UnifiedFlow: Git Branching Strategy
In this article, learn pros and cons of UnifiedFlow, as well as how to deploy stable features signed off by QA according to the release plan.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
Pros
- Every branches fork from a stable state.
- Prevent side-effects (defect/ad-hoc/config) from merging develop into feature, release and main.
- Group stable features according to release plan.
- Easily remove features from release.
Cons
- Require optional merge branch if using with Pull-Request. PR will merge the target branch on your feature; may cause unknown side-effects and stall you for days to fix it.
- Multiple merge conflicts in develop and release.
Getting Started
init: main
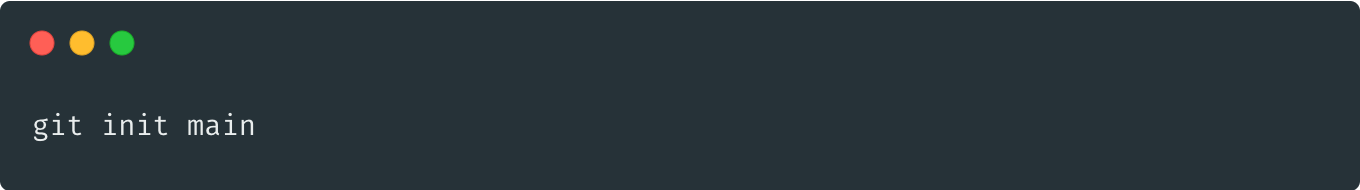
fork: main -> develop
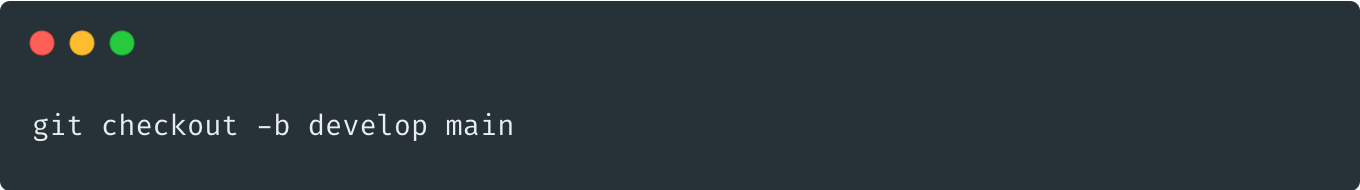
Features
fork: main -> feature
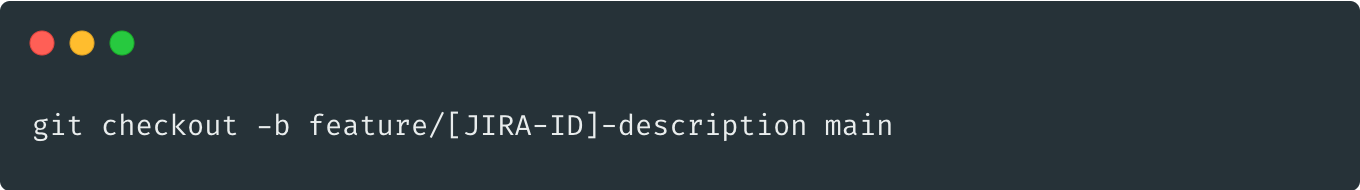
merge: develop <- feature
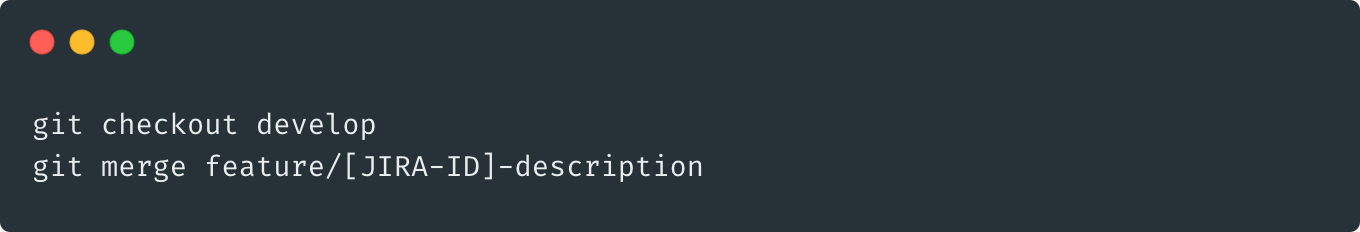
deploy: develop to SIT, test, and approve as Release Candidate by QA
Bug Fixes
fork: main -> bugfix
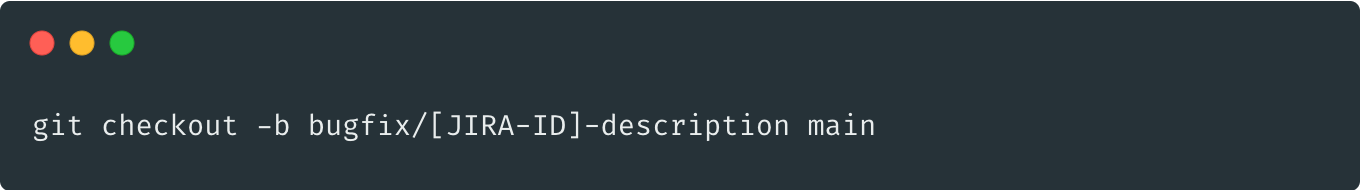
merge: develop <- bugfix
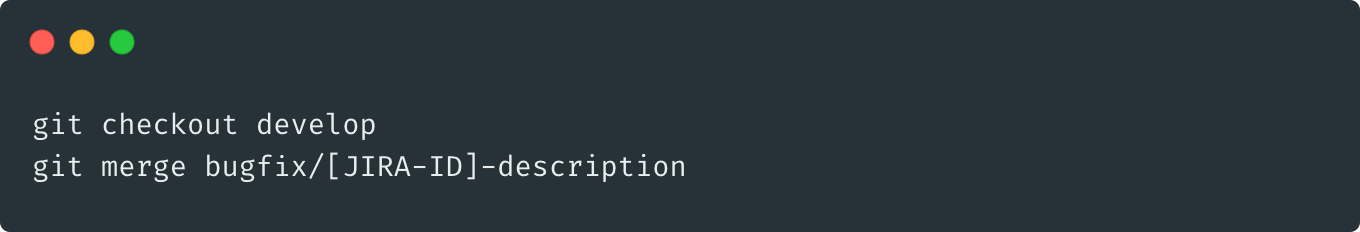
deploy: develop to SIT, test and approve as Release Candidate by QA
Releases
fork: main -> release

merge/squash: release <- {bugfix, feature}

deploy: release to UAT, test and sign off by QA
merge: main <- release

tag: {version: YY.MM.buildNumber}

deploy: main to PROD, test and verify by QA
Hot Fixes
fork: main -> hotfix
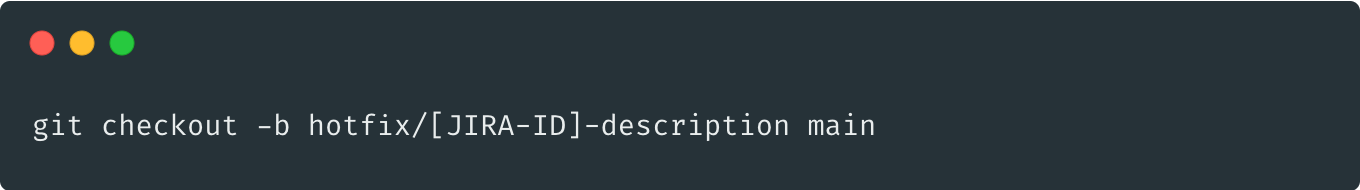
deploy: hotfix to UAT, test and verify by QA
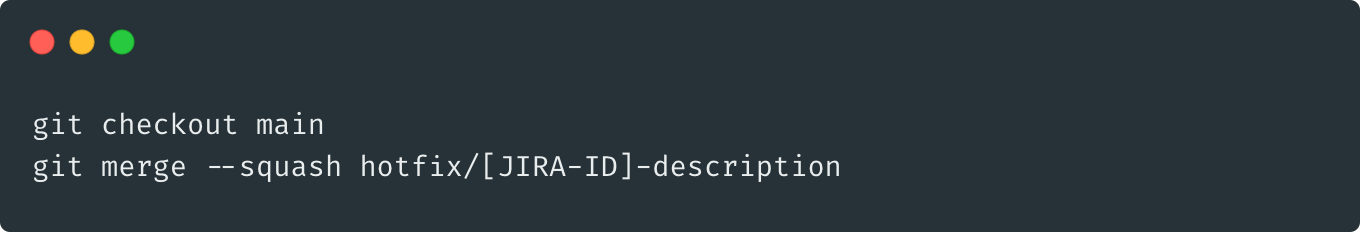
merge/squash: main <- hotfix
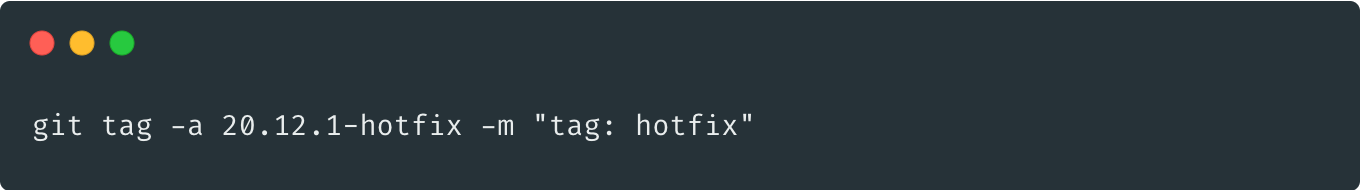
tag: {version: YY.MM.buildNumber-hotfix}
deploy: main to PROD, test and verify by QA
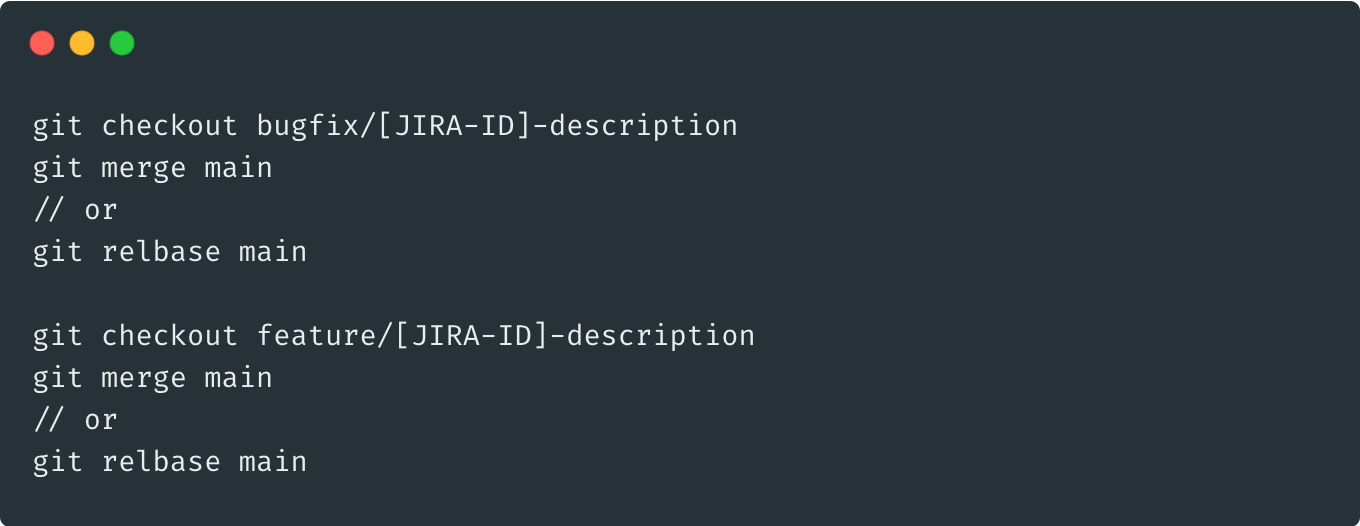
Update Branches From Main (Stable) Not Develop (Unstable)
merge/rebase: main -> {feature, bugfix}
Published at DZone with permission of Putthiphong Boonphong. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments