Using a Raspberry Pi as Your Development Server
In this tutorial, I will show you how to set up a Raspberry Pi 4 as a development (or testing) server.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn this tutorial, I will show you how to set up a Raspberry Pi 4 as a development (or testing) server. You can use this as a place to push your code and test it in a web browser. For the demo, I’ll use a React application, but with a few modifications, you can build just about anything with it.
For this project, I’m using a Canakit Raspberry Pi 4 Complete Kit. This gives you everything you need to get going, including a case, power supply, and SD Card.
Why Bother?
A solid development environment is important. You need a place where you can look at your application to make sure it’s running fine. Many times folks do this on their local machine. It’s better to test on a separate machine from what you’re working on. This way, you can catch things like dependency and configuration changes.
This development/testing server has the following advantages:
- A configuration and environment that matches production (if you have a Linux host)
- Build code on any machine push it to a centralized location
- Continuous Integration - Push and refresh in your browser
Ideally, you can set up a workflow that looks like this:
- Develop your code locally and commit it.
- Push to development and test it out
- Approve changes, push it live
This enables a great workflow where you can make changes and edits, commit, then push them and refresh your browser. You can then develop your code from any machine on the network that has git. Once you’re satisfied with the changes, you can copy the artifacts to production. In fact, you can integrate production pushes into this workflow to make it all automatic.
Setting Up the Pi as a Server
For this project, I’m using the full Canakit Raspberry Pi kit. It comes with everything you need. I won’t go into setting this up in this article, but I should note that I’m using the Ubuntu Server image for this project, and recommend you do the same.
I used my Pinebook pro to burn the image to a card, but you can do this in Windows or with a Mac if you need to.
Here’s a good guide for setting up one of these kits.
We will set this up as a development/test server and use GIT to communicate with it. So here is what we’ll do:
- Set up Git for Publishing
- Install Nginx
- Install NPM
- Create deployment from a repo on your machine to the Raspberry Pi web server in a single step.
When we’re done, we can change our React application and push the changes to the Pi to view them as a web page.
1. Set Up Git for Publishing
First, we need to install Git.
sudo apt install git
Now we need to add git shell to /etc/shells
which git-shell
and we will add that output to /etc/shells
Now we want to set up a git user that doesn’t have the cool permissions that your account does.
sudo adduser --disabled-password git
Switch to the git user
sudo su git
change to the git users home
cd ~
make a directory for ssh files:
mkdir ~/.ssh && chmod 700 ~/.ssh
Then, we'll create our authorized_keys file
touch ~/.ssh/authorized_keys && chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
Now you can add the public keys of any machine you’d like to access the server by adding them to:
/home/git/.ssh/authorized_keys
Then we’ll set the git users’ shell to git-shell
sudo chsh git -s $(which git-shell)
Create a folder for our www files that we’ll be serving later:
mkdir ~/www
2. Create Our Project Folder
This is a remote repository set up so we can work on the project on any other machine, then push it to the Raspberry Pi.
cd ~ mkdir /home/git/react-hello-world.git
Now, let’s initiate it:
cd react-hello-world.git && git init --bare
Let’s go back to our machine and test it out.
On your developer machine, type in:
git clone git@[your IP address]:react-hello-world .
You should be able to clone it your local machine.
If this works, we’ll go back to the Raspberry Pi.
3. Install Nginx
Location: On Raspberry Pi
Next, we will install Nginx on our Raspberry pi and use it to serve web pages.
In this tutorial, we will set it up for a single project, so we’ll be using a single www directory. However, if you have multiple projects, you want to break them into folders.
sudo apt install nginx
This will install Nginx.
You may need to add a firewall exception to ufw. You can list the available profiles by typing in:
sudo ufw app list
You can add an exception with:
sudo ufw allow 'Nginx HTTP'
Now when you bring up the IP in the web browser, you will see the Nginx welcome page.
Now you have an Nginx server up and running.
4. Configure Nginx
Location: On Raspberry Pi
Next, we will change the Nginx config.
Make a copy of the default config in your home folder as a backup:
sudo cp /etc/Nginx/sites-available/default ~
Edit the conf file and add in the www folder we created earlier.
sudo vim /etc/Nginx/sites-available/default
Look for the “root” and change the default to our www folder:
Then save the file and reload Nginx.
sudo systemctl reload Nginx
Now you’re serving files from the www folder instead of git. This is where we publish files after committing.
Let’s go back to our developer machine.
5. Set Up Our React Project
Location: On Your Developer Machine
We will build a React project and deploy that to our Pi. So let’s set that up.
First, we’ll remove the repo we cloned earlier.
rm -rf react-hello-world/
And we’ll use the React CLI to create an app with the same name.
npx create-react-app react-hello-world
Now we’ve created a basic React project. Next, initialize it as a git repository.
git init
We’ll add our existing files and commit them.
git add .
git commit -m "Our first commit"
We’ll set the remote to our Raspberry Pi. We set this, so when we push it to remote, the files will go to our Raspberry Pi.
git remote add origin git@[Your IP Address]:
react-hello-world.git
And we’ll push it to the Raspberry Pi:
git push --set-upstream origin master
If you go to the Pi, you will see the repository in your react-hello-world.git folder:
Now that we have that setup, we must set up the Pi to build your React application.
6. Set Up the Server to Build
Location: On Raspberry Pi
We have our git remote repository set up, and Nginx installed, but we need to tie it all together. We need to build our application.
We now need to install Node and NPM on the Raspberry Pi to start.
curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_10.x | sudo -E bash -
sudo apt install nodejs
You can verify they’re installed by typing in:
node --version
npm --version
We now have Node up and running.
7. Setup React to Build
Location: On Raspberry Pi
Let’s build our React App on the Raspberry Pi, just to test it out.
Check out the repo locally:
cd ~ && git clone react-hello-world.git/ test
Then we will install react and react-scripts (-g makes it global)
npm install react -g
npm install react-scripts -g
If we run:
npm run-scripts build
We can see it built properly.
Once we know we can build the React app manually, we can automate it.
8. Tying It All Together
Location: On Raspberry Pi
Now we need to copy those files into our www folder. We want to do that automatically every time we push to the git repo.
Make sure you’re in your git remote folder on the Raspberry Pi(for me it’s /home/git/react-hello-world.git/)
And create a new file:
vim hooks/post-receive
Add this into the file:
#!/bin/bash
unset GIT_INDEX_FILE
echo "Publishing our React App"
git --work-tree /home/git/build --git-dir=/home/git/react-hello-world.git checkout -f
cd /home/git/build
npm run-script build
cp -r /home/git/build/build/* /home/git/www
Use your own folder names for this. I have created a /home/git/build folder, and its job is to hold the source files and build them.
What this file does is create a post-receive hook in git, so after you push to remote, these actions will be run.
- It checks out the repo into the build folder
- Runs a build script
- copies the artifacts to our www folder.
There are a few different ways you can do this, but this is a simple way to build and push the application to the www folder.
You could build the application locally and just commit/push artifacts. I am building it on the “server” (our Raspberry Pi). This is a better way to do it because you can match your Raspberry Pi to your production server and only push over the source to be automatically built. You don’t have to worry about a config change on your development machine that won’t be on your production machine. This enforces some consistency.
You can also run tests here if you’d like.
Once you’re done adding in these changes, then mark the file as executable.
chmod +x hooks/post-receive
9. Testing Your Integration
Location: Your local machine and the Raspberry Pi
Now it’s time to test it all. In your React app, open up App.js and make some kind of change.
Add it and commit it.
xxxxxxxxxx
git add .
git commit "small change"
git push origin master
You will see the output from your remote:
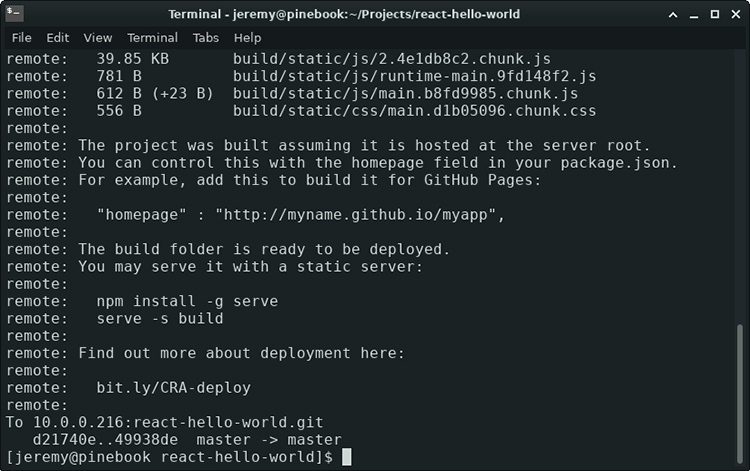
Now you’re ready to test it in a web browser!
Here’s what we’ve been waiting for!
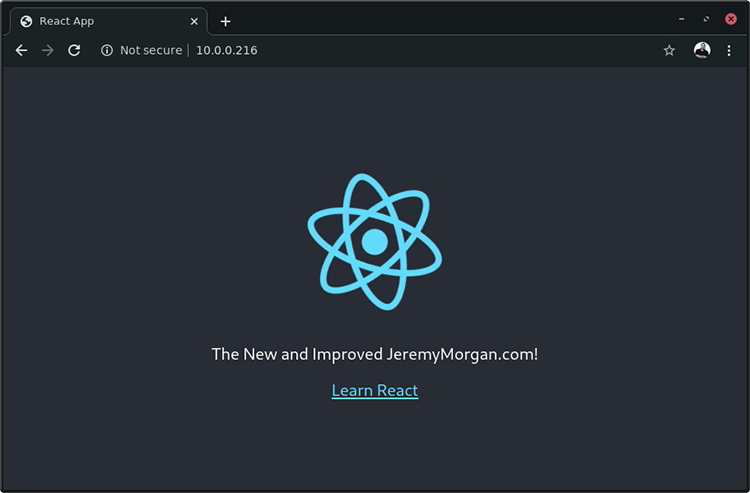
There’s my React site in all its glory.
Now, I can update this application by:
- Making changes
- Committing
- Pushing to Master
All in a matter of seconds, I can see the results of my changes. Easy and simple. You could easily extend this, so you push it to here, do a spot check then push it to a staging or production server. The possibilities are endless.
10. Start Developing!
I created this tutorial with a React app as an example, but it could just as easily be Angular, Vue, Golang, Python, PHP, or whatever. The concepts are the same. I hope this will speed up your workflow and give you a nice place to spot check and test your application before pushing it live.
It’s not exactly an enterprise solution, but it’s a cheap alternative to an actual server.
Here’s how I have it set up:

I used my Pinebook Pro as a development machine for this article. What you’re looking at here is a fully capable development setup for ~$300. I could easily develop tons of apps and push them to production with this setup. Thanks to ARM processors and the tireless work of innovators such as the Raspberry Pi Foundation and the Pine64 Project.
Published at DZone with permission of Jeremy Morgan, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments