Secure Spring REST With Spring Security and OAuth2
In this tutorial, learn how to add security mechanisms, such as an authorization process and access tokens, to your REST API with Spring Security and OAuth2.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn this post, we are going to demonstrate Spring Security + OAuth2 for securing REST API endpoints on an example Spring Boot project. Clients and user credentials will be stored in a relational database (example configurations prepared for H2 and PostgreSQL database engines). To do it we will have to:
- Configure Spring Security + database
- Create an Authorization Server
- Create a Resource Server
- Get an access token and a refresh token
- Get a secured Resource using an access token
Related Tutorial: Set up a Spring Boot application with PostgreSQL
To simplify the demonstration, we are going to combine the Authorization Server and Resource Server in the same project. As a grant type, we will use a password (we will use BCrypt to hash our passwords).
Before you start you should familiarize yourself with OAuth2 fundamentals.
The OAuth 2.0 specification defines a delegation protocol that is useful for conveying authorization decisions across a network of web-enabled applications and APIs. OAuth is used in a wide variety of applications, including providing mechanisms for user authentication.
The Significance of Securing REST APIs
REST APIs serve as the backbone of modern applications, facilitating data exchange and communication between various components. Whether it's a banking application handling financial transactions, a healthcare platform managing sensitive patient data, or an e-commerce system processing user information, the stakes for securing API endpoints are exceptionally high. Unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security threats not only jeopardize user privacy but also pose significant legal and financial risks to organizations.
Securing REST APIs is not merely a best practice, it's a critical necessity in an era where cyber threats continue to evolve in sophistication. Unsecured APIs can be exploited to gain unauthorized access, manipulate data, or disrupt services, leading to severe consequences for businesses and users alike.
Why Spring Security and OAuth2?
In the complex landscape of web security, Spring Security has emerged as the framework of choice for implementing authentication and authorization in Java applications. Its modular and extensible architecture makes it well-suited for securing REST APIs, providing developers with a powerful toolset to enforce access controls and protect resources.
OAuth2, on the other hand, addresses the specific challenges of authorization by introducing a standardized protocol for delegated access. This protocol allows applications to obtain limited access to a user's resources without exposing sensitive credentials. OAuth2's flexibility makes it particularly suitable for scenarios where third-party applications or services need controlled access to protected resources.
By combining Spring Security and OAuth2, developers can establish a formidable defense against a variety of security threats. Spring Security's capabilities extend from user authentication to intricate authorization scenarios, while OAuth2 simplifies the process of managing access tokens and permissions, enabling a secure yet user-friendly experience.
OAuth Roles
OAuth specifies four roles:
- Resource owner (the User): An entity capable of granting access to a protected resource (for example end-user)
- Resource server (the API server): The server hosting the protected resources, capable of accepting and responding to protected resource requests using access tokens
- Client: An application making protected resource requests on behalf of the resource owner and with its authorization
- Authorization server: The server issuing access tokens to the client after successfully authenticating the resource owner and obtaining authorization [Build an OAuth 2.0 authorization server with Spring Security]
Grant Types
OAuth 2 provides several "grant types" for different use cases. The grant types defined are:
- Authorization Code
- Password
- Client credentials
- Implicit
The overall flow of a Password Grant:
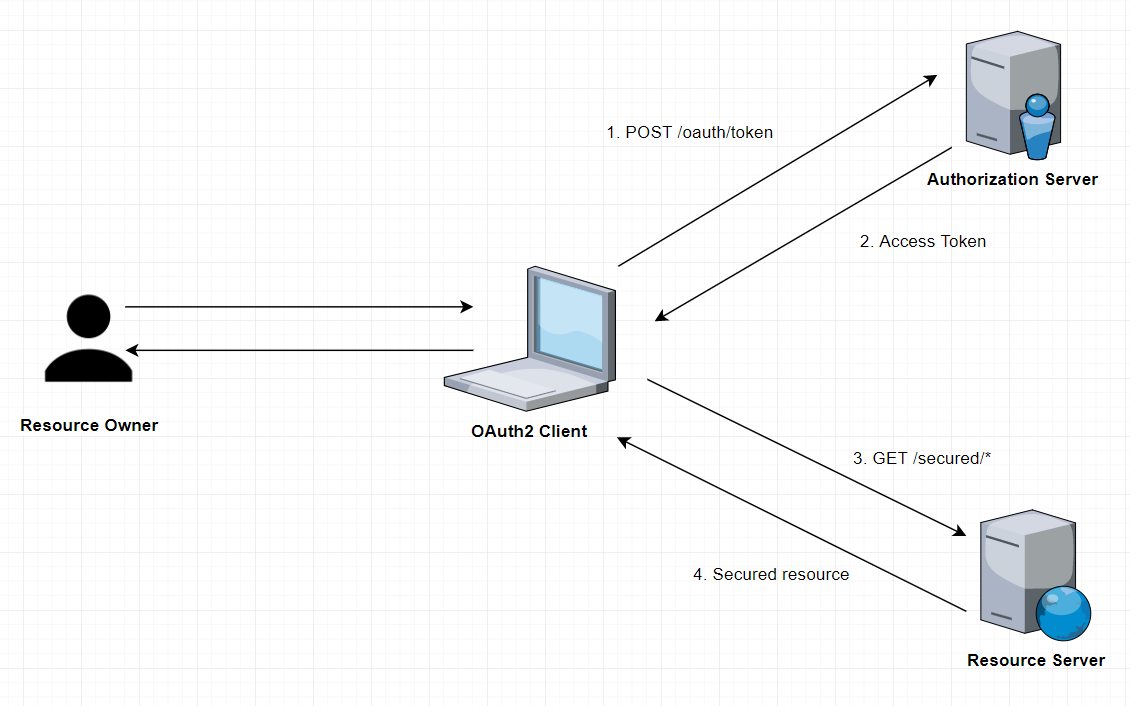
Application
Let's consider the database layer and application layer for our example application.
Business Data
Our main business object is Company:
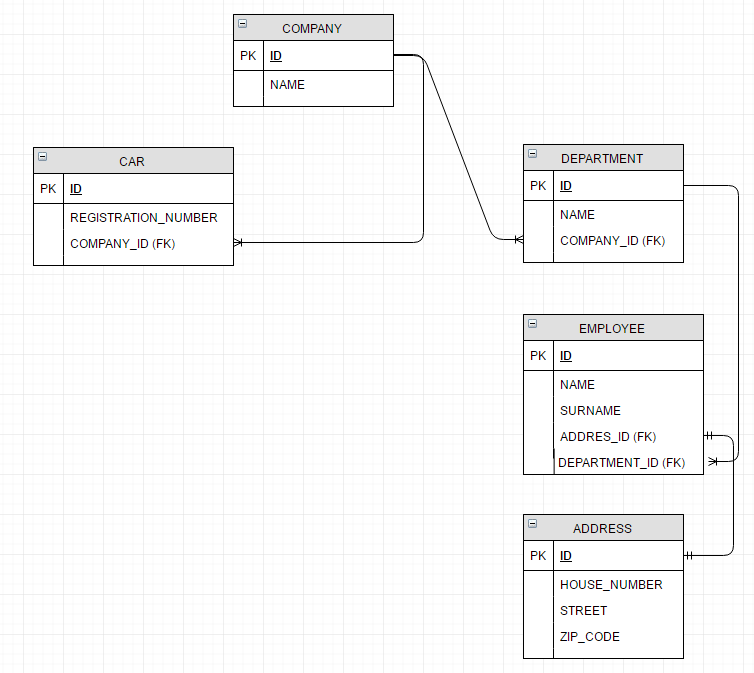
Based on CRUD operations for Company and Department objects, we want to define the following access rules:
COMPANY_CREATECOMPANY_READCOMPANY_UPDATECOMPANY_DELETEDEPARTMENT_CREATEDEPARTMENT_READDEPARTMENT_UPDATEDEPARTMENT_DELETE
In addition, we want to create a ROLE_COMPANY_READER role.
OAuth2 Client Setup
We need to create the following tables in the database (for internal purposes of OAuth2 implementation):
OAUTH_CLIENT_DETAILSOAUTH_CLIENT_TOKENOAUTH_ACCESS_TOKENOAUTH_REFRESH_TOKENOAUTH_CODEOAUTH_APPROVALS
Let's assume that we want to call a resource server like resource-server-rest-api. For this server, we define two clients called:
spring-security-oauth2-read-client(authorized grant types:read)spring-security-oauth2-read-write-client(authorized grant types:read,write)
INSERT INTO OAUTH_CLIENT_DETAILS(CLIENT_ID, RESOURCE_IDS, CLIENT_SECRET, SCOPE, AUTHORIZED_GRANT_TYPES, AUTHORITIES, ACCESS_TOKEN_VALIDITY, REFRESH_TOKEN_VALIDITY)
VALUES ('spring-security-oauth2-read-client', 'resource-server-rest-api',
/*spring-security-oauth2-read-client-password1234*/'$2a$04$WGq2P9egiOYoOFemBRfsiO9qTcyJtNRnPKNBl5tokP7IP.eZn93km',
'read', 'password,authorization_code,refresh_token,implicit', 'USER', 10800, 2592000);
INSERT INTO OAUTH_CLIENT_DETAILS(CLIENT_ID, RESOURCE_IDS, CLIENT_SECRET, SCOPE, AUTHORIZED_GRANT_TYPES, AUTHORITIES, ACCESS_TOKEN_VALIDITY, REFRESH_TOKEN_VALIDITY)
VALUES ('spring-security-oauth2-read-write-client', 'resource-server-rest-api',
/*spring-security-oauth2-read-write-client-password1234*/'$2a$04$soeOR.QFmClXeFIrhJVLWOQxfHjsJLSpWrU1iGxcMGdu.a5hvfY4W',
'read,write', 'password,authorization_code,refresh_token,implicit', 'USER', 10800, 2592000);Note that the password is hashed with BCrypt (4 rounds).
Authorities and Users Setup
Spring Security comes with two useful interfaces:
- UserDetails: Provides core user information
- GrantedAuthority: Represents an authority granted to an Authentication object
To store authorization data we will define the following data model:
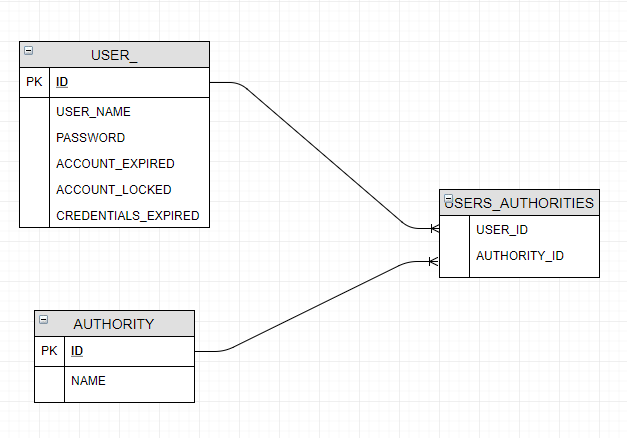
Because we want to come with some pre-loaded data, below is the script that will load all authorities:
INSERT INTO AUTHORITY(ID, NAME) VALUES (1, 'COMPANY_CREATE');
INSERT INTO AUTHORITY(ID, NAME) VALUES (2, 'COMPANY_READ');
INSERT INTO AUTHORITY(ID, NAME) VALUES (3, 'COMPANY_UPDATE');
INSERT INTO AUTHORITY(ID, NAME) VALUES (4, 'COMPANY_DELETE');
INSERT INTO AUTHORITY(ID, NAME) VALUES (5, 'DEPARTMENT_CREATE');
INSERT INTO AUTHORITY(ID, NAME) VALUES (6, 'DEPARTMENT_READ');
INSERT INTO AUTHORITY(ID, NAME) VALUES (7, 'DEPARTMENT_UPDATE');
INSERT INTO AUTHORITY(ID, NAME) VALUES (8, 'DEPARTMENT_DELETE');Here is the script to load all users and assigned authorities:
INSERT INTO USER_(ID, USER_NAME, PASSWORD, ACCOUNT_EXPIRED, ACCOUNT_LOCKED, CREDENTIALS_EXPIRED, ENABLED)
VALUES (1, 'admin', /*admin1234*/'$2a$08$qvrzQZ7jJ7oy2p/msL4M0.l83Cd0jNsX6AJUitbgRXGzge4j035ha', FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, TRUE);
INSERT INTO USER_(ID, USER_NAME, PASSWORD, ACCOUNT_EXPIRED, ACCOUNT_LOCKED, CREDENTIALS_EXPIRED, ENABLED)
VALUES (2, 'reader', /*reader1234*/'$2a$08$dwYz8O.qtUXboGosJFsS4u19LHKW7aCQ0LXXuNlRfjjGKwj5NfKSe', FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, TRUE);
INSERT INTO USER_(ID, USER_NAME, PASSWORD, ACCOUNT_EXPIRED, ACCOUNT_LOCKED, CREDENTIALS_EXPIRED, ENABLED)
VALUES (3, 'modifier', /*modifier1234*/'$2a$08$kPjzxewXRGNRiIuL4FtQH.mhMn7ZAFBYKB3ROz.J24IX8vDAcThsG', FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, TRUE);
INSERT INTO USER_(ID, USER_NAME, PASSWORD, ACCOUNT_EXPIRED, ACCOUNT_LOCKED, CREDENTIALS_EXPIRED, ENABLED)
VALUES (4, 'reader2', /*reader1234*/'$2a$08$vVXqh6S8TqfHMs1SlNTu/.J25iUCrpGBpyGExA.9yI.IlDRadR6Ea', FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, TRUE);
INSERT INTO USERS_AUTHORITIES(USER_ID, AUTHORITY_ID) VALUES (1, 1);
INSERT INTO USERS_AUTHORITIES(USER_ID, AUTHORITY_ID) VALUES (1, 2);
INSERT INTO USERS_AUTHORITIES(USER_ID, AUTHORITY_ID) VALUES (1, 3);
INSERT INTO USERS_AUTHORITIES(USER_ID, AUTHORITY_ID) VALUES (1, 4);
INSERT INTO USERS_AUTHORITIES(USER_ID, AUTHORITY_ID) VALUES (1, 5);
INSERT INTO USERS_AUTHORITIES(USER_ID, AUTHORITY_ID) VALUES (1, 6);
INSERT INTO USERS_AUTHORITIES(USER_ID, AUTHORITY_ID) VALUES (1, 7);
INSERT INTO USERS_AUTHORITIES(USER_ID, AUTHORITY_ID) VALUES (1, 8);
INSERT INTO USERS_AUTHORITIES(USER_ID, AUTHORITY_ID) VALUES (1, 9);
INSERT INTO USERS_AUTHORITIES(USER_ID, AUTHORITY_ID) VALUES (2, 2);
INSERT INTO USERS_AUTHORITIES(USER_ID, AUTHORITY_ID) VALUES (2, 6);
INSERT INTO USERS_AUTHORITIES(USER_ID, AUTHORITY_ID) VALUES (3, 3);
INSERT INTO USERS_AUTHORITIES(USER_ID, AUTHORITY_ID) VALUES (3, 7);
INSERT INTO USERS_AUTHORITIES(USER_ID, AUTHORITY_ID) VALUES (4, 9);Note that the password is hashed with BCrypt (8 rounds).
Application Layer
The test application is developed in Spring Boot + Hibernate + Flyway with an exposed REST API. To demonstrate data company operations, the following endpoints were created:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/secured/company")
public class CompanyController {
@Autowired
private CompanyService companyService;
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.OK)
public @ResponseBody
List<Company> getAll() {
return companyService.getAll();
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET, produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.OK)
public @ResponseBody
Company get(@PathVariable Long id) {
return companyService.get(id);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/filter", method = RequestMethod.GET, produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.OK)
public @ResponseBody
Company get(@RequestParam String name) {
return companyService.get(name);
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST, produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.OK)
public ResponseEntity<?> create(@RequestBody Company company) {
companyService.create(company);
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
ControllerLinkBuilder linkBuilder = linkTo(methodOn(CompanyController.class).get(company.getId()));
headers.setLocation(linkBuilder.toUri());
return new ResponseEntity<>(headers, HttpStatus.CREATED);
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PUT, produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.OK)
public void update(@RequestBody Company company) {
companyService.update(company);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE, produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.OK)
public void delete(@PathVariable Long id) {
companyService.delete(id);
}
}PasswordEncoders
Since we are going to use different encryptions for OAuth2 client and user, we will define separate password encoders for encryption:
- OAuth2 client password – BCrypt (4 rounds)
- User password - BCrypt (8 rounds)
@Configuration
public class Encoders {
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder oauthClientPasswordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(4);
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder userPasswordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(8);Spring Security Configuration
Provide UserDetailsService
Because we want to get users and authorities from the database, we need to tell Spring Security how to get this data. To do it we have to provide an implementation of the UserDetailsService interface:
@Service
public class UserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Override
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
User user = userRepository.findByUsername(username);
if (user != null) {
return user;
}
throw new UsernameNotFoundException(username);
}
}To separate the service and repository layers we will create UserRepository with JPA Repository:
@Repository
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
@Query("SELECT DISTINCT user FROM User user " +
"INNER JOIN FETCH user.authorities AS authorities " +
"WHERE user.username = :username")
User findByUsername(@Param("username") String username);
}Learn more about how to upgrade to Spring Boot 3.0 for Spring Data JPA
Setup Spring Security
The @EnableWebSecurity annotation and WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter work together to provide security to the application. The @Order annotation is used to specify which WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter should be considered first.
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@Order(SecurityProperties.ACCESS_OVERRIDE_ORDER)
@Import(Encoders.class)
public class ServerSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder userPasswordEncoder;
@Override
@Bean
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception {
return super.authenticationManagerBean();
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(userPasswordEncoder);
}
}OAuth2 Configuration
First of all, we have to implement the following components:
- Authorization Server
- Resource Server
Authorization Server
The authorization server is responsible for the verification of user identity and providing the tokens.

Spring Security handles the Authentication and Spring Security OAuth2 handles the Authorization. To configure and enable the OAuth 2.0 Authorization Server we have to use @EnableAuthorizationServer annotation.
@Configuration
@EnableAuthorizationServer
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
@Import(ServerSecurityConfig.class)
public class AuthServerOAuth2Config extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("dataSource")
private DataSource dataSource;
@Autowired
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder oauthClientPasswordEncoder;
@Bean
public TokenStore tokenStore() {
return new JdbcTokenStore(dataSource);
}
@Bean
public OAuth2AccessDeniedHandler oauthAccessDeniedHandler() {
return new OAuth2AccessDeniedHandler();
}
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer oauthServer) {
oauthServer.tokenKeyAccess("permitAll()").checkTokenAccess("isAuthenticated()").passwordEncoder(oauthClientPasswordEncoder);
}
@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception {
clients.jdbc(dataSource);
}
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints) {
endpoints.tokenStore(tokenStore()).authenticationManager(authenticationManager).userDetailsService(userDetailsService);
}
}Some important points to note - we:
- Defined the
TokenStorebean to let Spring know to use the database for token operations - Overrode the configure methods to use the custom
UserDetailsServiceimplementation,AuthenticationManagerbean, and OAuth2 client’s password encoder - Defined handler bean for authentication issues
- Enabled two endpoints for checking tokens (/oauth/check_token and /oauth/token_key) by overriding the configure (
AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigureroauthServer) method
Resource Server
A Resource Server serves resources that are protected by the OAuth2 token.
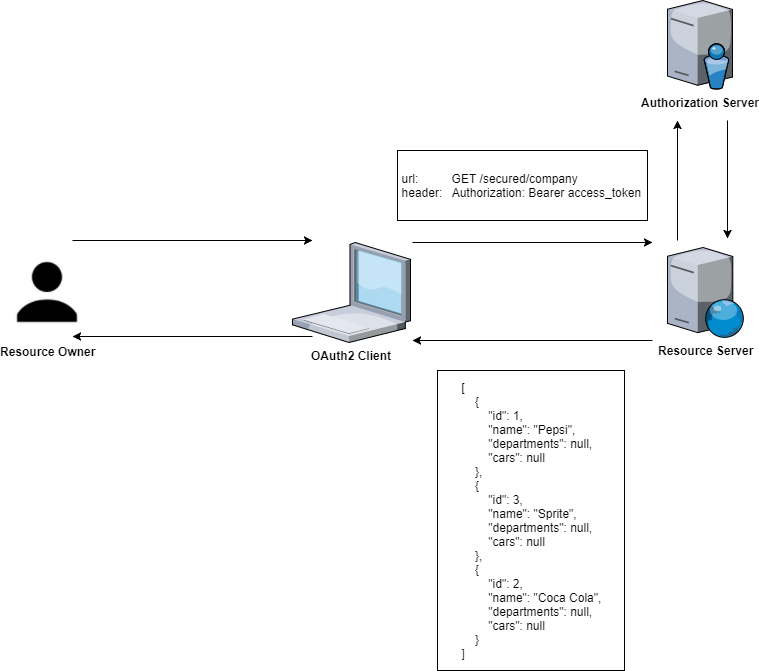
Spring OAuth2 provides an authentication filter that handles protection. The @EnableResourceServer annotation enables a Spring Security filter that authenticates requests via an incoming OAuth2 token.
@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
public class ResourceServerConfiguration extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter {
private static final String RESOURCE_ID = "resource-server-rest-api";
private static final String SECURED_READ_SCOPE = "#oauth2.hasScope('read')";
private static final String SECURED_WRITE_SCOPE = "#oauth2.hasScope('write')";
private static final String SECURED_PATTERN = "/secured/**";
@Override
public void configure(ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer resources) {
resources.resourceId(RESOURCE_ID);
}
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.requestMatchers()
.antMatchers(SECURED_PATTERN).and().authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.POST, SECURED_PATTERN).access(SECURED_WRITE_SCOPE)
.anyRequest().access(SECURED_READ_SCOPE);
}
}The configure(HttpSecurity http) method configures the access rules and request matchers (path) for protected resources using the HttpSecurity class. We secure the URL paths /secured/*. It’s worth noting that to invoke any POST method request, the write scope is needed.
Let's check if our authentication endpoint is working – invoke:
curl -X POST \
http://localhost:8080/oauth/token \
-H 'authorization: Basic c3ByaW5nLXNlY3VyaXR5LW9hdXRoMi1yZWFkLXdyaXRlLWNsaWVudDpzcHJpbmctc2VjdXJpdHktb2F1dGgyLXJlYWQtd3JpdGUtY2xpZW50LXBhc3N3b3JkMTIzNA==' \
-F grant_type=password \
-F username=admin \
-F password=admin1234 \
-F client_id=spring-security-oauth2-read-write-clientBelow are screenshots from Postman:
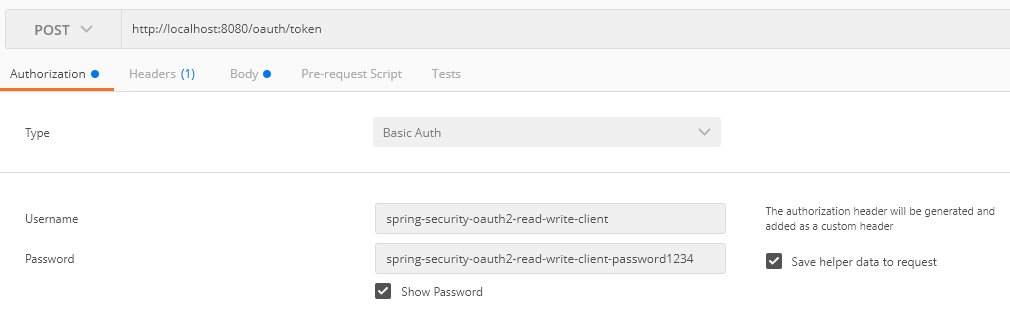
As well as:
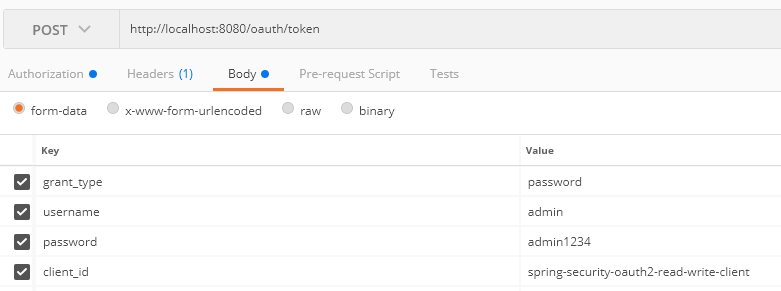
You should get a response similar to the following:
{
"access_token": "e6631caa-bcf9-433c-8e54-3511fa55816d",
"token_type": "bearer",
"refresh_token": "015fb7cf-d09e-46ef-a686-54330229ba53",
"expires_in": 9472,
"scope": "read write"
}Access Rules Configuration
We decided to secure access to the Company and Department objects on the service layer. We have to use the @PreAuthorize annotation.
@Service
public class CompanyServiceImpl implements CompanyService {
@Autowired
private CompanyRepository companyRepository;
@Override
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('COMPANY_READ') and hasAuthority('DEPARTMENT_READ')")
public Company get(Long id) {
return companyRepository.find(id);
}
@Override
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('COMPANY_READ') and hasAuthority('DEPARTMENT_READ')")
public Company get(String name) {
return companyRepository.find(name);
}
@Override
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('COMPANY_READER')")
public List<Company> getAll() {
return companyRepository.findAll();
}
@Override
@Transactional
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('COMPANY_CREATE')")
public void create(Company company) {
companyRepository.create(company);
}
@Override
@Transactional
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('COMPANY_UPDATE')")
public Company update(Company company) {
return companyRepository.update(company);
}
@Override
@Transactional
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('COMPANY_DELETE')")
public void delete(Long id) {
companyRepository.delete(id);
}
@Override
@Transactional
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('COMPANY_DELETE')")
public void delete(Company company) {
companyRepository.delete(company);
}
}Let’s test if our endpoint is working fine:
curl -X GET \
http://localhost:8080/secured/company/ \
-H 'authorization: Bearer e6631caa-bcf9-433c-8e54-3511fa55816d'Let's see what will happen if we authorize with it spring-security-oauth2-read-client – this client has only the read scope defined.
curl -X POST \
http://localhost:8080/oauth/token \
-H 'authorization: Basic c3ByaW5nLXNlY3VyaXR5LW9hdXRoMi1yZWFkLWNsaWVudDpzcHJpbmctc2VjdXJpdHktb2F1dGgyLXJlYWQtY2xpZW50LXBhc3N3b3JkMTIzNA==' \
-F grant_type=password \
-F username=admin \
-F password=admin1234 \
-F client_id=spring-security-oauth2-read-clientThen for the below request:
http://localhost:8080/secured/company \
-H 'authorization: Bearer f789c758-81a0-4754-8a4d-cbf6eea69222' \
-H 'content-type: application/json' \
-d '{
"name": "TestCompany",
"departments": null,
"cars": null
}'We are getting the following error:
{
"error": "insufficient_scope",
"error_description": "Insufficient scope for this resource",
"scope": "write"
}Summary
In this blog post, we showed OAuth2 authentication with Spring. Access rights were defined straightforwardly — by establishing a direct connection between User and Authorities. To enhance this example, we can add an additional entity — Role — to improve the structure of the access rights.
The source code for the above listings can be found in this GitHub project.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments