Spring Boot: Metrics With Micrometer and AWS CloudWatch
Learn more about how to make Spring Boot work with Micrometer and AWS CloudWatch.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeSome time ago, I wrote a blog on how to configure CloudWatch metrics with Spring Boot. It was all before micrometer and depended heavily on Netflix Servo Metrics. Time was slowly passing and civilizations prospered, but it’s still difficult to find info on how to make Spring Boot work with Micrometer CloudWatch.
So, here it goes.
TL;DR
If you are not interested in why and just want to make Spring Boot work with AWS CloudWatch, do the following:
- Add dependencies (build.gradle)
dependencies {
compile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-actuator')
compile('org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-aws')
compile('io.micrometer:micrometer-registry-cloudwatch:1.0.6')
}- Set the required properties:
management.metrics.export.cloudwatch.namespace=m3trics2
management.metrics.export.cloudwatch.batchSize=20That’s it. If you are interested in learning the details, then please continue reading :). You can also check and follow everything in the working code
Micrometer.io and CloudWatch Metrics Exporter
It’s not my goal here to describe Mirometer itself, nor the concept of different metrics, as all the info can be easily found in the Micrometer docs.
Setting up Micrometer with Spring Boot is super easy, and it’s mostly just adding a specified registry as a dependency, where the registries are different metrics systems that again are listed on Micrometer page:
- Atlas
- Datadog
- Ganglia
- Graphite
- Influx
- JMX
- New Relic
- Prometheus
- SignalFx
- StatsD
- Wavefront
Study the list; however, you will not find CloudWatch there. Still, the registry exists and can be found both in the repo and on GitHub waiting to be used.
When making a particular metric system (like e.g. datadog) work with Spring boot through Micrometer, the required components can be found in two places:
micrometer-registry-datadog.jar(in case of datadog) containing a Spring-Boot-independent meter registry and utils-
spring-boot-actuator-autoconfigure.jarwhere we can findautoConfigurationsfor different systems (like DatadogMetricsExportAutoConfiguration), thus automatically creating an exporter for metrics system when given registry is present on the classpath.
The situation with CloudWatch, however, is a little different and we won’t find it’s AutoConfiguration in the actuator jar.
The thing is: when creating metrics exporter for CloudWatch, we will need Amazon CloudWatch client. With region providers, detecting if an app is running in the cloud or not, login profiles, etc., such a client is not a trivial piece to write. Luckily, everything is already written — not in Spring Boot but in Spring Cloud.
Because it’s Spring Cloud that should depend on Spring Boot, not the other way around, CloudWatchExportAutoConfiguration can’t be put together with other systems in Spring Boot’s actuator. So, to use it, we need to add one more dependency:
-
spring-cloud-aws-autoconfigure.jar(spring-boot-actuator-autoconfigure.jaris still needed because of classes likeStepRegistryProperties)
Properties
Check the CloudWatchExportAutoConfiguration and you will find that the only property needed to enable metrics export to CloudWatch is:
management.metrics.export.cloudwatch.namespace=m3trics2
As the name suggests, property names the custom CloudWatch namespace where you will find your metrics.
Because of the bug in the cloud/ Micrometer code, one more property is needed:
management.metrics.export.cloudwatch.batchSize=20
To understand it, you need to know that metrics are sent to CloudWatch asynchronously in batches and Amazon CloudWatch client has a limit of max 20 metrics sent in a single batch. CloudWatchConfig handles it correctly, but then, the actual properties are taken from CloudWatchProperties. And this one just takes the batchSize from the property or sets the default value to 10000, not caring about AWS restriction.
Example Metrics
Example code generating metrics can be found here. It’s a super simple web application generating a random number every time a particular URL is hit (/lucky-number). There is also scheduler hitting this URL every five seconds to generate demo traffic.
The app demonstrates that dozens of metrics are added automatically by Spring Boot, for example:
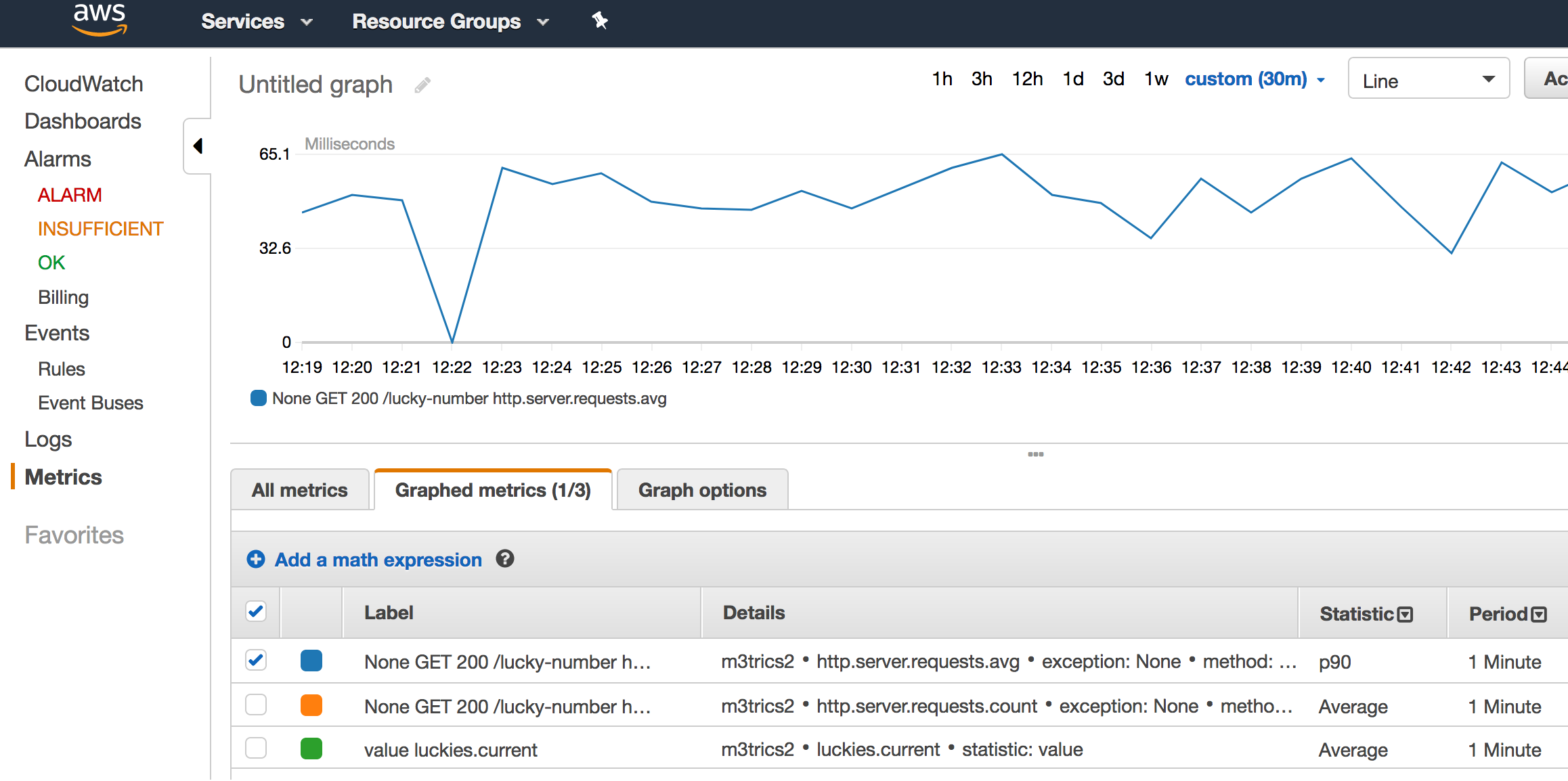
-
http.server.requests.avgdemonstrates how long it took, on average in one minute, to respond with the lucky number,
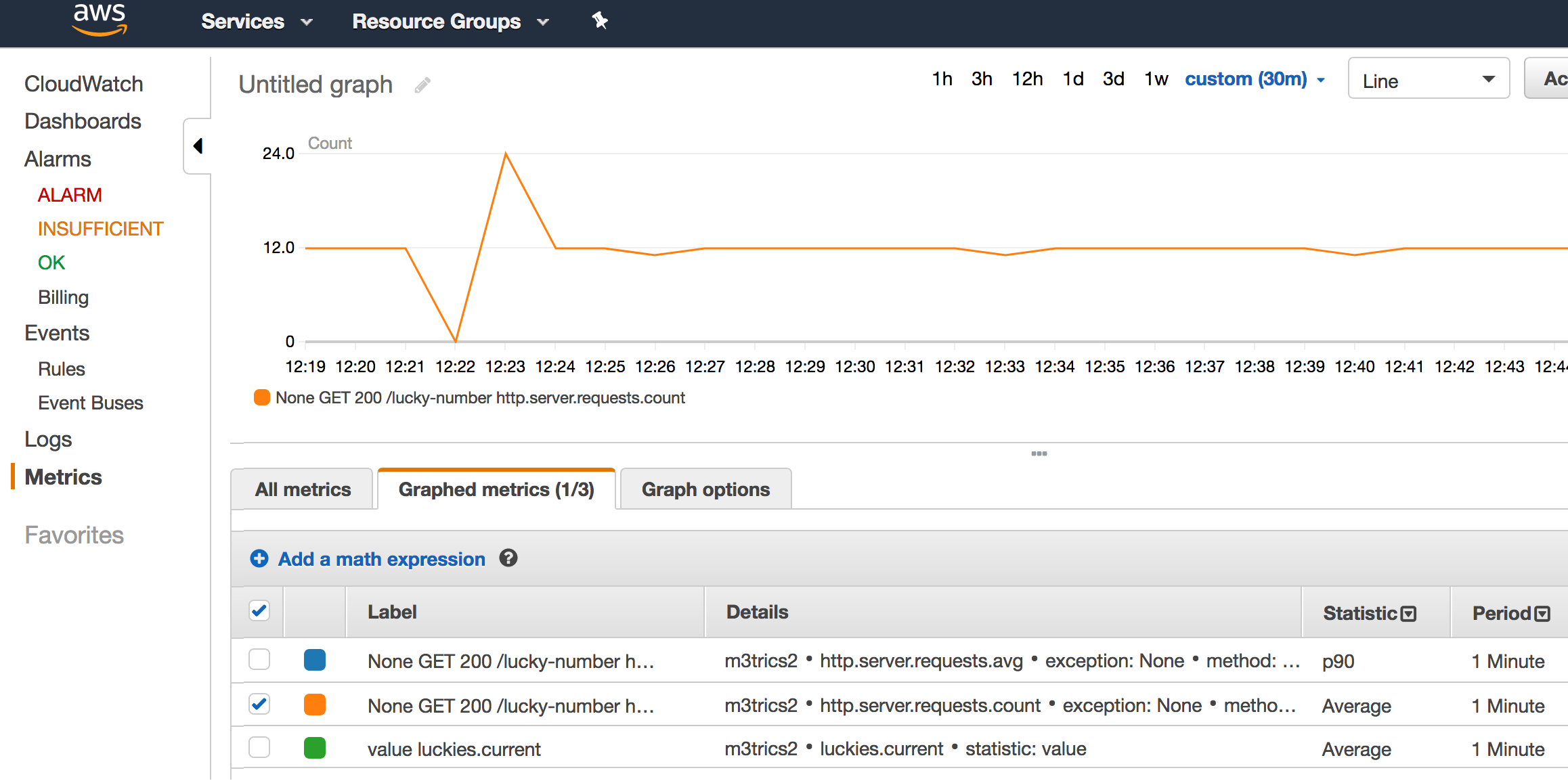
-
http.server.requests.countcounts how many requests were made in one minute
I also added one custom metric — luckies. current (check LuckyNumbersController), which just stores the last lucky number that was generated.
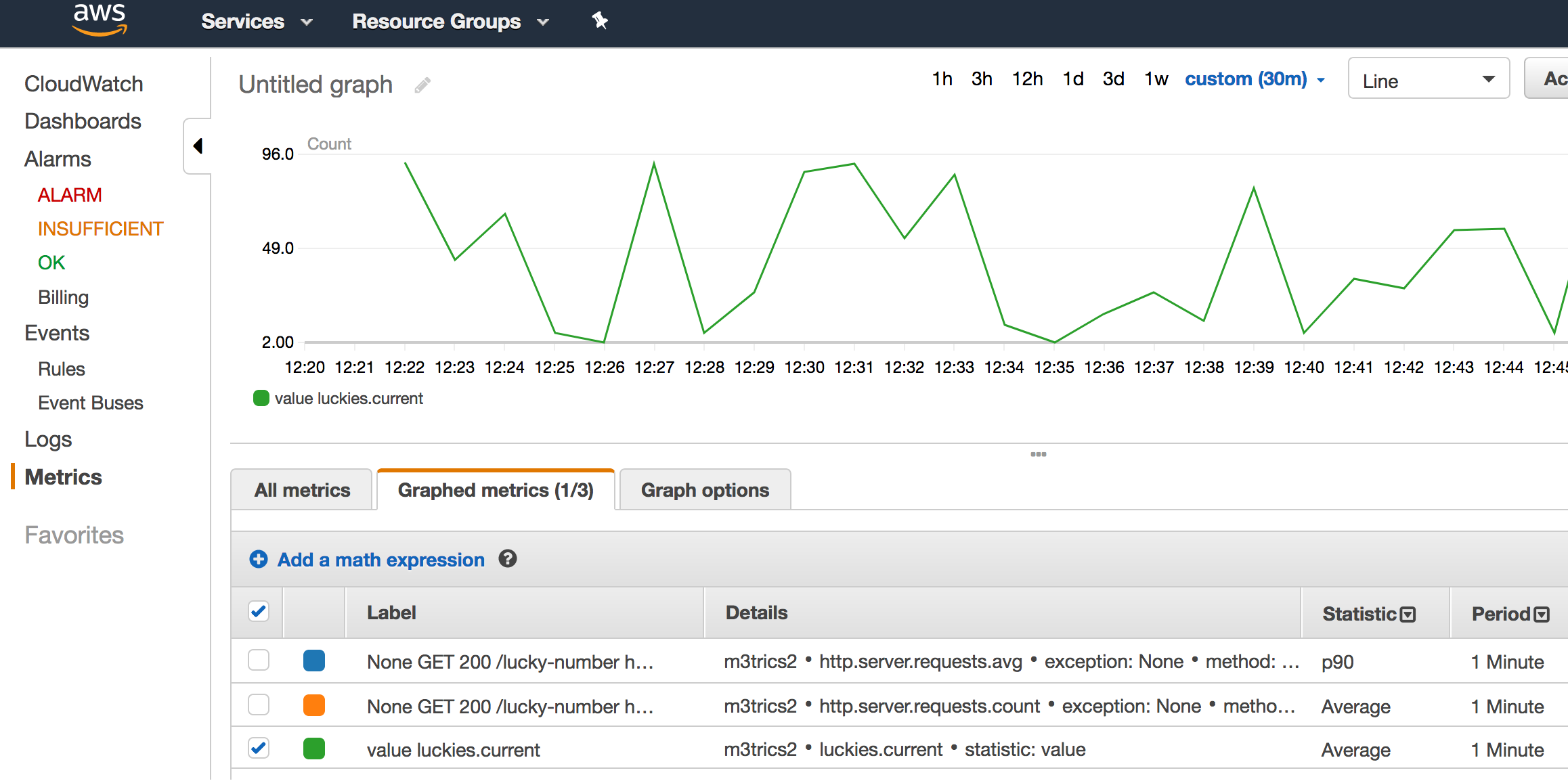
Lastly, please keep in mind that not all generated numbers will be sent to CloudWatch, as gauge metric used here is probed periodically. Again, additional details can be found in the Micrometer docs.
Also, you can check the code here.
Published at DZone with permission of Dawid Kublik, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments