Top 20 Git Commands With Examples
Now that you (presumably) know what Git is and how it works, take a look at examples of how to use the top 20 Git commands.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn the previous blog, you got an understanding of what git is. In this blog, I will talk about the Top 20 Git Commands that you will be using frequently while you are working with Git.
Here are the Git commands which are being covered:
- git config
- git init
- git clone
- git add
- git commit
- git diff
- git reset
- git status
- git rm
- git log
- git show
- git tag
- git branch
- git checkout
- git merge
- git remote
- git push
- git pull
- git stash
So, let's get started!
Related: Gitlab CI/CD Tutorial.
Git Commands
git config
Usage: git config –global user.name “[name]”
Usage: git config –global user.email “[email address]”
This command sets the author name and email address respectively to be used with your commits.
![]()
git init
Usage: git init [repository name]
This command is used to start a new repository.
![]()
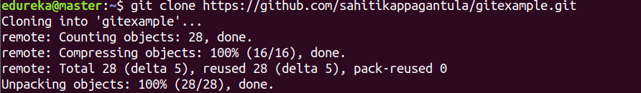
git clone
Usage: git clone [url]
This command is used to obtain a repository from an existing URL.
git add
Usage: git add [file]
This command adds a file to the staging area.
![]()
Usage: git add *
This command adds one or more to the staging area.
![]()
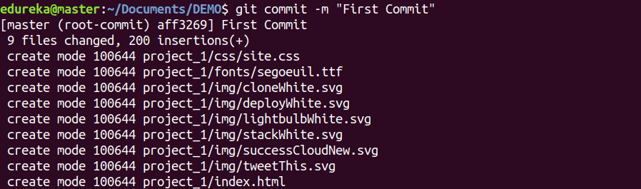
git commit
Usage: git commit -m “[ Type in the commit message]”
This command records or snapshots the file permanently in the version history.
Usage: git commit -a
This command commits any files you’ve added with the git add command and also commits any files you’ve changed since then.

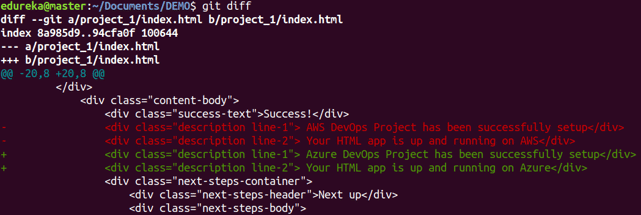
git diff
Usage: git diff
This command shows the file differences which are not yet staged.
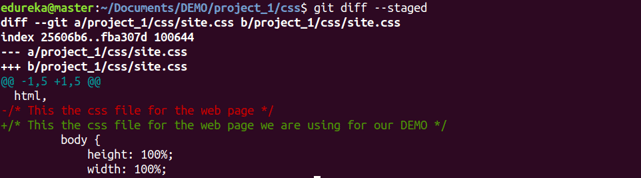
Usage: git diff –staged
This command shows the differences between the files in the staging area and the latest version present.
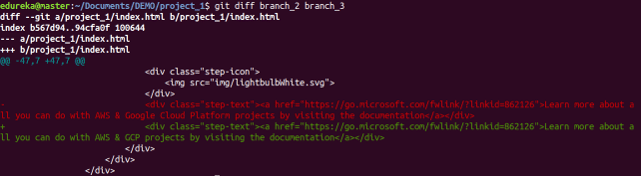
Usage: git diff [first branch] [second branch]
This command shows the differences between the two branches mentioned.
git reset
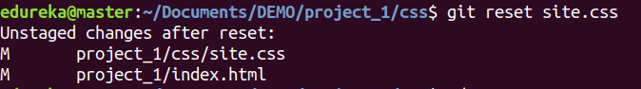
Usage: git reset [file]
This command unstages the file, but it preserves the file contents.
Usage: git reset [commit]
This command undoes all the commits after the specified commit and preserves the changes locally.

Usage: git reset –hard [commit] This command discards all history and goes back to the specified commit.
![]()
Learn how to connect Git secrets with a Jenkins pipeline.
git status
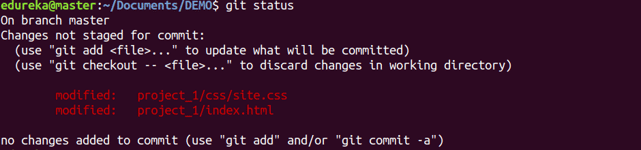
Usage: git status
This command lists all the files that have to be committed.
git rm
Usage: git rm [file]
This command deletes the file from your working directory and stages the deletion.
![]()
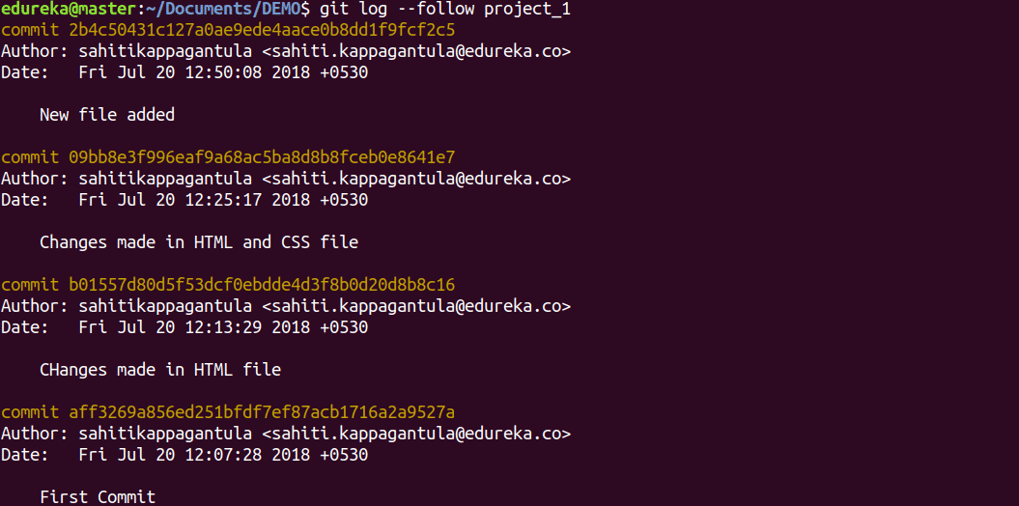
git log
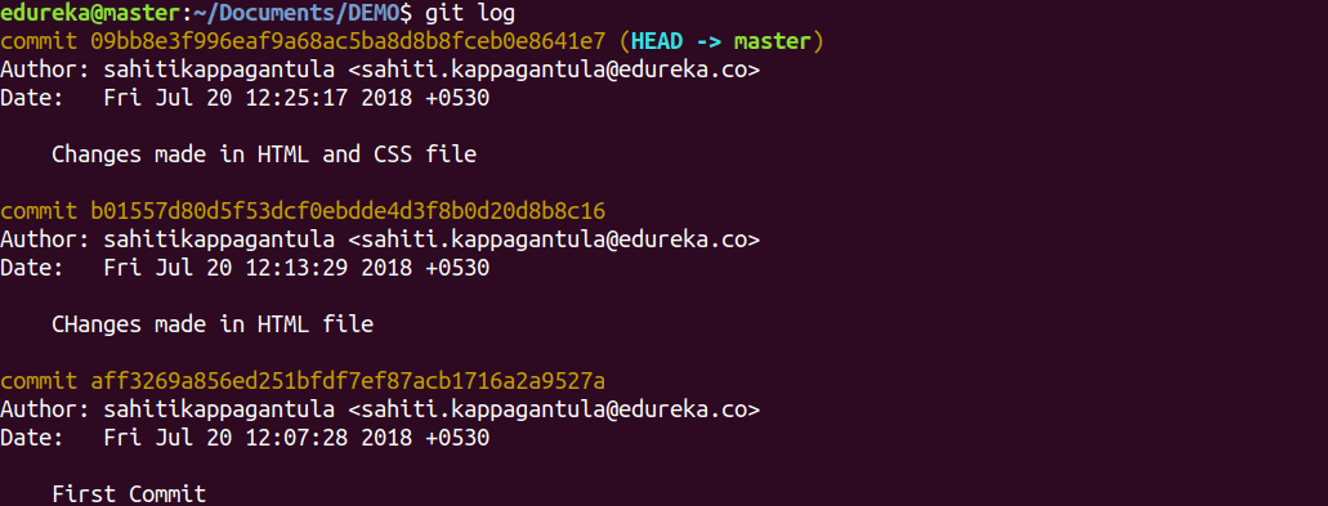
Usage: git log
This command is used to list the version history for the current branch.
Usage: git log –follow[file]
This command lists version history for a file, including the renaming of files also.
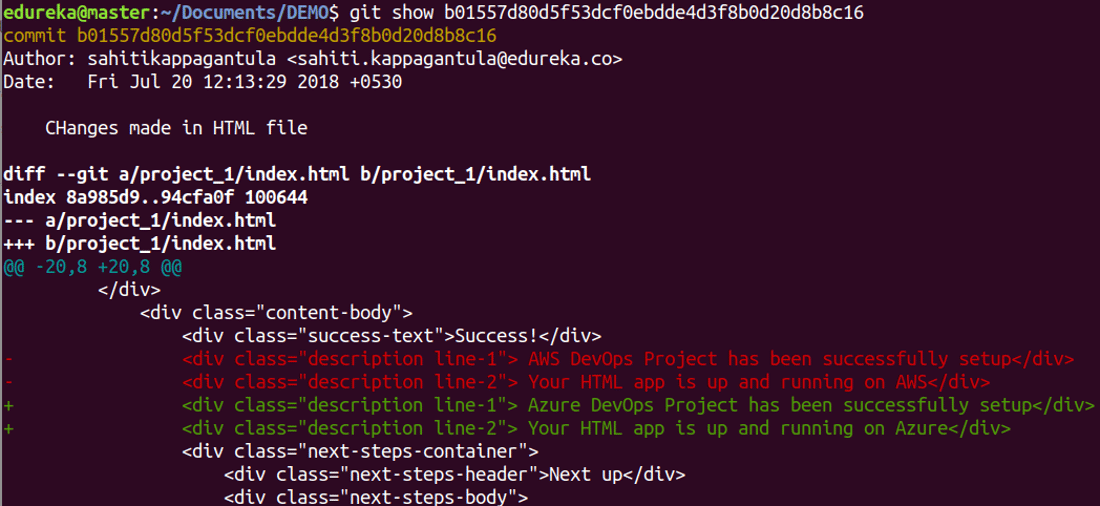
git show
Usage: git show [commit]
This command shows the metadata and content changes of the specified commit.
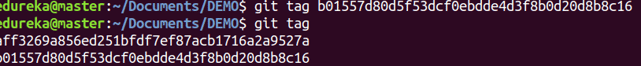
git tag
Usage: git tag [commitID]
This command is used to give tags to the specified commit.
git branch
Usage: git branch
This command lists all the local branches in the current repository.
![]()
Usage: git branch [branch name]
This command creates a new branch.
![]()
Usage: git branch -d [branch name]
This command deletes the feature branch.
![]()
git checkout
Usage: git checkout [branch name]
This command is used to switch from one branch to another.
![]()
Usage: git checkout -b [branch name]
This command creates a new branch and also switches to it.
![]()
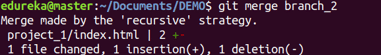
git merge
Usage: git merge [branch name]
This command merges the specified branch’s history into the current branch.
git remote
Usage: git remote add [variable name] [Remote Server Link]
This command is used to connect your local repository to the remote server.
![]()
git push
Usage: git push [variable name] master
This command sends the committed changes of master branch to your remote repository.
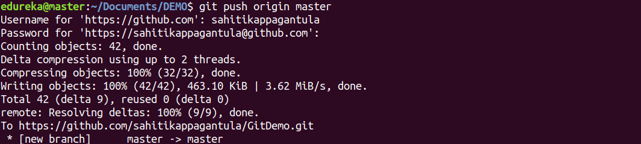
Usage: git push [variable name] [branch]
This command sends the branch commits to your remote repository.
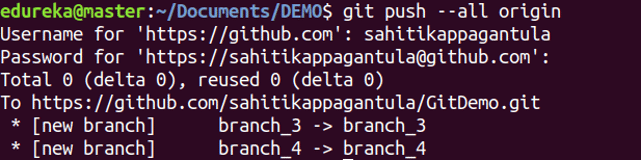
Usage: git push –all [variable name]
This command pushes all branches to your remote repository.
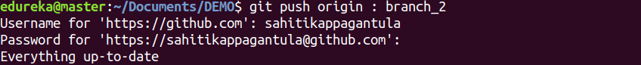
Usage: git push [variable name] :[branch name]
This command deletes a branch on your remote repository.
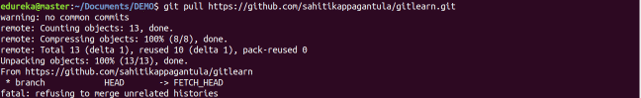
git pull
Usage: git pull [Repository Link]
This command fetches and merges changes on the remote server to your working directory.
Related Guide: Jenkins VS Gitlab
git stash
Usage: git stash save
This command temporarily stores all the modified tracked files.
![]()
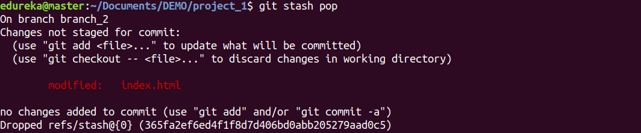
Usage: git stash pop
This command restores the most recently stashed files.
Usage: git stash list
This command lists all stashed changesets.
![]()
Usage: git stash drop
This command discards the most recently stashed changeset.
![]()
DZone’s previously covered how to automate deployments for Mule 4 applications with Gitlab. Want to learn more about git commands? Here’s a guide to using Git and GitHub to get you started. Alternatively, you can take a top-down approach and start with this DevOps Tutorial.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments