Time Zone Change in Mule Application
In this article, readers will use a tutorial to learn how to change the time zone in their MuleSoft application, including guide code and helpful visuals.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeMuleSoft DataWeave is a powerful tool for transforming data within MuleSoft applications. Time zone changes can be a common challenge when working with DataWeave, but there are several functions and operators that can help you manipulate and transform time zones to meet your needs.
There are two ways to change a time zone:
- On the runtime level
- On the application level.
In this article, we will focus on changing the time zone on the application level.
Why Change the Time Zone on the Application Level?
When working with DataWeave, you may need to convert datetime values to different time zones based on the requirements of your application. For example, if your application is used in multiple regions with different time zones, you may need to convert datetime values to the local time zone of each region.
Challenges We Faced in Real-Time Due To Different Time Zones
Let’s say you have a Mule application that stores timestamps for events in the database, and the server hosting the application is located in New York, USA, (which is in the Eastern Time Zone). You have a user in Tokyo, Japan, (which is in the Japan Standard Time Zone), who wants to add an event to the database that will occur at 10:00 PM Tokyo time on March 23, 2023.
The server in New York is thirteen hours behind Tokyo time, so when the user adds the event to the database at 10:00 PM Tokyo time on March 23, 2023, the timestamp stored in the database will be March 23, 2023, 9:00 AM Eastern Time.
Now, let’s say another user in London, UK, (which is in the GMT Time Zone), wants to store the event in the database through Mule application. London is five hours ahead of New York, so when the user in London tries to insert the event in the database after midnight local time on March 24, 2023, the timestamp in the database will have changed to March 24, 2023, 2:00 AM Eastern Time. This means that even though the event is scheduled to occur on March 23 at 10:00 PM Tokyo time, in the database, it will appear to occur on March 24 at 2:00 AM New York time, (which is after midnight in London).
So, due to the time zone differences, the date of the event in the database appears to change before it actually occurs in Tokyo time, which can be confusing for users in different time zones. Changing the time zone on the application level allows you to handle time zone conversions in a centralized way, making it easier to manage and maintain your DataWeave code.
Tips and Best Practices for Working With Time Zones in DataWeave
Understand the Basics of Time Zones
Before you start working with time zones in DataWeave, it’s important to have a good understanding of what time zones are and how they work. This includes understanding the differences between UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) and local time zones, as well as understanding how daylight saving time (DST) can affect time zone conversions.
Convert Time Zones by Time Zone ID’s
DataWeave helps us convert the date and time to any time zone.
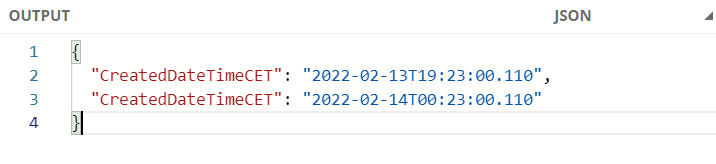
DataWeave Expression
%dw 2.0
output application/json
fun format(d: DateTime) = d as String {format: "yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSS"}
---
{
CreatedDateTimeCET: format(|2022-02-13T18:23:00.110Z| >> "CET"),
CreatedDateTimeCET: format(|2022-02-13T18:23:00.110Z| >> "BST")
}Output
Test Your Code
It’s important to test your DataWeave code to ensure it’s working as expected. This can be done by creating test cases that cover different scenarios, such as different time zones and DST changes.
Conclusion
By following these tips and best practices, you should be able to effectively work with time zones in DataWeave. Good luck with your DataWeave projects!
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments