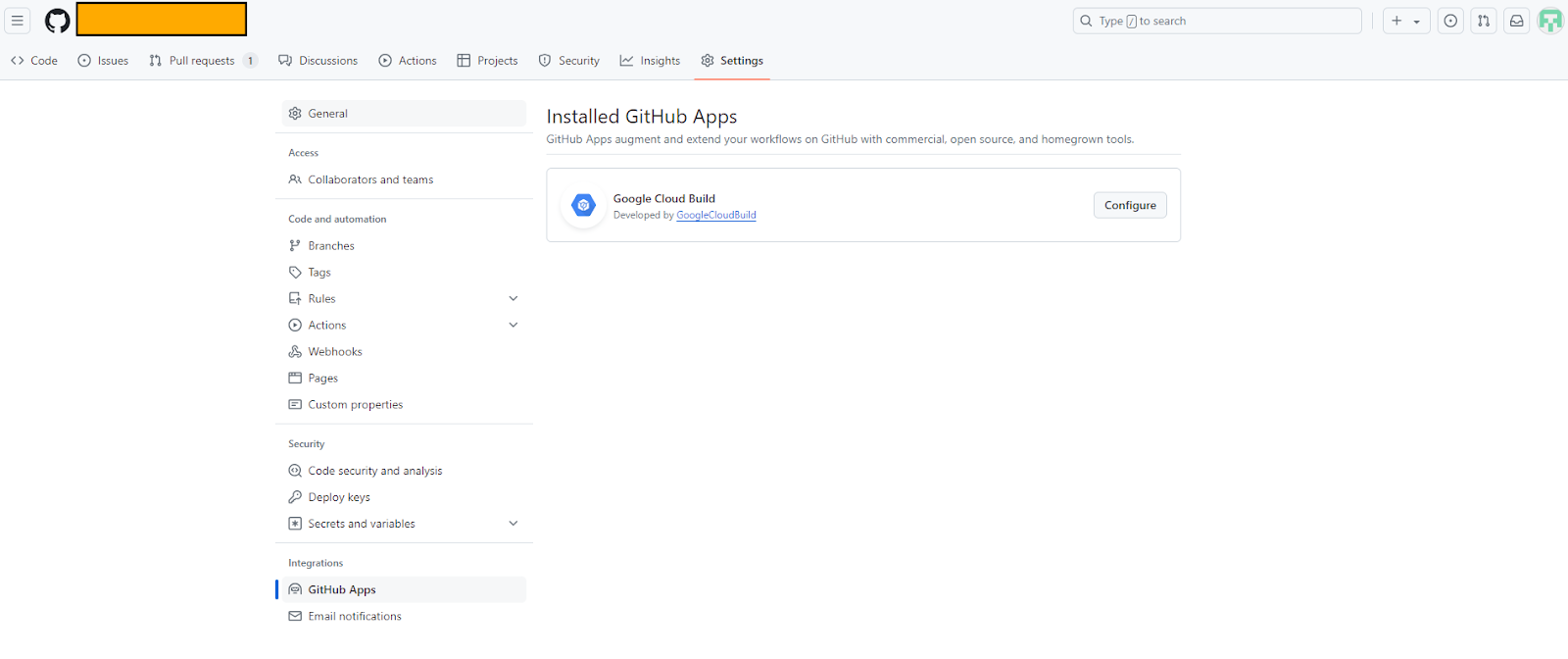
GitHub Apps
GitHub Apps are applications that can be integrated with GitHub repositories to provide additional functionality. In the context of Cloud Build, GitHub Apps can be used to trigger builds and report build statuses directly within GitHub.
Images
- Prebuilt images: These are standard Docker images provided by Google Cloud or the community that can be used as build steps without additional configuration.
- Custom images: The user creates these Docker images to carry out specific tasks as part of the build process. Custom images can include all necessary dependencies and configurations for specialized build steps.
See Cloud builders documentation for more.
Build Config Files
Build config files define the build steps and their execution order. They are typically written in YAML or JSON format. Read more at Create a build configuration file.
Artifacts and Storage
- Artifacts: These are files produced by the build process, such as compiled binaries, Docker images, or test results. Artifacts can be stored and retrieved for further use or deployment.
- Storage: Cloud Build can store artifacts in Google Cloud Storage (GCS) or Google Container Registry (GCR). GCS is used to store general files, while GCR is specifically used for Docker images.
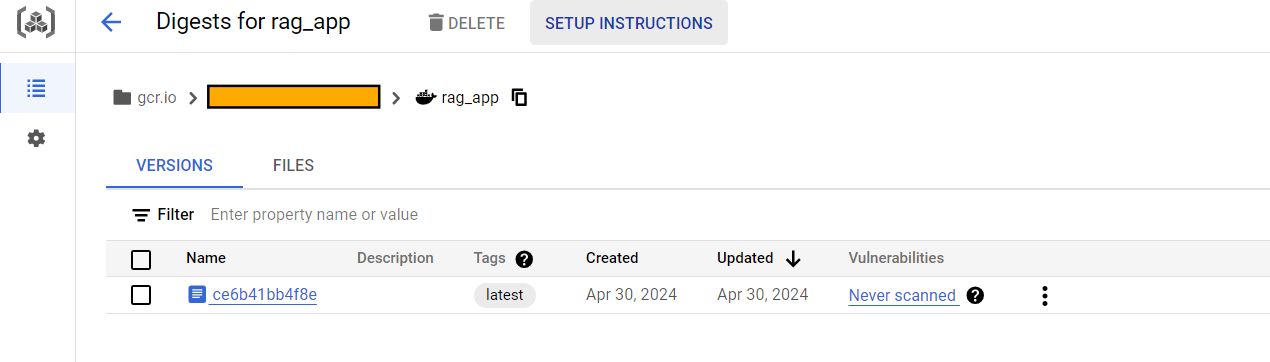
Optimization Techniques for Cloud Build CI/CD
Even though Cloud Build offers many key concepts and greatly simplifies CI/CD, we still need a few optimization techniques to achieve excellence in this area.
Let us categorize the optimization techniques into the following:
Speed and Efficiency
We will explore the elements that enhance the speed and efficiency of the CI/CD pipelines.
Caching
Utilize caching to store and reuse previously built artifacts or dependencies, reducing build times.
- Docker layer caching: Cache Docker image layers to avoid rebuilding unchanged layers.
- Dependency caching: Cache dependencies to speed up subsequent builds.
As you can see in the screenshot above, a rebuild happens on the components that have changed from the previous build, making it efficient and utilizing caching in this process.
Parallel Steps
Execute build steps in parallel whenever possible to reduce overall build time.
Docker Image Optimization
- Unwanted installs: Remove unnecessary packages and files from Docker images to reduce size and build time.
- Dependency management: Use multi-stage builds to keep final images lightweight by including only necessary dependencies.
Resource Allocation
We must allocate appropriate resources (CPU, memory) to ensure optimal performance when building steps. We can do so by specifying resource limits and requests in the build config.
Reliability
Reliability and maintainability are other important aspects of CI/CD that, if worked on diligently, can add significant value.
Build Stages
Break larger builds into smaller manageable stages by using multiple build steps and conditional execution to split tasks.
Error Handling
Implement conditionals to handle different scenarios within the build process. Monitor exit codes to determine the success or failure of build steps. Ensure that builds fail gracefully and notify relevant stakeholders.
Security
Ensuring security in CI/CD is critical for protecting sensitive information and maintaining application integrity.
Secrets Manager Injection
Securely manage and inject sensitive information (e.g., API keys, passwords) into the CI/CD pipeline using tools like Google Cloud Secret Manager. Implementing this measure effectively safeguards sensitive data from unauthorized access and significantly minimizes the risk of leaks.
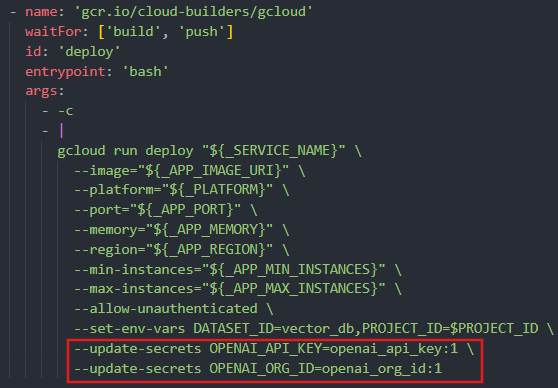
In the previously outlined scenario, it is notable that until the deployment stage, the containers do not possess access to any secret values. They solely reference an environment variable under the assumption that it will be available during runtime. The utilization of the "--update-secrets" flag ensures that secret values tagged as version 1 from the "openai_api_key" and "openai_org_id" secret manager entries are appropriately assigned to their corresponding environment variables. This procedural approach mitigates the risk of inadvertent secret exposure.
Image Vulnerability Scans
Scan Docker images for vulnerabilities before deployment to identify and mitigate security vulnerabilities early, preventing compromised software from reaching production. This is a built-in feature of Artifact Registry.
Integrations in Cloud Build
Another important aspect of a CI/CD tool is its efficiency in integrating with other tools and processes to enhance various aspects of release management.
Infrastructure as Code: Terraform
Integrating Terraform with Cloud Build enables automated and consistent infrastructure deployment alongside your application code. It also ensures reproducible and consistent infrastructure setups, simplifies infrastructure management, and allows for version-controlled infrastructure code.
Compliance (SonarQube, FOSSA, Checkmarx)
The important aspect of optimizing CI/CD is integrating compliance tools with Cloud Build.
- SonarQube: Static code analysis for identifying code quality issues
- FOSSA: License compliance and vulnerability scanning
- Checkmarx: Static Application Security Testing (SAST) for identifying security vulnerabilities
Integrating the above tools will massively help increase code quality, security, and licensing compliance.
Substitutions (User Subs, Dynamic Subs, Secret Manager Subs, Trigger-Based Subs)
Cloud Build offers a wide range of substitution options for allowing users to make substitutions during various stages of their builds depending on their DevOps practices.
Here are a few:
- User substitutions: User-defined key-value pairs under the substitution flag, which can be re-used at any build stage
- Default substitutions: By default, Cloud Build offers a wide range of substitution values, from Project ID, Region, and Location to Trigger Name, Commit SHA, and so on.
See the full list here.
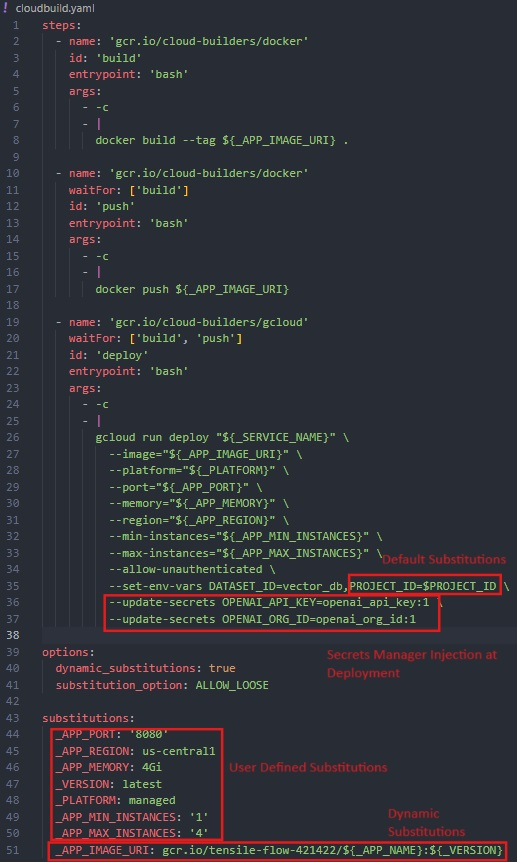
Learn more about substitutions here.
Conclusion
In conclusion, optimizing and securing your Cloud Build pipeline is crucial for delivering high-quality software quickly and reliably. By leveraging techniques such as caching, parallel steps, Terraform for IaC, and integrating security measures like secret management and vulnerability scans, you can build a robust and efficient CI/CD process. These strategies enhance speed and efficiency and ensure that your deployments are secure, compliant, and resilient, positioning your development team for sustained success.
Learn more about various Cloud Build features here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments