Oracle TimesTen: An In-Memory Database Booster
Some of the benefits of using Oracle TimesTen include real-time performance enhancement, zero data loss, and automated database failover.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeTimesTen is a product from Oracle that can boost Oracle database performance drastically. TimesTen is not only memory-optimized but it also provides high throughput, high durability, better scalability, and low response times while working with performance-critical applications. Compared to conventional databases, TimesTen is very efficient and resides entirely in physical memory (RAM).
Architecture and Components of Oracle TimesTen
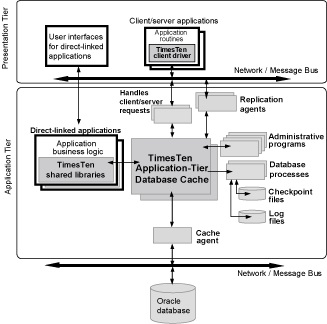
Oracle TimesTen is normally deployed at application tier (middle tier). For existing databases, it can be deployed as in-memory cache database and can be automatically synchronized. It caches performance critical tables and table fragments from the database at application tier and functions same as that of traditional relational databases. With the help of powerful access algorithms and optimized data structures, transactional operations are executed faster and in a much shorter time compared to client/server databases. Moreover, Oracle TimesTen can be embedded in an application that will reduce network overheads and lessen inter-process communications.
The approximate time taken to read a transaction record from the database by Oracle TimesTen is 2.37 microseconds while to insert or update transaction records in a database is less than eight microseconds, as claimed by Oracle.
Key Functionalities of Oracle TimesTen
The software can be upgraded online without any downtime.
It offers a standby database as well as failover to the standby database and automated failure detection by seamless integration with Oracle Clusterware.
The synchronous replication of active databases between standby databases provides zero data loss with maximum data consistency. The application is blocked until the transaction is received and committed on a standby database.
There is a wide range of topologies over LAN and WAN due to the flexible configuration.
Asynchronous replication provides maximum performance and decouples the application from the subscriber receipt process of replicated elements.
Parallel replication provides replication throughput scaling while maintaining transaction execution order.
Oracle TimesTen Accessibility
Applications can access Oracle TimesTen easily via JDBC, ODBC, SQL*Net, Oracle Call Interface (OCI), ODP.NET, and Pro*C/C++ using normal SQL and PLSQL interfaces.
Database objects creation syntax in TimesTen is similar to that of conventional Oracle database.
Application of Oracle TimesTen in Industries
Due to its faster responsive feature, Oracle TimesTen can turn out to be widely suitable for OLTP applications as well as analytic applications where one has to deal with real-time data for decision-making purposes.
Oracle TimesTen can be the boon to industries such as Telecommunications, finance, ticket booking, and reservation and various others which could not endure service downtime and simultaneously requires secure trading systems.
Applications of Oracle TimesTen in Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) further covers high volume web applications, call centers, billing websites, e-commerce websites, financial trading platforms, travel reservations, and booking as well as gaming and many others.
In analytics, we can use Oracle TimesTen in real time decision-making systems, business intelligence dashboards, real-time fraud detection, and stock exchanges.
Limitation in Size of Oracle TimesTen
The limit of size for TimesTen database is in persistence with storage space of physical memory. It varies in both 32-bit as well as 64-bit platforms. In 64-bit you can get the size up to the limit of physical memory available in your machine while in 32-bit it can be maximum up to 4 GB or less depending on the Operating System you are using.
Hardware and Software Requirements for Oracle TimesTen
As Oracle TimesTen resides entirely in physical memory, the more memory you have the more performance you will get. However, there are very few hardware considerations such as a suitable number of CPUs to access applications faster and quicker. Also, if you write your code to use multiple threads, you can take maximum advantage of multiple CPUs.
TimesTen and Oracle 12c
Oracle TimesTen is a separate product comprised of TimesTen database and replication components which an organization needs to purchase. There is an option for Oracle TimesTen Database Cache in Oracle Database 12c, Oracle Database 11g Release 1, and Oracle Database 11g Release 2 that will deploy TimesTen as in-memory database cache in synchronization with Oracle database.
Supported Platforms
Linux: Linux x86, Linux x86-64.
Solaris: Solaris SPARC (64-bit), Solaris SPARC (32-bit client only), Solaris x86-64 (64-bit).
Microsoft Windows: Microsoft Windows x86, Microsoft Windows x64 (64-bit).
IBM: IBM AIX on POWER Systems (64-bit), IBM AIX on POWER Systems (32-bit client only).
Summarizing TimesTen
Benefits
- Support Analytics and OLTP.
- Consistent response time.
- Real-time performance enhancement.
- Zero data loss.
- Automated database failover.
Features
- Response time in microseconds.
- Persistence.
- Durability.
- Scalability.
- Low latency.
- Transactional parallel replication.
- Supports SQL and PLSQL via ODBC, JDBC, ODP.NET, SQL*NET, OCI, and Pro*C/C++.
View the original article here.
Published at DZone with permission of Paras Shah. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments