Implementation of Hybrid Encryption Using Java 1.8 and OpenSSL
Here we are going to understand why to use hybrid encryption and see an implementation of hybrid encryption out of AES symmetric encryption algorithm and RSA asymmetric algorithm using Java 1.8 and OpenSSL.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeSymmetric encryption is a type of encryption in which a single key is used to both encrypt and decrypt the data, whereas in asymmetric encryption approach public/private key pair is used to do the same. This rules out the risk of mishandling of the key as the public key is only shared with the clients and the private key is kept secret. Client can encrypt the data with the key and send the data securely over any standard data sharing protocols. At the receiver end, the private key is used to decrypt the data.
But the time to encrypt the data with asymmetric encryption grows significantly proportionately with the size of data. Here symmetric encryption does the job quite efficiently.
What Is Hybrid Encryption?
Hybrid encryption as the name suggests combines the best of both the worlds of symmetric and asymmetric encryption and allows us to encrypt the data efficiently while ensuring secrecy is not compromised .
At the client end, we encrypt the data with symmetric encryption using secret key. The secret key is then encrypted with the asymmetric public key. Then, both the encrypted key and encrypted data are sent to the receiver.
At the receiver end the secret key is retrieved by decrypting the encrypted secret key with the private key. The secret key is then used to decrypt the encrypted data.
Now we are going to take a journey from RSA public/private key generation via OpenSSL to key importing in Java, then data encryption, data exporting till data decryption in step by step manner. The steps are shown below...
- How to create RSA public/private key with certificate
- How to extract modulus, public exponent and private exponent from the private key and certificate
- How to extract modulus and public exponent from certificate
- How to validate the key with certificate
- How to construct RSA key pair in java using modulus and public/private exponent
- Example of data encryption using hybrid encryption technology.
- Example of data decryption using hybrid decryption technology.
1. Generation of RSA Key-Pair Using OpenSSL With Self-Signing Certificate
xxxxxxxxxx
openssl req -x509 -sha256 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout privateKey.key -out certificate.crt
- -x509 is a certificate signing utility
- -newkey rsa:2048 is for creating RSA key of size 2048bytes (privateKey.key)
- -days 365 is the validity time frame for the certificate (certificate.crt)
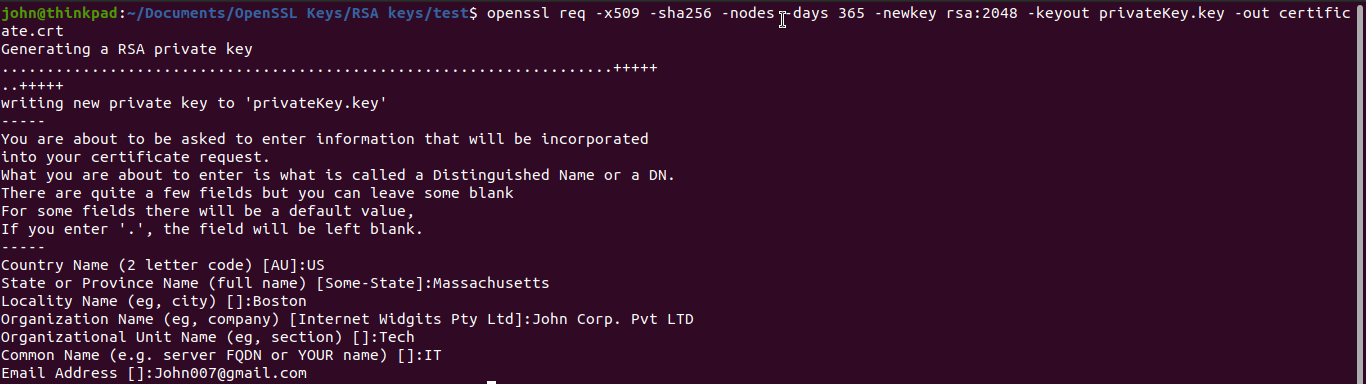
The certificate contains the details of the organization (who is generating the key) along with the public key.
The private key holds the details of both private and public key. Therefore the private key is kept secured within the key generating organisation, whereas the certificate is shared with the clients who wants to send encrypted data to the organisation.
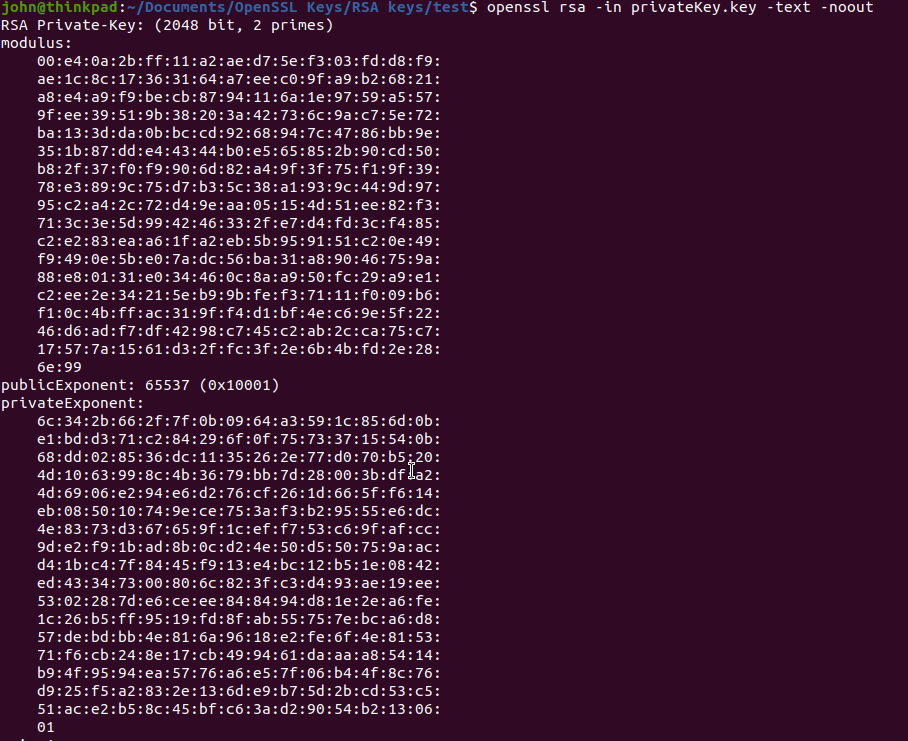
1.1 How to Extract Modulus, Public Exponent and Private Exponent From the Private Key
xxxxxxxxxx
openssl rsa -in privateKey.key -text -noout
1.2 How to Extract Modulus and Public Exponent from The Certificate
xxxxxxxxxx
openssl x509 -in certificate.crt -text -noout
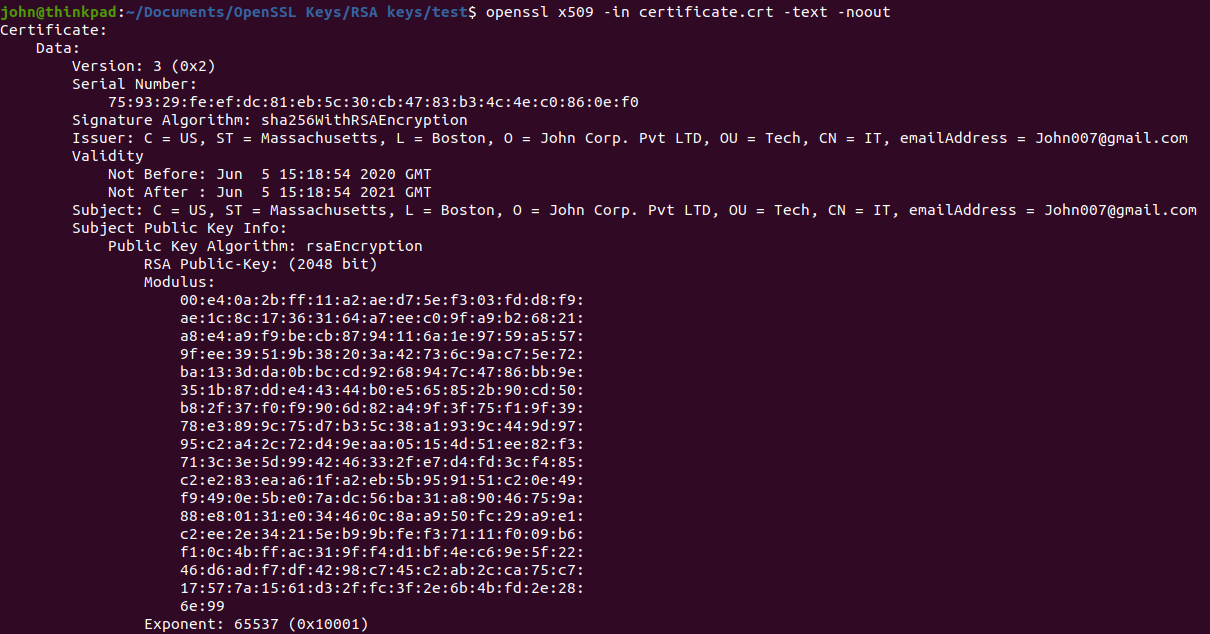
1.3 How to Validate the Certificate with The Private Key?
The modulus and the public exponent of the certificate will be the same as that of the private key.
2. Construction of RSA Key-Pair in Java Using Modulus and Public/Private Exponent
Class: RsaKeyExtractor.class
xxxxxxxxxx
package utilities;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.security.KeyFactory;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import java.security.spec.InvalidKeySpecException;
import java.security.spec.RSAPrivateKeySpec;
import java.security.spec.RSAPublicKeySpec;
public class RsaKeyExtractor {
private BigInteger mod;
private BigInteger pubExp;
private BigInteger pvtExp;
public RsaKeyExtractor(BigInteger mod, BigInteger pubExp) {
this.mod = mod;
this.pubExp = pubExp;
this.pvtExp = null;
}
public RsaKeyExtractor(BigInteger mod, BigInteger pubExp, BigInteger pvtExp) {
this.mod = mod;
this.pubExp = pubExp;
this.pvtExp = pvtExp;
}
public PrivateKey getPrivateKey()
throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidKeySpecException, InvalidRsaKey {
if(pvtExp==null || mod==null)
throw new InvalidRsaKey("PrivateExponent or Modulus is Null");
RSAPrivateKeySpec keySpec = new RSAPrivateKeySpec(mod, pvtExp);
KeyFactory fact = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
PrivateKey privKey = fact.generatePrivate(keySpec);
return privKey;
}
public PublicKey getPublicKey()
throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidKeySpecException, InvalidRsaKey {
if(pvtExp==null || mod==null)
throw new InvalidRsaKey("PublicExponent or Modulus is Null");
RSAPublicKeySpec keySpec = new RSAPublicKeySpec(mod, pubExp);
KeyFactory fact = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
PublicKey pubKey = fact.generatePublic(keySpec);
return pubKey;
}
}
This class shows how to instantiate PublicKey and PrivateKey objects in java 1.8. For instantiating the PublicKey object we need modulus and public exponent. Similarly to instantiate PrivateKey object we need modulus and the private exponent.
3. Example of the Implementation of Hybrid Encryption Technology for Data Encryption
Class: Encrypter.java
xxxxxxxxxx
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Base64;
import javax.crypto.KeyGenerator;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import utilities.AsymmetricCipher;
import utilities.SymmetricCipher;
public class Encrypter {
public static File encryptionFlow(String path, PublicKey publicKey, int secretKeySize, String secretKeyAlgo, String symmetricAlgo, String asymmetricAlgo) {
// Secret Key Generation
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
File encryptedFile = null;
try {
File file = new File(path);
// AES 128
keyGenerator = KeyGenerator.getInstance(secretKeyAlgo);
keyGenerator.init(secretKeySize);
SecretKey secretKey = keyGenerator.generateKey();
byte[] secretkeyByte = secretKey.getEncoded();
System.out.println("\n@EncFlow: Original Secret Key");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(secretkeyByte));
// Reading content
FileReader reader = new FileReader(file);
BufferedReader buffReader = new BufferedReader(reader);
char[] buffer = new char[100];
int nChar = buffReader.read(buffer);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (nChar>0) {
for(int i=0; i<nChar; i++) {
sb.append(buffer[i]);
}
nChar = buffReader.read(buffer);
}
String content = sb.toString();
byte[] contentBytes = content.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("\n@Content Bytes");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(contentBytes));
byte[] encDataBytes = SymmetricCipher.encrypt(contentBytes, symmetricAlgo, secretKey);
System.out.println("\n@Encrypted Content Bytes");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(encDataBytes));
byte[] encSecretkey = AsymmetricCipher.encrypt(secretkeyByte, asymmetricAlgo, publicKey);
System.out.println("\n@Encrypted Secret Key : ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(encSecretkey));
Base64.Encoder encoder = Base64.getEncoder();
byte[] base64EncSecKey = encoder.encode(encSecretkey);
byte[] base64EncData = encoder.encode(encDataBytes);
String encSecretkeyString = new String(base64EncSecKey, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
String encDataString = new String(base64EncData, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("\n@Encrypted Secret Key String: ");
System.out.println(encSecretkeyString);
System.out.println("\n@Encrypted Data String: ");
System.out.println(encDataString);
// FileContent
sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(encSecretkeyString).append(System.lineSeparator()).append(encDataString);
// Creation of encrypted file
String encFilePath = file.getPath().concat(".enc");
encryptedFile = new File(encFilePath);
FileWriter writer;
writer = new FileWriter(encryptedFile);
BufferedWriter bufWriter = new BufferedWriter(writer);
bufWriter.write(sb.toString());
bufWriter.close();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
return encryptedFile;
}
}
Here first the AES symmetric secret key is generated. Then the data which is read from the file is encrypted using the secret key and suitable AES symmetric key algorithm. The secret key byte array is then encrypted using the public key of RSA asymmetric encryption technique.
Now both encrypted secret key and encrypted data are encoded with base64 encoder in order to preserve the encrypted data from any kind of data corruption/misinterpretation during or after data transfer process.
Finally the encoded and encrypted secret key and the data is written to a file sequentially, each in separate line. Now the new file is secured and safe to transfer via any standard file transfer protocol to the certificate owning organisation.
4. Example of Implementation of Hybrid Encryption Technology for Data Decryption
Class: Decrypter.java
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Base64;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import utilities.AsymmetricCipher;
import utilities.SymmetricCipher;
public class Decrypter {
public static File decryptionFlow(String path, PrivateKey pvtKey, String secretKeyAlgo, String symmetricAlgo, String asymmetricAlgo) throws IOException {
File inFile = new File(path);
String[] contents = extractDataElements(inFile);
System.out.println("Content Count: "+contents.length);
for (int i = 0; i < contents.length; i++) {
contents[i] = filterNewlineChars(contents[i]);
}
System.out.println("\n@Base64 encoded Encrypted Secret Key String: ");
System.out.println(contents[0]);
System.out.println("\n@Base64 encoded Encrypted Data String: ");
System.out.println(contents[1]);
Base64.Decoder decoder = Base64.getDecoder();
byte[] encSecretKeyByte = decoder.decode(contents[0]);
System.out.println("\n@Enc SecretKey");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(encSecretKeyByte));
byte[] secretKeyBytes = AsymmetricCipher.decrypt(encSecretKeyByte, asymmetricAlgo, pvtKey);
System.out.println("\n@Secret Key Bytes: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(secretKeyBytes));
SecretKey secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(secretKeyBytes, 0, secretKeyBytes.length, secretKeyAlgo);
ArrayList<byte[]> dataList = new ArrayList<byte[]>();
for (int i = 1; i < contents.length; i++) {
byte[] encStrByte = decoder.decode(contents[i]);
System.out.println("\n@Encrypted Data Bytes: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(encStrByte));
byte[] messageByte = SymmetricCipher.decrypt(encStrByte, symmetricAlgo, secretKey);
System.out.println("\n@Data Bytes: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(messageByte));
dataList.add(messageByte);
contents[i] = new String(messageByte, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
int lastIndx = inFile.getPath().lastIndexOf(".");
String outpath = inFile.getPath().substring(0, lastIndx);
lastIndx = outpath.lastIndexOf(".");
outpath = outpath.substring(0, lastIndx).concat(".dat");
outpath = outpath.substring(0, lastIndx).concat(".dat");
File nwFile = new File(outpath);
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(nwFile);
for (byte[] data : dataList) {
os.write(data);
}
os.close();
return nwFile;
}
private static String[] extractDataElements(File file) {
String[] dataArr = null;
FileReader reader;
BufferedReader bufReader;
try {
char nwLine = '\n';
char cr = '\r';
reader = new FileReader(file);
bufReader = new BufferedReader(reader);
//Extracting the Encrypted Secret Key
String encSecretKey = bufReader.readLine();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
char[] buffer = new char[10];
int nChars = bufReader.read(buffer);
while (nChars>0) {
for(int i=0; i<nChars; i++) {
sb.append(buffer[i]);
}
nChars = bufReader.read(buffer);
}
dataArr = new String[2];
dataArr[0] = encSecretKey;
dataArr[1] = sb.toString();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return dataArr;
}
private static String filterNewlineChars(String data) {
if (data == null) {
return null;
}
char carriageReturn = '\r';
char newLine = '\n';
int length = data.length();
int indx = 0;
// Checking nextLine chars at the start of the line
while (indx < length && (data.charAt(indx) == carriageReturn || data.charAt(indx) == newLine)) {
indx++;
}
int startIndx = indx;
indx = length-1;
// Checking nextLine Chars at the end of the line
while (indx >= startIndx && (data.charAt(indx) == carriageReturn || data.charAt(indx) == newLine)) {
indx--;
}
int endIndx = indx+1;
String cleanData = data.substring(startIndx, endIndx);
System.out.println("AcLength:" + data.length() + ", ModLength:" + cleanData.length());
return cleanData;
}
}
Similar to the data encryption process, now during decryption we have to follow the reverse process of that of encryption flow.
The contents of the encrypted file is read line by line and filtered off any newline chars. The first line is the base64 encoded encrypted secret key while the second line is the base64 encoded encrypted data. Both are decoded using the Base64 decoder. Next, the secret key byte array is decrypted using the private key and RSA asymmetric algorithm, as used during encryption. Then the SecretKey is instantiated in java using the secret key byte array and the AES symmetric algorithm, same as used to create the secret key during the encryption flow. The data is then decrypted using the secret key. Finally, the decrypted data is extracted.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments