Refactoring Java Application: Object-Oriented And Functional Approaches
Learn how you can achieve better design using object-oriented and functional approaches. This post includes examples with inheritance and functional interfaces.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeJava Refactoring Approaches
Refactoring in Java has many aspects, but among all of them, there are two fundamentals: object-oriented and functional. Object-oriented existed almost from the first Java version, whereas functional appeared only with Java 1.8 (March 2014).
Object-Oriented (OO) and Functional Approaches
Java is a classical object-oriented language and allows the creation of flexible object structures. After Java 1.8 received functional features, it became capable to operate not only with objects or methods but with lambdas (which is executable code itself). In the functional world, you can operate with functions as with objects in the OO world.

Refactoring Code Using OO Approach
Playing with interfaces and classes using inheritance or composition, you can create reusable generic solutions that can reduce the code amount and increase readability. Classes can be united in the same common structure if they:
- Have similar fields and recognized as the same entity
- Have relations parent/children
- Have similar purpose methods
Refactoring Code Using Functional Approach
Unlike the OO approach, this one extracts the code that has the same behavior. For example, we can recognize similarities in the next examples:
- Implementation has the same return type
- Implementation has the same functionality
Refactoring Example Using Both Approaches
Let's assume we have a small application that makes payments to permanent and contract employees. After each payment, we print a report about Employee and show the in data different formats (JSON and XML for permanent and contractor).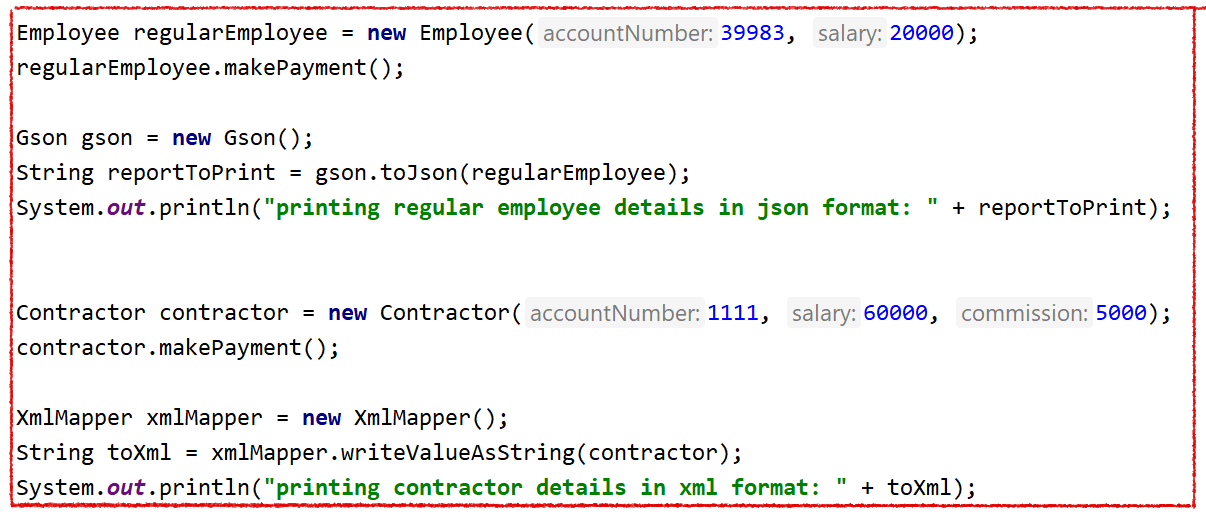
Now let's take a look at the default structure:
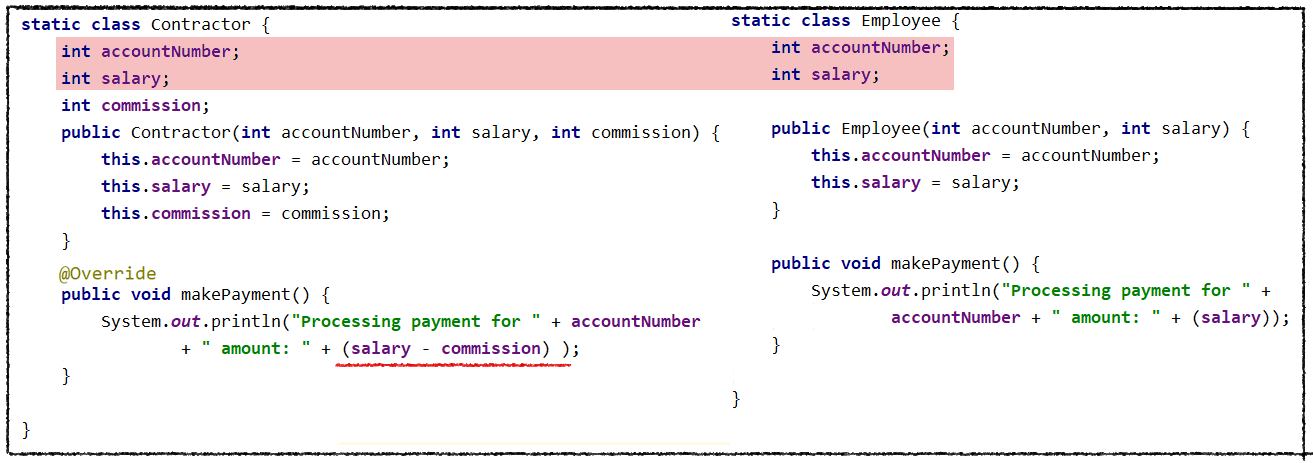
Refactoring Classes Structure
It is pretty visible that Contractor can be a child of Employee class. makePayment can be overridden (also we might create a Payable interface and extract makePayment method, but let's keep it simple). So after refactoring, we might have some fields in common together with reused constructors.

Refactoring Functional Aspects
Now we can review and find similarities from a functional perspective:
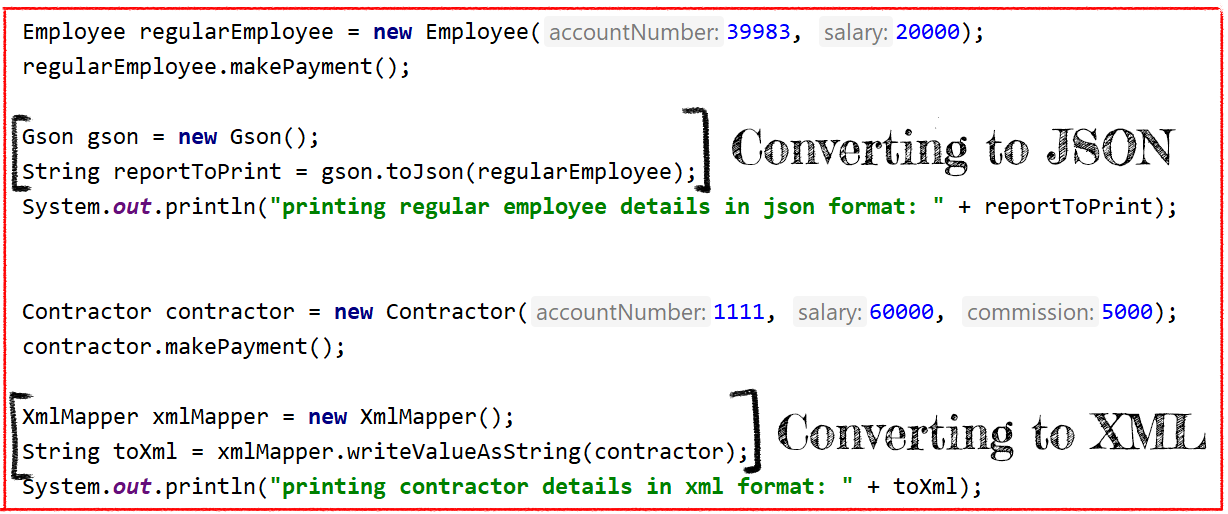
As you can see from the printing report, we process it in the same way: we pass an object and return a string. So we can extract that code as a reusable function and use it dynamically for this business logic or even outside of it.
Creating Function Interface
In order to decide the right functional interface (e.g., Predicate, Consumer, Function, etc.), we need to check our inputs and outputs. In our case, we get an Object and convert it to a String.

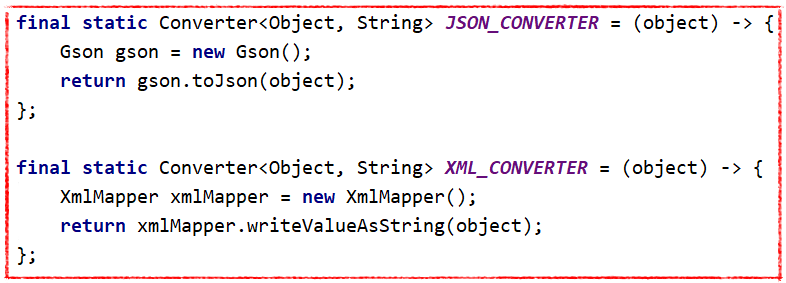
Such an interface is provided by function, but in order to make it more clear, we create our own Converter interface with method serialize. In that case, it would be easily readable:
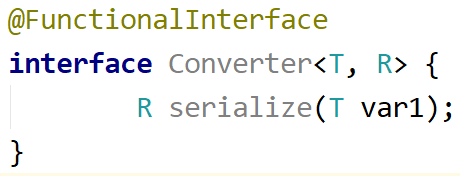
Creating Lambdas: Converter Functional Interface
Now having a functional interface we create two Converters: json and xml. Both of them will match the defined signature (object input and string output).
Now let's use them in our code:
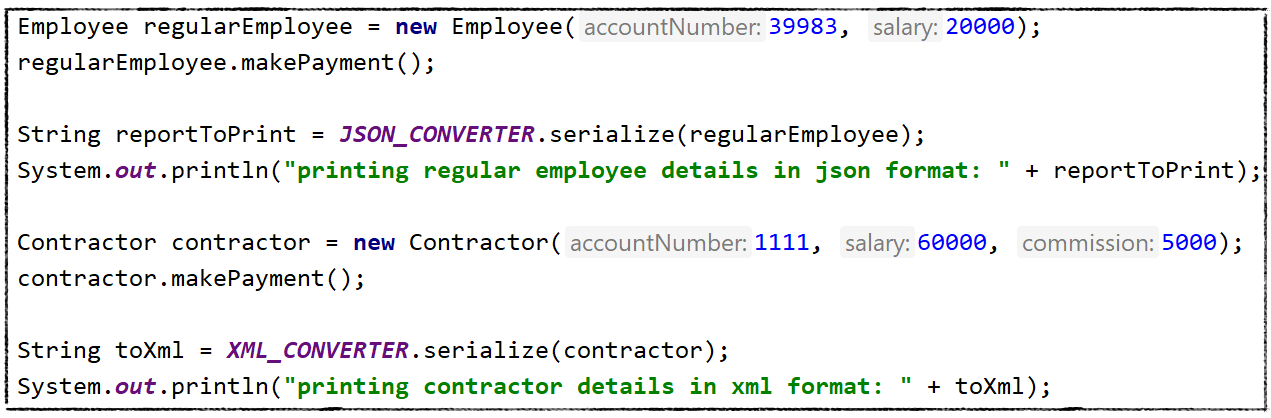
Encapsulating Converters Inside Employee Class
As in the last step, we can encapsulate this function right inside the parent Employer class and use them inside the internal function:

Reviewing the Final Version
As in the last step, we initialize both employers and iterate through them executing payment and printing methods. 
So what do we have at the end?
- Commons fields and methods from parent Employer class are now reused in
Contractor - Extracted functions converters can be replenished in the future without changing the Employer class
- Extracted functions can be reused outside of the Employer class
Criticism

The shown example is not perfect and can be improved. For example, we can hide the Employee/Contractors class behind the interface, and it's good practice! I tried to write a simple example and decided to show just some OO and Functional features.
The functions I've created are not pure functions and some developers insist it's much better to have only pure functions in Java. It's a big discussion outside of this article.
My Personal Criticism About Functions
One of the purposes of this article was to make readers more confident with a functional approach; but at the same time, I'm a person who prefers methods or static methods over functions. Why? Because the old method approach allows you to read code line by line from top to bottom and you can easily see the logic. With a functional approach, you have to return back (or memorize) the function content when the function is called. So, as I think about extracting the same functionality code into methods/static methods - personally, I think it might be better.
Final Message

The main message of this article is:
- Use the object-oriented approach in order to unite similar-by-nature objects in one structure
- Use a functional approach to unite similar-by-functionality code. Together they make code significantly more readable and maintainable. The code used in this article is available here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments