Setting Up a Spring Cloud Config Client
Learn how to create a configuration client which can communicate with a configuration server to access a git repository and fetch configuration files.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis post is a continuation of another post of mine, "How to Setup the Spring Cloud Config Server With Git," i.e., setting up of Spring cloud config server with a git repository. In my earlier post, successful communication was established between a cloud config server and a git repository. In this post, the focus will be on the development of a cloud config client and its interaction with a cloud config server.
Prerequisites
Cloud Config Client Setup
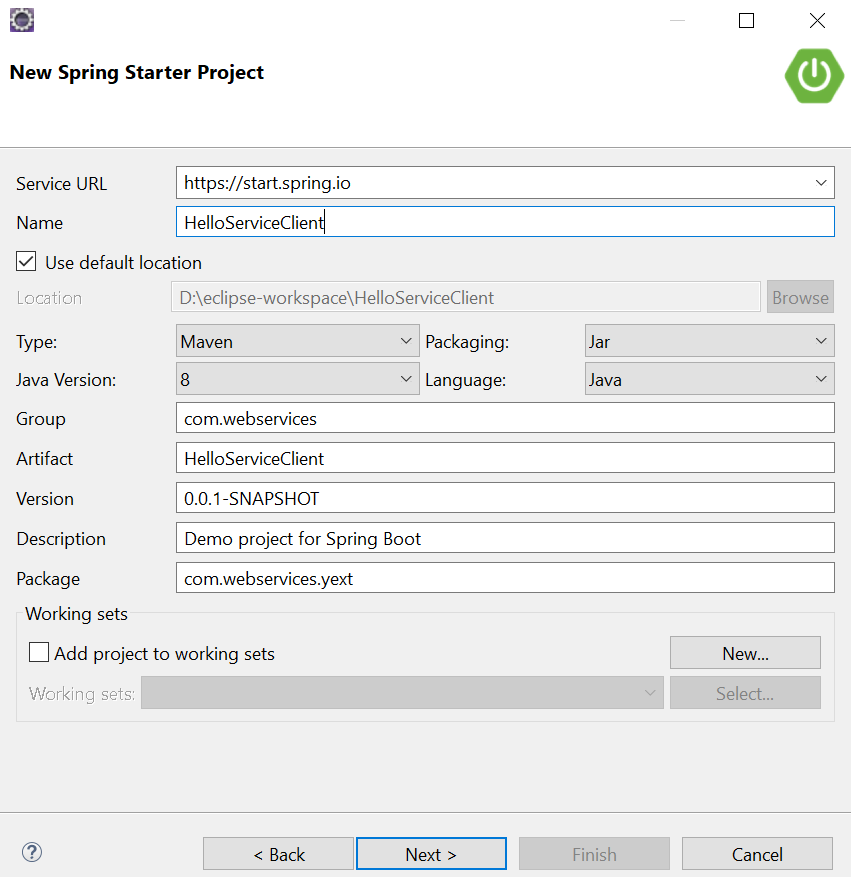
- Create a new Spring Starter Project with the name "HelloServiceClient".
![]()
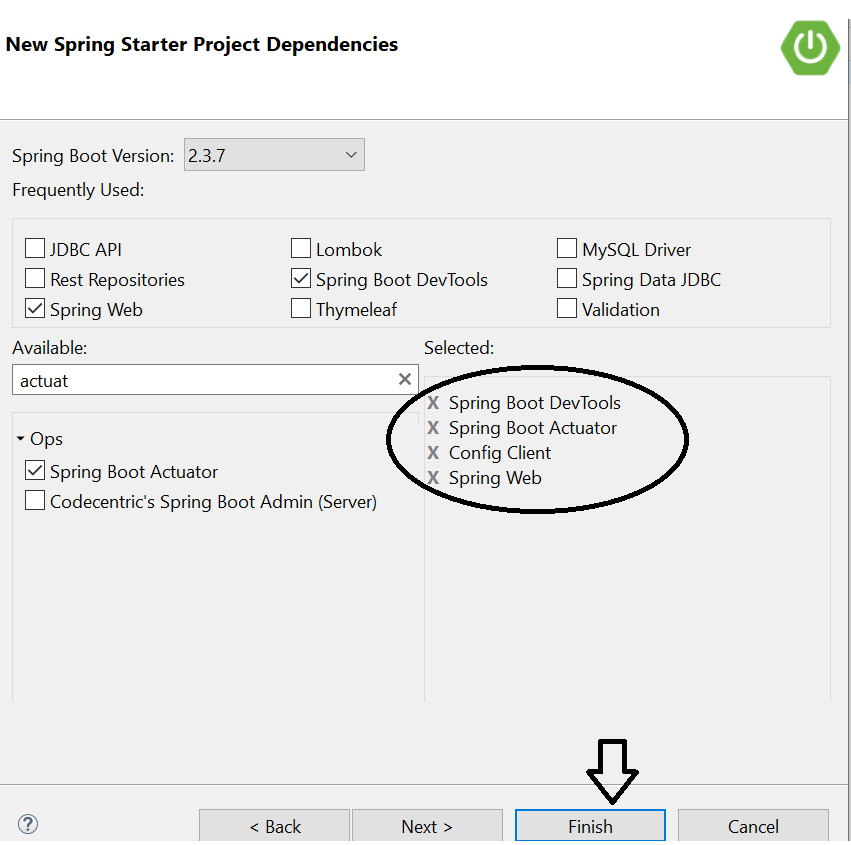
- On the "Next" screen, select Spring version 2.3.7 with dependencies like Spring Web (for REST Controller development), Config Client (to make it a cloud config client), Actuator (for easy monitoring), and DevTools (for easy redeployment). Click "Next" to create a project. If you choose to work in Spring v.2.4+, then "Cloud Bootstrap" will be added as an additional dependency.
![]()
- Once the project is created, go to the resource folder and delete the
application.propertiesfile. The application specific properties will be read from the git repository, so this file is no longer required. You will to add a new file,bootstrap.properties, in place ofapplication.propertiesinside the resource folder. This file will be loaded during the service start process and will be used to access the cloud config server.![]()
- The
bootstrap.propertiesfile will have following properties:Properties files
x
1spring.application.name=hello-service2server.port=80803spring.profiles.active=development4spring.cloud.config.uri=http://localhost:8888
- spring.application.name - This is the identifier for the microservice application and there will be a property file with the same name in the repository. This will identify which property file to fetch from the repository for a particular microservice. For example, for
hello-service.properties, we would usehello-service-development.properties(the-developmentsuffix tells the system to fetch code for development profile). - spring.profile.active - Identifier used to for environment, i.e. development/production, etc.
- spring.cloud.config.uri - Specifies the URL for the Spring cloud config server.
- spring.application.name - This is the identifier for the microservice application and there will be a property file with the same name in the repository. This will identify which property file to fetch from the repository for a particular microservice. For example, for
- Now create a REST Controller to access the attribute available in the git property file.
Java
xxxxxxxxxx123
1package com.hello.example.controller;23import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;4import org.springframework.cloud.context.config.annotation.RefreshScope;5import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;6import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;7import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;8import org.springframework.ui.Model;9import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;10import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;11121314public class HelloController {151617private Environment env;1819("/hello")20public ResponseEntity<String> getHello(Model model) {21return new ResponseEntity<String>( env.getProperty("message"), HttpStatus.OK);22}23}
Here, the
"message"attribute is available inside thehello-service-development.propertiesfile which is available in the git repository.Properties files
xxxxxxxxxx1
1message=Hello world - this message is from development
The basic setup is now complete. Let's run the application as "Spring Boot App." The application will run at default port, 8080 (make sure, the HelloConfigServer application is running at port 8888. If it's not running, then first start the HelloConfigServer application. Later. start the HelloConfigClient application, as the client application load properties during the start up process).
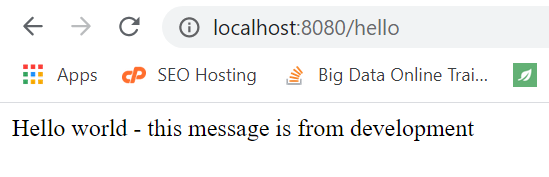
To test the config client, go to the URL http://localhost:8080/hello. The config client will look for the configuration file (
hello-service-development.properties) in our git repo – the expected response is below:![]()
Congratulations on setting up the cloud config client successfully and creating communication with the config server!
Configuration Update
Now that communication is set up between the cloud config client, the cloud config server, and the git repository, w will happen if any property file is updated after the application's deployment? Can the config client fetch the latest configuration? No, Service/Application needs to be restarted to get the latest update. This is a problem.
To solve this problem, Spring Boot has provided an approach to fetch the latest configuration information from repository at runtime with the help of the @RefreshScope annotation and and the Actuator dependency.
@RefreshScope - By default, the configuration values are read at the client’s server startup. This annotation forces the bean to refresh its configuration, i.e. to pull updated configurations from the repository via a config server without the application restarting in real-time.
Actuator - Once the /actuator/refresh event for the application is triggered, all the beans that are annotated with @RefreshScope get refreshed. This means updating values retrieved from the config server and updating the client's microservice bean.
We can trigger the refresh event with the help of the URL http://localhost:8080/actuator/refresh. This will result in refreshing all the beans annotated with @RefreshScope. Since the HelloController is annotated with @RefreshScope, its properties will get refreshed.
Conclusion
We are able to create a configuration client which can communicate with a configuration server to access a git repository and fetch configuration files.
The source code related to this tutorial is available on GitHub.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.


Comments